* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diarrhea Telephone Triage
Ulcerative colitis wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Kawasaki disease wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Acute pancreatitis wikipedia , lookup
Behçet's disease wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Ankylosing spondylitis wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatoid arthritis wikipedia , lookup
Urinary tract infection wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Food intolerance wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Multiple sclerosis signs and symptoms wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Inflammatory bowel disease wikipedia , lookup
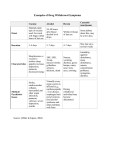
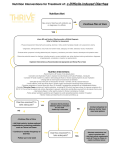
Diarrhea Telephone Triage Questions to ask: 1. Length of time of symptom duration. (Acute- less than one week vs. chronic) 2. How often/many times a day does patient have a bowel movement? 3. What is the typical pattern? 4. Is consistency liquid, mushy or semi-solid? Larger volume? 5. Any urgency or incontinence? 6. Unusual foul odor? 7. Blood in bowel movement, toilet, diaper, or after wiping? 8. Mucous or undigested food in the bowel movement? 9. Abdominal pain, bloating, distension, gas? 10. Vomiting, nausea, decreased appetite, weight loss? 11. Fever or other signs of illness? Any contact with others with diarrhea? 12. Any foreign travel, drinking from well water or eating potentially uncooked food? 13. Do certain foods trigger symptoms? 14. Current medications? Antibiotics, laxatives, fiber, motility agents? 15. Any relevant past medical history, such as constipation, celiac dz, IBD, carbohydrate malabsorption, short gut or allergic disease, pancreatic insuff, hyperthyroid 16. Any signs or symptoms of dehydration such as dry lips, decreased urinary output, no tears, decreased skin turgor, sunken eyes, less wet diapers. Red Flags: **Referral to ER/PCP/sooner clinic visit if available 1. Blood 2. Vomiting 3. Fever 4. Abdominal pain 5. Dehydration signs/symptoms 6. Significant past medical history 7. Symptoms lasting for greater than one week Treatment Goals: 1. Rehydration 2. Relieve discomfort, if any 3. Return to normal activities 4. Maintain skin integrity 5. Compliance with medications Advice: 1. Give plenty of fluids 2. Clear liquids if not tolerating normal diet. Pedialyte, Infalyte if necessary. 3. Avoid drinks with sorbitol or fructose. 4. Consider fiber supplements to add bulk (chronic diarrhea). 5. Food avoidance if identified triggers. 6. If diarrhea persists for more than one week, follow up call. Teaching: 1. Refer to GI Kids for patient teaching sheet (www.gikids.org) 2. Acute diarrhea common in children; more so in winter 3. When acute, diarrhea will stop when the infection or toxin has cleared. Most likely will not require antibiotics or anti-diarrheal 4. Important to follow up if it continues or for “red flag” symptoms appear 5. Should continue to eat regular diet, if possible Possible Causes: Acute diarrhea is one of the most common illnesses in children. Most likely causes are infection, food sensitivity or medications. Chronic diarrhea can be caused by one of the underlying conditions below: 1. Malabsorptive diarrhea a. Celiac disease b. Lactose intolerance c. Sorbital intolerance 2. Steatorrhea a. Cysic fibrosis b. Chronic pancreatitis c. Liver disease 3. Exudative diarrhea a. Infectious b. IBD 4. Secretory diarrhea a. Congenital diarrhea (microvillous atrophy) b. Malignancy 5. Non-Specific a. Toddler’s diarrhea