* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Central nervous system demyelinating diseases - Multiple sclerosis -
Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Cysticercosis wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Visceral leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
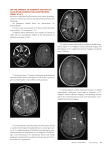
Central nervous system demyelinating diseases - Multiple sclerosis Amilton Antunes Barreira Department of Neurology Faculdade de Medicina and Hospital das Clínicas de Ribeirão Preto - USP Diseases of myelin Autoimmune Acute hemorrhagic leukoencephalopathy Multiple sclerosis Infectious Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy Toxic/metabolic Carbon monoxide Vitamin B12 deficiency Mercury intoxication (Minnamata disease) Alcohool/tobacco amblyopia Central pontine myelinolysis Machiafava-Bignami syndrome Hypoxia Radiation Vascular Binswanger’s disease (chronic microvascular leukoencephalopathy) Hereditary disorders of myelin metabolism Adrenoleukodystrophy Metachromatic leukodystrophy Krabbe’s disease Alexander’s disease Canavan-van-Bogaert disease Pelizaeus-Merzbacher disease Phenylketonuria Multiple sclerosis Diseases of myelin Autoimmune Acute hemorrhagic leukoencephalopathy Diseases of myelin Vascular Binswanger’s disease Diseases of myelin Infectious Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy Diseases of myelin Hereditary disorders of myelin metabolism Canavan-van-Bogaert disease Deficiency of the enzyme aspartoacylase and the accumulation ofN-acetylaspartic acid lead to a severe leukodystrophy and spongy degeneration of the brain, Canavan disease (McKusick 271900). Epidemiology • 1,1 million people with MS worldwide • 2/3 experiment the first symptom between the age of 20 and 40 • For a minority MS starts in late adult life • Women are committed 1.4 to 3.1 times more • In temperate zones MS is five times more common than in the tropics • In Brazil: 20 cases per 100 000 inhabitants (38 000 cases) • In Uruguay: 30 000 cases for a population of 3 000 000 inhabitants • In United States: 300 000 cases • MS in first degree relatives is 20 times higher than in general populations • Monozygotic twin studies show the concordance rate of 30% • Dizygotic twins show concordance rate of less than 5% PATHOLOGY Trapp - 2003 MRI IMAGES Signs and symptoms • Visual loss • Ocular motility Diplopia • Trigeminal neuralgia • Equilibrium alterations • Ataxia • Pyramidal signs Monoplegia Paraplegia Hemiplegia Sphincter disturbances • Cognitive commitments Course DIAGNOSTIC CRITERIA Diagnosis criteria are very specific and the Brazilian Ministry of Health recommend that it must be confirmed by neurologists. An exacerbation (relapse) is defined as: the appearance of a new clinical Sign/Symptom or the clinical worsening of a previous sign/symptoms that had been stable for at least the previous 30 days and which persisted for a minimum of 24 hours. International Panel Criteria (McDonald Criteria) for Diagnosis MS Clinical Presentation Additional Data Needed for MS Diagnosis Two or more attacks; objective clinical evidence of 2 or more lesions Nonea Two or more attacks; objective clinical evidence of 1 lesion Dissemination in space demonstrated by: • MRIb, or • 2 or more MRI lesions consistent with MS plus positive CSFc, or • await further clinical attack implicating a different site. One attack; objective clinical evidence of 2 or more lesions Dissemination in time demonstrated by: • MRIb, or • second clinical attack. One attack; objective clinical evidence of 1 lesion (clincally isolated syndrome) Dissemination in space demonstrated by: • MRIb, or • 2 or more MRI lesions consistent with MS plus positive CSFc And dissemination in time, demonstrated by: • MRIb, or • Second clinical attack Insidious neurological progression suggestive of MS Positive CSFc, and dissemination in space, demonstrated by: • 1) 9 or more T2 lesions in brain, or 2) 2 or more lesions in spinal cord, or 3) 4-8 brain lesions plus 1 spinal cord lesion; or • Abnormal visual evoked potentials with MRI demonstrating 4-8 brain lesions, or fewer than 4 brain lesions plus 1 spinal cord lesion; and • Dissemination in time demonstrated by MRIb; or • Continued progression for 1 year MRI Criteria for Brain Abnormality: Space and Time Dissemination MRI lesions disseminated in space: At least three of the following criteria must be met: 1. One gadolinium-enhancing lesion or nine T2-hyperintense lesions if there is no gadolinium-enhancing lesion 2. At least one infratentorial lesion 3. At least one juxtacortical lesion 4. At least three periventricular lesions MRI lesions disseminated in time: At least one criterion must be met: 1. If MRI is more than 3 months after clinical event, then a gadolinium-enhancing lesion at a site different from the original clinical event is sufficient; if there is no gadolinium enhancement, then a follow-up scan is required (usually > 3 months later). A new T2 or gadolinium-enhancing lesion on this second or subsequent MRI fulfills the requirement. 2. If first MRI scan occurs less than 3 months after the onset of the clinical event, then a second scan > 3 months later showing a new gadolinium-enhancing lesion fulfills requirement. If no gadolinium enhancement is seen at this second scan, a further scan not less than 3 months after the first scan that shows a new T2 lesion or an enhancing lesion will suffice. Pathogenesis Specific pharmacologic Treatment MS – The dimension of the problem August 2003 - 1 400 patients in São Paulo state use IFN-β - CEREM of HC de Ribeirão Preto – 140 patients are using IFN-β - CEREMs of SP city – More than 200 pacientes in each center are in IFN-β MS – The dimension of the problem US in 1991: - U$ 1 500 000 000,00 US in 2001: 50%: MS chronic progressive (MSCP) US in 2006: 70% will have EMCP US in 2016: 85% will have o EMCP MS – The dimension of the problem Malignant form (1 a 3% dos pacientes): - Loss of walk in weeks or months - Life expectancy for MS patients: 10 years less than the general population MS – The dimension of the problem What is the real cost of the incapacities? How many working ours are lost? What is the dimension of the human suffering? Specific treatment for MS Relapses • Pulsotherapy with metyil-prednisolone Different regimens: l 250mg l • (IV) each 6 hours in 1g EV in 4 to 6 hours Plasmapheresis Specific treatment for MS Ø Interfere in the course of MS l Preventing l Possible or attenuating the relapses intensity reduction in the course velocity Specific treatment for MS Intérferons β-interferons Glatiramer acetate Mitoxantrone Action of the medicines used for MS Intérferon β - change the MHC expression; - Inhibits the cell trafficking; - l essens the hemato-encephalic barrier permeability; - change the balance between pro and antiinflammatory cytokines Glatiramer acetate - Blockade of the T cells antigen receptors Mitoxantrone - cytotoxicity Collateral effects - reversible mielotoxicity; - transitory amenorrhea ; Mitoxantrone - nausea; - alopecia; - Cardio toxicity ( cardio myopathy – cumulative effect) Collateral effects Intérferon β (discrete or moderated) Glatiramer - influenza; - local inflammation (injection); - worsening of the previous depression; - do not approved for use during pregnancy; - leucopenia, hepatitis, hipo or hypertirheodism; - uncommon: worsening or starting of asthma or Raynaud phenomenon, - myastenia gravis, psoriasis, urticaria, cerebral hemorrhage; - Hepatic necrosis, anaphylaxis. - local pain in the site of injection; - thoracic pain; - death sensation; - lynphadenopaty; - do not approved for use during pregnancy. EMPP: there is no specific treatment (?) Thank you very much for your attention!!!!