* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Early Astronomy Pre-Renaissance (the west)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
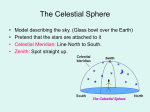
● Early Astronomy – – ● Dealt with movement of the Sun, Moon, and stars Keep time, seasons, and determine direction Pre-Renaissance (the west) – – Made measurements of the stars Use simple idealized models in the West, more sophisticated models in the East Astronomy and History ● Renaissance (west) – – ● Used science preserved in the East to resurrect Western science Devised better models Modern Science – – Natural science (physics) applied to astronomy Better mathematical tools (calculus and beyond) Astronomy and Science Preserved ● Before and after renaissance; what happened? – Initially, science progresses in ancient Egypt, Greece, and Italy (Rome) - West – But, science falls back in the west during the “Dark Ages.” – However, science is preserved by Eastern scientists – Eventually, science is recovered by Western scientists Astronomy's legacy to history ● ● Now that we discussed history we need to discuss the “jargon” used by astronomers that has its roots in history The next couple of slides will do that Astronomy's legacy ● Celestial Sphere is an imaginary sphere that has the Earth as it center – – – Celestial objects rest on the sphere Celestial equator, celestial north pole, and celestial south pole are projections from the Earth Assumes stars are equidistance from the Earth Astronomy's legacy ● ● ● Right Ascension and Declination used to describe position of celestial objects Uses angles and hence trigonometry for advance calculations Right Ascension and Declination (RA, Dec) are heavily used today even though they are based off a “celestial” sphere concept Classical Astronomy ● Celestial Sphere – “latitude” is declination (dec) ● ● ● – 0 degrees is the celestial equator +90 is North Celestial Pole -90 is South Celestial Pole “longitude” is right ascension (RA) ● ● ● ● Measured in hours rather than degrees Uses “the First Point of Aries” as 0 hours (and 24 hours) 1 hour = 15 degrees Changes in time and date! – Due to Earth Procession Classical Astronomy ● Vernal Equinox IS the First Point of Aries – – Where celestial equator intersects the ecliptic In Pisces now and will be in Aquarius in 2600AD Zodiac/Zodiacal Light ● Planets move in band that is 23.5 degrees from the Celestial equator – Called the Zodiac (“Little Animal”) ● ● – ● Constellations Stars grouped based of Celestial Sphere Pluto doesn't though... Zodiacal Light – – Faint Light corresponding to Zodiac Believed to be reflection by dust particles around the solar system Zodiacal Light (The Zodi) ● ● ● The S in images of the infrared sky Between the Sun and Jupiter Evidence was initial found because the spectrum resembled our own solar system (hence must be reflection) The Zodiac (Astrology) ● Astronomy is NOT Astrology – – ● Astrology is akin to a religion, astronomy is a science Astrology however did provide the background for Astronomy in ancient civilizations Clearly still use the terms (the Zodi) The Solar System ● The Solar System – – – – – – – – – – – – – – Sun Mercury Venus Earth Mars Asteroid belt (Ceres!) Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune (Pluto) – Dwarf planet (Eris originally known as Xena) – Dwarf planet Kuiper belt Oort Cloud The Solar System ● Kuiper Belt – – – – From within Neptune’s orbit to 50 AU from the Sun Trans-Neptunian objects (minor planets) Kuiper gap Oort Cloud (theory) The Planets ● Kepler’s Law – – – Planets in elliptical orbit around the Sun (the Sun is one focus point) Orbit speed varies so that in equal time intervals equal area will be swept Amount of time a planet takes to orbit the Sun is related to its orbit’s size