* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ERSD: End Stage Renal Disease
Epidemiology of metabolic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Fetal origins hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Nutrition transition wikipedia , lookup
Electronic prescribing wikipedia , lookup
Adherence (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Seven Countries Study wikipedia , lookup
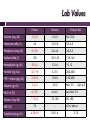
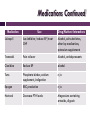
ERSD: END STAGE RENAL DISEASE Kathryn Atwater PVAMU Intern 2012-2013 Patient Background 71 year old Hispanic, white female Middle Class Separated Lives with daughter 3 children History of tobacco use but no alcohol Stage 5 Renal Failure General Health History Sleeps well Light physical activity Limited due to walker Housework Tries to “walk” as much as possible Lost 50 lb over past year Food intake varies based on daughter Alert with some memory loss Recent Medical History First hospitalized 1/30/13 for: Chronic CHF exacerbation Anemia 2/3/13 CVC placed in right chest High creatinine finalized decision (5.06 mg/dL) Started hemodialysis immediately No previous dialysis Plans to get AVF as soon as possible Past Medical History Diabetes Mellitus Hypertension Congestive Heart Failure Coronary Artery Disease Hypercholesterolemia Legally Blind Glaucoma Anemia Heart Attack Stroke Family History Mother: Heart Attack Diabetes Kidney Cancer Colon Cancer Hypertension No known medical history for father Children in good health Admission Values Ht: 60” Wt: 54.4 kg Current Wt: 53.8 IBW: 54 kg %IBW: 99.6% BMI: 23.11 BP: 208/86 Minor Edema Stable Weight Trend No swallowing or GI problems Lab Values Patient Normal 7.6 (L) 12-16 8.4-10.2 4.2 3.5-5.0 3.5-5.5 5.2 (H) 2.5-4.5 3.0-5.5 138 135-145 9.8 (L) 12-16 10-12 Ferretin (ng/mL) 1217 (H) 3-151 200-500 PTH – Intact (pg/mL) 333 (H) 10-65 150-600 Albumin (g/dL) 3.4 (L) 3.5-5 Min: 3.5 Hb A1c (%) 6.2 (H) 4.4-6.1 Less than 7.0 Glucose (mg/dL) 172 (H) 70-105 80-180 76 - 4.38 (H) 0.8-1.6 Calcium (mg/dL) Potassium (mEq/L) Phosphorus (mg/dL) Sodium (mEq/L) Hemoglobin (g/dL) URR (%) Creatinine (mg/dL) Dialysis Rec. 135-145 Opt: 4.0 65 or above 2-15 Medications Oral: IV Acetaminophen Epogen Nifedipine Hectoral Clonidine Pravastatin Docusate Escitalopram Lisinopril Tramadol Tums Medication Descriptions Medication Use Drug/Nutrient Interactions Acetaminophen Pain Reliever/Fever reducer BP medication, cholesterol medication, antibiotics, etc Nifedipine Reduce BP/reduce angina grapefruit products Clonidine Reduce BP alcohol Primvastatin HMG CoA reductase inhibitor, or, Alcohol, grapefruit statin, reduce LDL and increase products, other statins, HDL spironolactone, Docusate Stool softener n/a Escitalopram Antidepressent Alcohol; Cold or allergy medicine, narcotics, sleeping pills, muscle relaxers Medications Continued Medication Use Drug/Nutrient Interactions Lisinopril Ace-Inhibitor/reduce BP/treat CHF Alcohol, salt substitutes, other bp medications, potassium supplements Tramadol Pain reliever Alcohol, antidepressants Clonidine Reduce BP alcohol Tums Phosphate binder, calcium supplement, indigestion n/a Epogen RBC production n/a Hectoral Decrease PTH levels Magnesium containing antacids, digoxin General Diet History Good appetite Lost 50 lbs in past year Small portions Tries to “eat healthy, but depends on my daughter” 3 meals a day 1 snack Says new renal diet is “tricky” but she’s trying 24-hr Recall Breakfast: 2 eggs over easy, 1 piece of white toast & 1 tsp butter Lunch: Pepper chicken with snap peas, red peppers, and carrots, ½ cup white rice Dinner: None (usually eats whatever daughter picks up after work) Snack: 1 Mexican Cookie and a half of an apple Dialysis Prescription Type: Hemodialysis Days: M-W-F Treatment Length: 2.5 hr BFR: 350 mL/min Dialysate Flow Rate: 800 mL/min Access: CVC catheter – Jugular (Right) Average Fluid Gain: 1.6 kg EDW: 52 kg Patient Estimated Needs Kcal: 1550-1600 Protein: 60 g Sodium: 2000 mg Potassium: 2000 mg Phosphorus: 800 mg Fluid: 1000 mL Diet Prescription Renal Diet Low Potassium Low Phosphorus High Protein Carbohydrate Controlled Low Fluid Monitoring & Evaluation Start taking Tums as a phosphate binder Start Hectoral to decrease PTH levels Increase Epogen to increase hemoglobin Get fistula as soon as possible Patient eager to participate actively Prognosis: GOOD! ESRD: What is it? End Stage Renal Disease Stage 5 kidney disease Kidneys stop working i.e. kidney failure <15% kidney function PERMANENT Need a transplant or dialysis to live No cure Goal of treatment: Slow progression ESRD: Etiology & Pathophysiology Progression of CKD Main causes: Diabetes Hypertension Kidney Failure=DEADLY GFR <15 mL/min Dialysis or Transplant required ESRD: Diagnosis GFR rate calculation Urine Test Blood Test MRI Biopsy ESRD: Signs & Symptoms General “ill” feeling Itchy skin Dry skin Loss of appetite Nausea Edema Muscle-twitching & cramps Headaches Decreased urine output Poor concentration ESRD: Treatment Hemodialysis Peritoneal Dialysis Transplant Not a cure Last about 5-10 years Strict guidelines Treatment: Hemodialyis Hemodialysis Filter blood Access Points Clinic Strict Diet Treatment: Peritoneal Dialysis Peritoneal Dialysis Filter through peritoneum Home Through abdomen Less Strict Diet ESRD: Common Medicines Binders Hectoral Sensipar Epogen Iron Calcitriol Renal Diet Hemodialysis Peritoneal Dialysis 30-35 30-35 Protein (g/kg SBW) 1.2 1.2 & higher Phosphorus (mg/kg SBW) 800-1000 800-1000 Potassium (mg/d) 2000-3000 3000-4000 Sodium (mg/d) 2000-3000 2000-3000 Fluid (mL/d) 750-1000 2000 Energy (kcal/kg SBW) Protein Protein loss with dialysis Affected by infection & trauma Essential for: Growth & development Prevent infection Healing Tissue Wound HBV sources Meat Fish Poultry Protein Supplement Potassium Limit high potassium foods Low Potassium Vomiting Tomatoes Diarrhea Potatoes Hypotension Bananas oranges High Potassium Muscle weakness Bradycardia Cardiac arrest Phosphorus Poorly dialyzed Phosphate binders Avoid high phosphorus foods Renvela Cheese PhosLo Dairy Tums Beans High phosorus Nuts Calciphylaxis Hardened arteries Weak bones cola Fluid Fluid restriction Approx 48 oz. per day Based on: Urine output Interdialytic weight gains Excess fluid: Rapid weight gain High blood pressure Edema Poor appetite Physical Activity Difficult for most Benefits Stimulate appetite & circulation Improve cardiovascular risk factors Hypertension Hyperlipidemia Diabetes Obesity Enhance sense of well-being PES Statement Limited kidney function related to end stage renal disease as evidenced by low serum calcium, anemia, low serum protein, high serum phosphorus, high PTH, and high serum creatinine levels. Follow-up Hemoglobin went up to 10.9, reduced Epogen dose Fistula placed in left arm on March 14th Understands disease & reason for treatment Adjusting slowly but well As of 3/15 moved out of daughters home Patient says, “Will make it!” Summary ESRD is DEADLY if not treated properly. Diet is the key component to keeping person in optimal health Prognosis: Good if sticks to plan QUESTIONS? References McMann, L (ed): Pocket Guide to Nutrition Assessment of the Patient with Chronic Kidney Disease (3 rd ed). New York, National Kidney Foundation, 2002. "Kidney Dialysis Basics - DaVita." Kidney Dialysis Basics - DaVita. DaVita Inc., 2013. <http://www.davita.com/kidney-disease/dialysis/the-basics>. 17 Mar. 2013. Bynam-Gray, L and Weisen, K (eds). A Clinical Guide to Nutrition Care in Kidney Disease. American Dietetic Association and National Kidney Foundation, 2004. Drug Information Online: Drugs.com. 2013-2014. < http://www.drugs.com>. 19 March 2013 K/DOQI: Clinical Practice Guidelines for Nutrition in Chronic Renal Failure. Am J Kidney Dis 35(6), Suppl 2, 2000. Kopple JD, Massry SG (eds): Nutritional Management of Renal Disease. Baltimore, Williams & Wilkins, 1997. National Renal Diet, 2nd Ed. American Dietetic Association, 2002. Pritchett, E. Medical Nutrition Therapy (MNT) for Chronic Kidney Disease. Real Nutrition Forum, the American Dietetic ASSN, Vol 22, No 1, Winter 2003. Staff, Mayo Clinic. "Definition." Mayo Clinic. Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, 11 Dec. 2010. <http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/hemodialysis/MY00281>. 18 Mar. 2013. Stover, J (ed). A Clinical Guide to Nutrition Care in End-Stage Renal Disease. American Dietetic Association, 1994. Wiggins, K. Nutrition Care of Renal Patients, 3rd Ed. The American Dietetic Association, 2001. Zieve, David, MD, and Herbert Lin, MD. "End-stage Kidney Disease." U.S National Library of Medicine. U.S. National Library of Medicine, 21 Sept. 2011. <http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/ency/article/000500.htm>. 16 Mar. 2013.