* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The URINARY SYSTEM
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
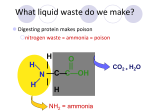
The URINARY SYSTEM Also called excretory, genitourinary (GU) or urogenital system Main functions: Filters substances from the blood – Eliminates fluid body wastes – Urology :is the medical and surgical specialty that focuses on the urinary tracts of males and females, and on the reproductive system of males. ur/o: Relating to urine – Specialties and practitioners – – Urologist: A physician who deals with the study and treatment of – disorders of the urinary tract in women and the urogenital system in men Nephrology (kidney = nephro – Nephrologist : is a doctor who specializes in kidney health and kidney disease – Anatomy & Physiology Consists of • Two kidney – Two ureters – One bladder – One urethra – Ending of tract – external urinary meatus (Opening for passage of urine) • KIDNEYS: Located just above the waist • Retroperitoneal area (retro = behind) – On either side of spinal column – Bean-shaped – Outer cortex • Inner medulla Attached to the ureter that drains urine into the bladder Composed of millions of nephrons – Microscopic, basic units • OTHER ORGANS – – – URETERS Muscular tubes, contract to move urine – Transport urine from kidneys to bladder – Urethra • Conveys urine to the outside, via urinary meatus – Male – urine and semen – URINARY BLADDER – Cyst/o, cyst/i, vesic/o • Muscular, membranous sac • Serves as reservoir for urine • Holds approximately 300 - 400 mL – Expands and contracts – Two sphincters seal off bladder and hold urine Sensory nerve receptors signal when full – Urine excretion terms • Urination, voiding, micturition – • – URINE FORMATION Consists of 95% water, 5% solid substances • Void about 1000 - 1500 mL/day • 3 Processes: • Filtration:All diffusable materials pass from the blood into the nephron Reabsorption:Substances moved out of nephons into surrounding capillaries (blood) – – Secretion:Substances move from capillaries into the urine – • WELLNESS & ILLNESS: Urination problems: • Dysuria – pain or difficulty • Anuria – inability to produce urine • Hematuria – blood in urine • Nocturia – excessive urination at night • Oliguria – scant amount of urine produced • Polyuria - Increased production of urine • Pyuria – pus in urine • Glycosuria – presence of sugar in urine • 1- INFANTS & CHILDREN : • Horseshoe kidney • Congenital anomaly, kidneys attached • • Glomerulonephritis • Acute kidney infection • Poststreptococcal infection • Nephrotic syndrome (nephrosis);May occur after glomerulonephritis • Proteinuria( protein in the urine) • Albuminuria( albumin in the urine) • Can become chronic, leading to kidney failure • Urinary tract infections (UTI): More common in girls • Causes dysuria, fever, frequency, urgency, chills, pyuria • Pyelonephritis (pyel/o = urinary pelvis) • Inflammation of internal structures:May result from UTIs • Enuresis: Bedwetting • Wilm ‘s tumor:Malignancy of kidney :Usually found in infancy 2- ADOLESCENTS • Sytemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) • Commonly called lupus (wolf = lupus) • Autoimmune disorder,Most often seen in teenage girls • Often begins with nephritis, Hematuria,Proteinuria • • • it is an Inflammatory connective tissue disease in many body areas • Calculus or nephrolith:Stone(s) in the kidney • Nephrolithiasis: condition of having kidney stones • VERY painful • Renal colic – pain in abdomen • Flank pain – kidney area of back • Treatment: • Drink lots of water – wait for stone to pass • Shock wave lithotripsy: breaking up stones in kidney or ureter using • ultrasound 4- OLD AGE • Problems often due to weakened bladder muscles • Incontinence:Inability to hold urine • • Cystocele: Space or cavity = cele • Hernia of bladder that pushes it into the vagina • • Vesicoureteral reflux:: Flow of urine backward from bladder into ureter • TESTS • • General urine examination:Lab study of urine Valuable diagnostic tool • Can detect: • 1- Blood – renal disease, trauma • 2- Bacteria –infection • 3- Protein – sign of renal disease • 4- Glucose – diabetes • 5- Bilirubin –liver disease • PH = acidic • Blood tests: • Creatinine clearance level • Measures how blood is being filtered by kidney Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) • • • Measures level of urea • Indication of kidney function • Imaging tests • KUB (kidneys, ureters, bladder) :For simple screening • Renal scan:Uses a radioactive substance to view kidneys • Cystoscopy:Cystoscope inserted up through meatus to view urethra • and bladder . Intravenous pyelogram (IVP):Dye injected into vein • To view kidneys and surrounding structures • DIALYSIS: Accessing the blood to clear it of waste products through • artificial means Kidney unable to do this (kidney failure) • Two types • Hemodialysis:Machine used as an artificial kidney • Machine contains a membrane acting as a filter, and fluid bath • Usually 2 - 3 times/week • Peritoneal (PD) • Special fluid into peritoneal cavity • SURGICAL PROCEDURES • • Nephrectomy:Total removal of a kidney • Cystectomy:Removal of all/part of bladder • Nephrostomy:To create an opening from the kidney to the outside, so • urine can drain Stoma on abdominal wall • Continuous drainage of urine − bag • COMMON DRUGS • • Diuretics:Promote urination – • • Antibiotics:Treat UTIs • • Analgesics: Relieve urinary pain • • •