* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cardiovascular System The Heart
Interstitial cystitis wikipedia , lookup
Urethroplasty wikipedia , lookup
Kidney stone disease wikipedia , lookup
IgA nephropathy wikipedia , lookup
Kidney transplantation wikipedia , lookup
Chronic kidney disease wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease wikipedia , lookup
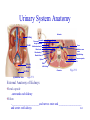
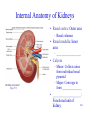
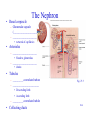
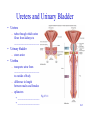
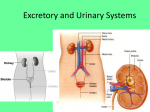
Lecture 24 Urinary System 28-1 Urinary System Anatomy Anterior Kidney Ureter Stomach Pancreas Large intestine Abdominal aorta Renal vein Renal artery Liver Inferior vena cava Right kidney Renal hilum Fibrous capsule Spleen Urinary bladder Urethra (a) Anterior view Fat Rib Left kidney Posterior Fig. 27.2 Fig. 27.1 External Anatomy of Kidneys •Renal capsule –surrounds each kidney •Hilum –________________________and nerves enter and ____________________ 28-2 and ureter exit kidneys Internal Anatomy of Kidneys • Renal cortex: Outer area – Renal columns • Renal medulla: Inner area – __________________ • Calyces Fig. 27.3 – Minor: Collects urine from individual renal pyramid – Major: Converge to form ______________ • ___________________: Functional unit of 28-3 kidney • Renal corpuscle The Nephron – Glomerular capsule (______________________) – ______________________ • network of capillaries • Arterioles – ______________________ • blood to glomerulus – ______________________ • drains • Tubules – _________ convoluted tubule – _______________________ Fig. 27.5 • Descending limb • Ascending limb – _________ convoluted tubule • Collecting ducts 28-4 Ureters and Urinary Bladder • Ureters – tubes through which urine flows from kidneys to ______________________ • Urinary bladder – stores urine • Urethra – transports urine from ______________________ to outside of body – difference in length between males and females – sphincters • ___________________ Fig. 27.11 • ___________________ 28-5 Points to Remember • Kidney filters blood to eliminate metabolic wastes (e.g. urea formed from ammonia that is removed from blood by liver) and reabsorb substances such as sugars, amino acids, sodium and chloride • Functional unit of kidney is nephron • Ureters, urinary bladder and urethra transport urine (product of nephron) outside of body 28-6 Questions? 28-7