* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AP Biology Review Chapters 23-27 Review Questions Chapter 23
Indigenous horticulture wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Cultivated plant taxonomy wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
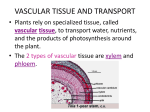
AP Biology Review Chapters 23-27 Review Questions Chapter 23: Evolution and Diversity of Plants 1. What evidence indicates that plants evolved from green algae? 2. What adaptations helped plants transition from a water habitat to a terrestrial habitat? 3. Understand the alternation of generations life cycle. What type of organism represents the diploid generation? The haploid generation? 4. What process does the sporophyte use to make spores? What process does the gametophyte use to make gametes? 5. What is the general term for nonvascular plants? What is the dominant generation in nonvascular plants? 6. What is required for fertilization to occur in nonvascular plants? What are the three main types of nonvascular plants? 7. What does “homosporous” mean? Heterosporous? What do xylem and phloem do in vascular plants? 8. Which type of plants was responsible for the great swamp forest during the Carboniferous period? 9. Define pollination. What are the main differences between gymnosperms and angiosperms? 10. Compare and contrast monocot and eudicot plant characteristics. What are the parts of a flower and what are their functions? 11. Understand the different types of flowering plants and their pollinators. What is coevolution? Chapter 24: Structure and Organization of Plants 1. What are the two main structural divisions of flowering plants and of what parts do they consist? 2. What is the function of the root system? Root hairs? 3. What are the parts and functions of a stem? 4. What are the parts of a leaf? What are the petiole and the axillary bud? 5. Again, compare and contrast monocot and eudicot characteristics. What are cotyledons? 6. What are three specialized tissues in plants and what are their functions? In what order would you find the tissues if you moved from the outside of the plant to the inside of the plant? 7. What is the function of a guard cell? 8. What three types of cells are found in ground tissue? Know characteristics and functions of each one. 9. What are the two types of vascular tissue? Know the two difference kinds of cells found in each. What does each type of tissue do for a plant? 10. Know the regions of the root and what happens in each. What is the function of the Casparian Strip? 11. What are the different types of root systems…taproot, fibrous root system, adventitious roots, mycorrihizae, and root nodules. Know what type of root system is typical for a monocot and eudicot plant. 12. What kinds of tissue make up the bark, cork, wood and pith of a woody stem? Which probably evolved first, the woody stem or the non-woody stem? 13. What is the difference between stolons and rhizomes? 14. What are some defense strategies of trees against infections? 15. What are the two different sections of mesophyll and what kinds of cells are found in each? 16. What are some adaptations of leaves to different climates? 17. Be familiar with the root diagram on page 444 and the leaf diagram on page 454. Chapter 25: Nutrition and Transport in Plants 1. What three elements make up 95% of a plant’s dry weight? What are the macronutrients and micronutrients? 2. Describe how soil forms. Define soil. Distinguish among humus, silt, clay and sand. 3. List the three soil horizons and what’s contained in each one. 4. Describe how water and minerals are absorbed by plants. 5. What adaptations of roots help in mineral and water uptake? 6. What kinds of cells make up xylem and phloem? 7. What are guttation and transpiration? 8. Understand the cohesion-tension model of xylem transport. 9. Explain the mechanism that opens and closes stoma. 10. Understand the pressure-flow model of phloem transport. Chapter 26: Control of Growth and Responses in Plants 1. What are phototropism, gravitropism, and thigmotropism? 2. What is the difference between tropisms and nastic movements? 3. What is a circadian rhythm? 4. Know the types of hormones, where they are produced and their effects (auxins, gibberellins, cytokinins, abscisic acid, and ethylene). 5. What is senescence? What causes it? 6. What is abscission? What causes it? 7. What is photoperiodism? 8. What are the three classes of plants based on photoperiodism? 9. What is phytochrome and what effect does it have on plants? Chapter 27: Reproduction in Plants 1. Be able to explain the alternation of generations for flowering plants (angiosperms) including sporophyte and gametophyte. 2. Review the parts of a flower. 3. What is the difference between monoecious and dioecious plants? 4. Describe the processes of pollination and fertilization and germination. 5. What is the endosperm and what does it provide for the embryo? 6. Understand the concept of coevolution and identify types of flowers with their insect pollinators. 7. What is the proembryo? To what do the epicotyls, hypocotyls, and radical contribute? 8. What is the difference between simple and compound fruits? Distinguish between fleshy and dry fruits. 9. How does asexual reproduction of a plant differ from sexual reproduction? 10. How is genetic engineering used with plants? 2003 Form B Question 2 Hormones play important roles in regulating the lives of many living organisms. For the following physiological responses, explain how hormones cause the response in plants. Increase in height Adjustment to change in light Adjustment to lack of water 2005 Question 3 Angiosperms (flowering plants) have wide distribution in the biosphere and the largest number of species in the plant kingdom. a) Discuss the function of four structures for reproduction found in angiosperms and the adaptive (evolutionary) significance of each. b) Mosses (bryophytes) have not achieved the widespread terrestrial success of angiosperms. Discuss how the anatomy and reproductive strategies of mosses limit their distribution c) Explain alternation of generations in angiosperms or mosses. (look at ch. 28) 2006 Question 3 The movement of water through vascular plants is important to their survival. a) Explain the mechanism of water movement through vascular plants during transpiration. Include a discussion of how the anatomy of vascular plants and the properties of water contribute to this process. b) Explain how gas exchange affects transpiration. c) Describe two adaptations that affect the rate of transpiration in desert plants. 2006 Form B Question 3 While studying transpiration, a scientist used a dendrometer to record the small daily changes in the diameter of a tree trunk at two different heights (2 meters and 3 meters) above the ground at the same time. The diameter decreased in the daytime. This decrease happened first at the higher location. Discuss the following in relation to water movement in plants. a) Identify how two different environmental factors could be involved in the daily fluctuations shown above. b) Discuss the mechanisms involved in the uptake and transport of water by vascular plants. c) Discuss the role of water in the normal functioning of plants. 2009 Form B Question 2 Discuss the patterns of sexual reproduction in plants. Compare and contrast reproduction in nonvascular plants with that in flowering plants. Include the following topics in your discussion: a) alternation of generations b) mechanisms that bring female and male gametes together c) mechanisms that disperse offspring to new locations 2011 Question 4 The regulation of transpiration is an important homeostatic mechanism in plants. a) Under controlled conditions, a transpiration experiment was conducted using two plant species. The data collected are shown in the figure below. Using the data from the experiment, calculate the rate of transpiration for species A and species B between the times of 5 and 15 minutes (show your work). Summarize the difference between the two transpiration rates. b) Identify and explain THREE different structural or physiological adaptations that could account for the different transpiration rates of species A and B. c) Discuss the variables in both formulas and how they affect water potential. Princeton 04-05 pg. 270 Before plants could survive on land, several adaptational problems had to be solved. a) Describe the problems associated with plant survival on land and discuss three structural adaptations that kept plants supplied with water. b) Describe two other structures that contributed to their success in a terrestrial environment. Campbell/Reese Review pg. 168 Describe the following processes in the plant life cycle and why they are important for the plant to complete, listing all of the plant hormones involved and describing their function. a) elongation of the plant shoot b) the process by which plants orient themselves with respect to the sun c) photoperiodism Campbell/Reese Review pg. 237 A flowering plant in a ceramic pot is placed in a window that has light shining through most of the day, and it is given adequate water and soil nutrients. a) Describe the daily and nightly events in the plant’s metabolism. b) Describe the changes in the plant that would be induced by rotating the plant 180o.