* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 8-2/8-3 lecture PDF
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
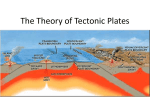
8-2 & 8-3 NOTES L A N D F O R M S AT P L AT E B O U N D A R I E S A N D M O U N TA I N B U I L D I N G L A N D F O R M S C R E AT E D B Y P L AT E M O T I O N • The large slow moving plates have so much force that they can form tall mountains and deep valleys. • At plate boundaries, three types of stresses can produce different types of landforms. • Tension • Compression • Shear L A N D F O R M S C R E AT E D B Y COMPRESSION • The largest landforms on Earth are produced by compression at convergent plate boundaries. • The collision of two continental plates causes tall mountains to form. • Takes millions of years to form • ex: The Himalayas LANDFORMS C R E AT E D B Y COMPRESSION • Through subduction, two plates can collide forcing the denser plate into Earth’s mantle creating a ocean trench. • Ocean trenches are deep, underwater troughs. • Volcanic mountains can form in the ocean where plates converge and one plate subducts under another. • Volcanic arc: a curved line of volcanic islands that forms parallel to a plate boundary. L A N D F O R M S C R E AT E D B Y T E N S I O N • Where plates move apart, tension stresses stretch Earth’s crust. • In the ocean, tension stresses produce a(n) mid-ocean ridge along divergent plate boundaries. • When divergent boundaries occur between two continental plates, tension stresses cause continental rifts. • Continental Rift: an enormous split in the Earth’s crust to form. • At the continental divergent plate boundary, tension stresses create faults where large blocks of crust move downward creating a rift valley. • Fault: a crack or a fracture in Earth’s lithosphere L A N D F O R M S C R E AT E D B Y S H E A R STRESSES • As two plates slide past each other, shear stresses occur at transform boundaries. • Shear stresses at transform boundaries produce faults. T R A N S F O R M F A U LT S • Transform faults form where tectonic plates slide horizontally past each other. • Some transform faults form perpendicular to a mid-ocean ridge, separating the midocean ridge. • Fault Zone: an area with many fractured pieces of crust along a large fault. T H E M O U N TA I N - B U I L D I N G C Y C L E • Mountain ranges form and change slowly over millions of years. • Many plate collision occur forming mountains made up of many different types of rocks. C O N V E R G E N T P L AT E S • When plates collide at a(n) plate boundary, a combination of folding, faulting, and uplift form mountains. • When two continents converge over millions of years, the forces become inactive, forming one continent. • With no compression at a convergent plate boundary, the mountains stop growing. COLLISIONS AND RIFTING • The movement of tectonic plates, causes the continents to always be changing. • A divergent plate boundary that forms on a continent often forms close to the place where two plates first collided. • Eventually plate movement changes and the continents collide again. W E AT H E R I N G • As a mountain stops forming weathering continues by rounding the peaks and lowering the elevation. • ex: The Appalachian mountains are not as tall and rugged as the Rocky mountains. EROSION AND UPLIFT • As a mountain erodes, the root under it must rise to restore the balance between what is left of the mountain and how it floats on the mantle. • Rocks deep under continents rise slowly toward Earth’s surface. • In old mountain ranges, metamorphic rocks that formed deep below the surface are exposed on the top of mountains.