* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 26
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Gamma-ray burst wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Observable universe wikipedia , lookup
Physical cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
Lambda-CDM model wikipedia , lookup
Structure formation wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Standard solar model wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
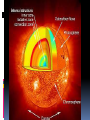
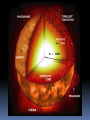
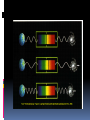
Chapter 26 26. 1 The Sun What is the sun? Without the sun’s radiation, Earth would be dark, cold, and lifeless. 70% hydrogen, 28% helium A. Energy from the sun Gives off energy in the form of electromagnetic radiation 2. The sun’s energy is produced in its central region by the fusion of hydrogen nuclei into helium nuclei. 3. Been a stable energy source for billions of years. 4. The sun remains stable because the inward pull of gravity balances outward push of thermal pressure from nuclear fusion. 5. The sun will remain stable as long as there is a steady energy source 1. • 5 billion more years B. The sun’s interior 1. Consists of: • Core, radiation zone, and convection zone 2. Core – central region where fusion occurs 3. Radiation zone- dense region of compressed gas, just outside the core, can take 100,000 years for energy to pass through it. 4. Convection zone- outer layer of the sun’s interior, Energy is transferred by convection currents. C. The Sun’s Atmosphere 1. Has 3 layers: • Photosphere, Chromospheres, and Corona 2. Photosphere- innermost, visible surface, temp. 5800K, bubbly appearance 3. Chromospheres- 10,000K, middle layer, only see during total solar eclipse The Sun’s Atmosphere Cont. 4. Corona- outer layer, can only see during a solar eclipse, very hot = 1 million K. a. Thins into solar winds- electrically charged particles flow into the solar system D. Features of the sun’s atmosphere 1. Sunspots- cooler areas on the sun’s surface that look darker. Gives off less energy. 2. Prominences- near sunspots, huge loops of gas that can be up to 10,000 km above the sun’s surface 3. Solar Flare- sudden release of energy Section 26.2: Stars 1. Star- large glowing ball of gas in space, gets its energy from nuclear fusion. 2. Light year- distance light travels in a vacuum in a year = 9.5 trillion km. A. Properties of Stars 1. Classified by: • • • • Color Size Brightness Composition 2. Color and Temperature a. Hot is blue b. Cold is red 3. Brightness- does not always tell the distance of the star. a. Apparent brightness- brightness of a star as it appears from Earth b. Absolute brightness- how bright a star really is. 4. Size and Mass a. No way to directly find this out, it is an estimate b. Use gravity to determine 5. Composition a. Most have a chemical make-up similar to the sun b. H and He make-up 96-99% of the mass B. H-R Diagram Graph of the surface temp., or color and absolute brightness of sample stars 2. Used to estimate the sizes of the stars and their distances, and to infer how stars change over time 3. Main sequence- diagonal line on the diagram where 90% of stars are found 4. Supergiants- very bright, very large stars 5. Giants- large and bright 6. White Dwarf- small, dense remains of low-medium mass stars, dimmer than the main sequence stars. 1. 26.3 Life Cycles of Stars 1. A star is formed when a contracting cloud of gas and dust becomes so dense and hot that nuclear fusion begins 2. A star’s mass determines the star’s place on the main sequence and how long it will stay there. 3. A dwindling supply in a star’s core ultimately leads to the star’s death as a white dwarf, neutron star or black hole. 26.4 Groups of Stars Star Systems 1. A group of 2 or more stars held together by gravity 2. Astronomers have determined that more than half of all stars are members of star systems Galaxies A huge group of individual stars, star systems, star clusters, dust, and gas bound together by gravity Galaxies Astronomers classify them into 4 main types: • Spiral, barred-spiral, elliptical, irregular Types of Galaxies 1. Spirals- has a bulge in the center and arms that extend outward like a pinwheel 2. Barred-Spiral- has a bar of stars running through the middle with arms extending off the bar. 3. Elliptical- spherical or oval with no spiral arms 4. Irregular- very disorganized appearance, lots of dust and gas The Milky Way Galaxy!!! Has 200- 400 billion stars and a diameter of over 100,000 light years. Our solar system is in one of the spiral arms 2/3 of the way from the center. Takes the sun 220 million years to orbit around the center of the galaxy. Evidence shows there is a massive black hole at the center of our galaxy. The Doppler Effect 1. When the wavelength and frequency of sound or light change because the waves are still moving 2. When stars move away/towards the Earth we use the Doppler Effect to look at the wavelengths. 3. To see this we use the visible light spectrum (ROY G BIV) 4. If the wavelengths are moving towards the blue end (shorter wavelengths) the star or galaxy is moving towards Earth. 5. If it moves towards the red end of the light spectrum (longer wavelengths) the star is moving away from the Earth. This is called the RED SHIFT. Hubble’s Law (1920) Hubble- 1920’s astronomers found a red shift on other galaxies. This means they are moving away from Earth. Galaxies farther away from Earth moved away faster than closer galaxies. HUBBLE’s LAW- the speed at which a galaxy moves away is proportional to it’s distance The observed red shift in the spectra of galaxies shows that the universe is expanding. The Big Bang Theory Astronomers theorize that the universe came into being at a single moment, in an event called the big bang. Big Bang Theory (not the tv show!)- states that the universe began in an instant, billions of years ago, in an enormous explosion. After the Explosion The universe expanded and cooled quickly Gravity started pulling elements together to form atoms Dust clouds stars. Evidence for the Theory The existence of cosmic microwave background radiation and the red shift in the spectra of distant galaxies strongly support the big bang theory. Age of the universe Use microwave background radiation to measure how fast the universe is expanding. They can now estimate that the universe is 13.7 billion years old. DARK MATTER matter that does not give off radiation It cannot be seen directly, but we can detect it by observing its gravitational force on visible matter. They do not know all the details about dark matter.