* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ELECTROCARDIOGRAM (ECG)
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
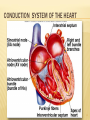
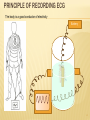
بسم هللا الرحمن الرحيم Cardiovascular System (CVS 227) ELECTROCARDIOGRAM (ECG) BASIC PRINICPLES Dr.Mohammed Sharique Ahmed Quadri Asst. professor in physiology Al Maarefa College 1 2 CONDUCTION SYSTEM OF THE HEART 3 PRINCIPLE OF RECORDING ECG The body is a good conductor of electricity Battery 4 ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Electrocardiogram: Measure of the electrical activity of the heart per unit time. Potential differences generated by heart are conducted to body surface where they can be recorded on electrodes on the skin. Does NOT measure the flow of blood through the heart. Electrocardiograph : device that records the electrical activity of the heart 5 ECG What is Lead? ECG recorded on the paper after putting the electrode. What is Electrode? It is a metallic plate which conducts electricity. 6 LEADS ARE LIKE PICTURES OF THE HEART 7 STANDARD 12-LEAD ELECTROCARDIOGRAM Six Limb Leads : Three Frontal plane currents (right, left, inferior, superior) named as , I, II , III Three Bipolar Limb Leads( standard limb leads) Unipolar Limb Leads ( augmented limb leads) named as aVR, aVL, aVF Six precordial leads Horizontal forces) plane (anterior, posterior, right and left 8 BIPOLAR / STANDARD LIMB LEADS Record the electrical potential difference in the frontal plane In bipolar lead, we record potential difference between two active electrodes. 9 UNIPOLAR (AUGMENTED) LEADS Record electrical potential in the frontal plane In Unipolar lead, we record potential difference between active electrode and other electrode at zero potential. 10 EINTHOVEN’S TRIANGLE The axis of the limb leads form an equilateral triangle around the heart’s electrical field 11 PRECORDIAL (CHEST) LEADS 12 HEART IN THREE DIMENSION 13 ELECTRODES & WAVES If current is flowing towards the recording electrode, we get upward deflection. If current is flowing away from the recording electrode, we get downward deflection. 14 Standard 12 Lead ECG 15 THE ECG PAPER Horizontally One small box - 0.04 s One large box - 0.20 s 1mm Vertically One large box - 0.5 mV 16 BASIC COMPONENTS Waves Segments & intervals 17 BASIC COMPONENTS NORMAL IMPULSE CONDUCTION Sinoatrial node AV node Bundle of His Bundle Branches Purkinje fibers 19 IMPULSE CONDUCTION & THE ECG Sinoatrial node AV node Bundle of His Bundle Branches Purkinje fibers 20 THE “PQRST” • P wave - Atrial Depolarization • QRS - Ventricular Depolarization • T wave - Ventricular Repolarization 21 THE PR INTERVAL Atrial depolarization + delay in AV junction (AV node/Bundle of His) (delay allows time for the atria to contract before the ventricles contract) 22 SEGMENTS & INTERVALS PR interval: 0.12 – 0.20 sec QRS interval : 0.08 – 0.10sec QT interval : 0.40-0.43sec ST interval :0.32 - sec 23 THE ELCTRICAL AXIS OF THE HEART Vector is diagrammatic way to show strength & direction of impulse 24 MEAN ELECTRICAL AXIS Is some total of all vectors generated by the action potential of individual ventricular myocytes. we measure the way the vectors looks as it travels under each of various electrode 25 MEAN ELECTRICAL AXIS OF THE HEART: QRS AXIS Normal range 26 Axis Determination of Mean Electrical The QRS axis is determined by overlying a circle, in the frontal plane. By convention, the degrees of the circle are as shown. The normal QRS axis lies between -30o and +110o. A QRS axis that falls between -30o and -90o is abnormal and called left axis deviation. -90o -60o -120o -150o A QRS axis that falls between +110o and +180o is abnormal and called right axis deviation. -30o 180o o A QRS axis that falls between +180 and -90o is abnormal and called Indeterminant (extende rt axis ) . 0o 30o 150o 120o 90o 60o REFERENCES Text book of medical physiology by GUYTON & HALL 11th edition Text book physiology by GANONG The ECG made Easy by John R.Hampton sixth edition 28