* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Impact on the Ecosystem
Environmental law wikipedia , lookup
Conservation psychology wikipedia , lookup
Soil contamination wikipedia , lookup
Eutrophication wikipedia , lookup
Environmental impact of pharmaceuticals and personal care products wikipedia , lookup
Environmental psychology wikipedia , lookup
Water pollution wikipedia , lookup
Name_____________________________
Human Impact Outline
Date_______________________________
Living Environment: Ms. Fazio 2006-2007
Human Impact on the Ecosystem
Upon completion of this unit the student will:
1. Recognize that humans have upset natural systems.
2. Describe some ways humans affect the following natural ecosystem processes;
maintenance of atmospheric quality, generation of soils, control of the water cycle,
removal of wastes, energy flow, and the cycling of nutrients.
3. Recognize that human population growth has increased rapidly, because of the
removal of checks on population growth, such as disease.
4. Recognize that increasing numbers of humans will ultimately be limited by the
earth's finite resources.
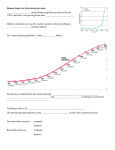
5. Interpret graphs describing human population growth.
6. List common kinds of water pollution.
7. Explain what is meant by biomagnification and list an example of this (DDT).
8. List examples of species damage and destruction by overhunting and habitat
destruction.
9. Explain the cause and some negative consequences of the Greenhouse Effect.
10. Explain the causes and some negative consequences of acid rain pollution.
11. Explain the causes and some negative consequences of ozone depletion.
12. Explain how our increasing population numbers are using up available living space
and farmlands.
13. Explain how timber depletion and the direct harvesting of timber is impacting land
use and atmospheric quality.
14. Discuss the waste disposal problems affluent human life styles have led to.
15. Describe the dangers of insecticide use.
16. Recognize that pollution can adversely change the chemical composition of our soil,
air, and water.
17. Explain how population growth and distribution can influence environmental quality.
18. Explain how the capacity of technology to solve problems can influence
environmental quality.
19. List and explain some examples of economic, political, cultural, and ethical views
influencing environmental quality (examples from “An Inconvenient Truth)
20. List several ways we are trying to preserve endangered species.
21. List several ways we are trying to reduce air pollution.
22. Recognize that through a greater awareness and application of ecological principles,
each individual can help assure that there will be suitable environments for future
generations on our planet.
23. Recognize that when new technologies are introduced, decisions must be made
to assess environmental risks, costs, benefits, and trade-offs.
1. “Blanket statement”: Natural systems have been upset because humans have not
realized that they not only influence other individuals, other species, and the nonliving
world, but are, in turn, influenced by them.
2. Some Natural Ecosystem Processes that humans affect
A.
B.
C.
D.
E.
F.
maintenance of atmospheric quality
generation of soils
control of the water cycle
removal of wastes
energy flow
recycling of nutrients
*Humans have changed many of these ecosystem processes -- frequently in a detrimental
way.
A GRAPH OF HUMAN POPULATION GROWTH
3-5. Human Population Growth
A. The total population of humans has risen at a rapid rate, partly because of the
removal of natural checks on the population, such as disease.
B. The earth has finite resources, increasing human population and consumption
places severe stress on natural processes that renew some resources and deplete
those resources which can not be renewed.
Some specific human influences on Ecosystem Factors
A. Increasing numbers:
-- results from an increased human life span
-- health advances largely led to this
B. Food: shortages and inadequate nutrition lead to starvation and malnutrition
-- population growth is outpacing food production in many world regions
starvation: body lacks sufficient calories for maintenance
malnutrition: diet lacks specific substances needed by the body
C. Soil: much loss of fertile topsoil due to erosion and poor management
-- the use of pesticides has contaminated the soil
-- some causes of topsoil loss include; cutting forests, farming dry
grasslands, damming rivers, draining wetlands, etc.
-- much valuable farmland has been lost due to increasing urbanization &
suburbanization
6. Water: much waste occurs -- cutting forests has led to increased, uncontrolled runoff
-- water pollution leaves water unfit for use and the living things remaining in it
unfit for consumption
7. Biomagnification: increase in the concentration of a substance (poison) in living tissue
as you move up the food chain
ex. DDT
8. Wildlife: much destruction and damage has been done to many species (hunting,
fishing, etc.)
** Other problems include habitat destruction, importation of some organisms have
caused problems for native organisms. (ex. rabbit - sheep {Australia}, starling &
english sparrow, mongoose -birds & mammals {West Indies} We also have alien
invasive species which have caused problems for our area in Northern New York.
These include the Water Chestnut, Eurasian Water milfoil, Alewife, Zebra Mussel, and
Purple Loosestrife. A great source of information in reference to these
invaders can be found at the following link.
Land use (includes increasing urbanization and the cultivation of marginal lands)
-- this decreases the space and resources available to other species
9-11. Air: is becoming increasingly polluted
a.) Greenhouse effect: adding carbon dioxide to the earth's atmosphere may be
increasing its temperature (holds in the earth's heat radiation)
b.) Acid Rain: air pollution from coal burning sources + rain
c.) Map Showing the relative pH of U.S. Acid Precipitation in 1998 (below)
(Acid rain kills aquatic life, crumbles buildings, and has many other effects, etc.)
c.) Ozone Depletion : CFC pollution from refrigerants and plastics are destroying our
stratospheric ozone layer ... this layer shields us from incoming ultraviolet radiation ....
increased skin cancers and cataracts are resulting from this destruction
12 Living space/available land: is greatly decreasing as a result of increasing population
-- creates increasing stress on individual humans
-- we are also taking up living space and resources needed by other organisms
13. Forests: are becoming increasingly depleted as a result of timber need & the need for
more agricultural land
-- the direct harvesting of timber has destroyed many forests
-- this destruction also impacts land use and atmospheric quality
14. Affluent human lifestyles have led to waste disposal problems. (solid, chemical,
nuclear)
15. Insects we have destroyed many beneficial insects and many enemies of harmful
insects with insecticides
16. Pollution -- this changes the chemical composition of the soil, air, and water
Nuclear fuels --- environmental dangers exist in reference to obtaining, using, and storing
the wastes from these fuels
**Fossil Fuels: are becoming rapidly depleted/add to air pollution problems
The search and demand for additional energy resources also impact ecosystems in a
negative way. Industrialization has brought an increased demand for and use of energy.
17-19. Some Other Factors which influence environmental quality
1. Population growth and distribution
2. Capacity of technology to solve problems
3. Economic, political, ethical, and cultural views
20. Species Preservation
-- Some efforts to sustain endangered species have included habitat protection
(wildlife refuges and national parks) and wildlife management (game laws and fisheries).
-- Animals which were once endangered but are presently successfully reproducing and
increasing their numbers are the bisons, gray wolves and egrets.
-- Endangered animals which are currently responding to conservation efforts and
beginning to make a comeback are the whooping crane, bald eagle, and peregrine
falcon.
** The future of many species remains in doubt.
Human activities that degrade ecosystems result in a loss of diversity in the living and
nonliving environment. These activities are threatening current global stability.
21. Ways to Reduce Air Pollution
1. Use fuels which contain less pollutant, such as low sulfur coal and oil.
2. Utilize industrial or energy producing processes which minimize the creation of
pollutants.
3. Remove pollutants by using such devices as afterburners or catalytic converters before
they enter the air.
4. Design new products which meet basic needs without generating pollution.
** There are laws which regulate and guide the use of natural habitats.
Ex. SEQR: A New York State law designed to provide the opportunity for citizen review
and comment of the environmental impact of any proposed development that has been
determined to have significant impact on the environment.
22. How can individual and societal choices contribute to improving the environment?
1. Through a greater awareness and application of ecological principles, each
individual can help to assure that there will be suitable environments for
succeeding generations on our planet.
2. Individuals in society must decide on proposals which involve the introduction
of new technologies. These decisions must assess environmental risks, costs,
benefits, and trade-offs. Some basic questions for assessing the value of these
technologies might include:
23. What could this technology do to the environment? (Positive and Negative Effectrs)