* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download prime number - Dr. Ben Weng
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
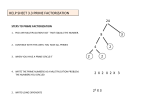
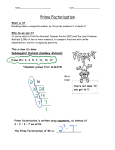
Discrete Mathematics Properties of Integers Pangyen Weng, Ph.D Metropolitan State University Prime Factorization and Greatest Common Divisors Prime and Composite Numbers (In this lesson all numbers discussed are positive.) A prime number is an integer that cannot be factored into the product of two smaller integers. Prime and Composite Numbers (In this lesson all numbers discussed are positive.) A prime number is an integer that cannot be factored into the product of two smaller integers. A composite number is an integer that can be factored into the product of two smaller integers. Prime and Composite Numbers (In this lesson all numbers discussed are positive.) A prime number is an integer that cannot be factored into the product of two smaller integers. A composite number is an integer that can be factored into the product of two smaller integers. – We can factor a composite number all the way down to the product of some prime numbers. Prime Factorization When factoring a number, if we… – factor down to prime numbers – arrange the prime factors in increasing order and – use exponents when necessary, then we get a prime factorization for a number. Prime Factorization When factoring a number, if we… – factor down to prime numbers – arrange the prime factors in increasing order and – use exponents when necessary, then we get a prime factorization for a number. Example. Find the prime factorization for 180. Prime Factorization When factoring a number, if we… – factor down to prime numbers – arrange the prime factors in increasing order and – use exponents when necessary, then we get a prime factorization for a number. Example. Find the prime factorization for 180. Exercise. How about 4004? Common Divisors If integer 𝑎 is a common divisor (or factor) of 𝑚 and 𝑛 then 𝑚 = 𝑎 ⋅ 𝑘 and 𝑛 = 𝑎 ⋅ ℎ for some integers 𝑘 and ℎ. Common Divisors If integer 𝑎 is a common divisor (or factor) of 𝑚 and 𝑛 then 𝑚 = 𝑎 ⋅ 𝑘 and 𝑛 = 𝑎 ⋅ ℎ for some integers 𝑘 and ℎ. Hint. Can the factored forms of 𝑚 and 𝑛 help us find 𝑎? Common Divisors If integer 𝑎 is a common divisor (or factor) of 𝑚 and 𝑛 then 𝑚 = 𝑎 ⋅ 𝑘 and 𝑛 = 𝑎 ⋅ ℎ for some integers 𝑘 and ℎ. Hint. Can the factored forms of 𝑚 and 𝑛 help us find 𝑎? Example. Find a few common divisors of 54 and 36. Common Divisors If integer 𝑎 is a common divisor (or factor) of 𝑚 and 𝑛 then 𝑚 = 𝑎 ⋅ 𝑘 and 𝑛 = 𝑎 ⋅ ℎ for some integers 𝑘 and ℎ. Hint. Can the factored forms of 𝑚 and 𝑛 help us find 𝑎? Example. Find a few common divisors of 54 and 36. Exercise. Find a few common divisors of 𝑚 = 2 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 5 ⋅ 7 ⋅ 7 ⋅ 7, 𝑛 = 2 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 2 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 7 ⋅ 11 Greatest Common Divisors Example. Find the greatest common divisor of 54 and 36. Greatest Common Divisors Example. Find the greatest common divisor of 54 and 36. Do you observe any strategy? Greatest Common Divisors Example. Find the greatest common divisor of 54 and 36. Do you observe any strategy? Exercise. Find gcd(𝑚, 𝑛) for 𝑚 = 22 ⋅ 3 ⋅ 5 ⋅ 73 , 𝑛 = 23 ⋅ 32 ⋅ 7 ⋅ 11