* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download grade 1 understanding life systems
Plant tolerance to herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
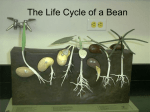
GRADE 1 UNDERSTANDING LIFE SYSTEMS - NEEDS AND CHARACTERISTICS OF LIVING THINGS THE PHYSICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF PLANTS UNIT OVERVIEW In this unit students will explore a variety of plant species through the use of picture books as an introduction to plants. Students will categorize plants into four main categories: trees, plants grown for food, plants with flowers and plants without flowers based on pictures of plants. Students will examine how plants are different based on their size, colour, shape and common elements. They will investigate the physical parts of plants and learn about the basic needs of plants. CURRICULUM CONNECTIONS Science and Technology, Grade 1, Understanding Life Systems – The Needs and Characteristics of Living Things. 3.1 investigate the physical characteristics of plants (e.g., basic parts, size, shape, colour) and explain how they help the plant meet its basic needs (e.g., roots anchor the plant and help provide the plant with food and water; some plants have brightly coloured flowers to attract bees) 3.2 identify the physical characteristics (e.g., size, shape, colour, common parts) of a variety of plants and animals (e.g., sunflowers are tall, with a long stalk, leaves, and big, round, yellow flowers with hundreds of seeds; dogs can be big or small, come in many shapes and colours, have four legs, and usually have a tail and are covered with fur) 2.3 investigate and compare the physical characteristics of a variety of plants and animals, including humans (e.g., some plants produce flowers and some do not; most plants have roots; some animals have two legs, while others have four; all animals have sense organs) 2.4 investigate the physical characteristics of plants (e.g., basic parts, size, shape, colour) and explain how they help the plant meet its basic needs (e.g., roots anchor the plant and help provide the plant with food and water; some plants have brightly coloured flowers to attract bees), using a variety of methods and resources CHARACTERISTICS OF PLANTS Lesson 1: Do You Know Your Plants? Lesson 2: Let’s Get to the Root of It: The Physical Structure of Plants Lesson 3: The Needs of Plants UNIT LEARNING GOALS: Explore a variety of plants Categorize plants based on common features Identify the basic parts of a plant Begin to understand the life cycle of a plant Understand and explain the needs of plants LESSON 1: Do You Know Your Plants? LESSON OVERVIEW By the end of this lesson students will be able to identify a variety of plants and categorize them based on four categories: trees, plants grown for food, plants with flowers, and plants without flowers. MATERIALS: Picture books on trees, plants, flowers Blackboard and chalk Large sheets of paper and marker Worksheet (included) Art supplies (paper, paint, crayons) LEARNING GOALS: Explore a variety of plants. Learn the differences and similarities between plants. Be able to categorize plants. CURRICULUM CONNECTIONS: Science and Technology, Grade 1, Understanding Life Systems – The Needs and Characteristics of Living Things 3.1 investigate the physical characteristics of plants (e.g., basic parts, size, shape, colour) and explain how they help the plant meet its basic needs (e.g., roots anchor the plant and help provide the plant with food and water; some plants have brightly coloured flowers to attract bees) 3.2 identify the physical characteristics (e.g., size, shape, colour, common parts) of a variety of plants and animals (e.g., sunflowers are tall, with a long stalk, leaves, and big, round, yellow flowers with hundreds of seeds; dogs can be big or small, come in many shapes and colours, have four legs, and usually have a tail and are covered with fur TEACHING AND LEARNING STRATEGIES: Assemble an assortment of primary books on plants from the school library as well as any resources you may have in your own classroom (picture books, non-fiction books). Ask students to look through these books on plants. Ask students to identify as many plants as possible. On the board make 4 columns TREES, PLANTS WE GROW FOR FOOD, PLANTS WITH NO FLOWERS, PLANTS WITH FLOWERS. Have students categorize the plants they have identified. Transfer these lists onto 4 large sheets of paper to hang in the classroom. Throughout the year challenge students to keep the lists growing by adding new plants as students think of them. Have students draw onto the sheets as well so that they become a growing piece of artwork. Use the cut and paste worksheet WHERE DO I BELONG? to have students categorize plants into common groups (trees, flowering plants, crops). Use this exercise to consolidate learning. As an Art Activity ask students to create a drawing or painting of a plant they like or have in their gardens at home, or which they see at the local park or on their way to school. Let the students share their creations with the class. Discuss how the plants they have chosen are similar and different. Hang the artwork in the classroom or create a “classroom garden” using the artwork. WHERE DO I BELONG? TREES PLANTS WE GROW FOR FOOD PLANTS WITH FLOWERS PLANTS WITHOUT FLOWERS LESSON 2: Let’s Get to the Root of It: The Physical Structure Of Plants LESSON OVERVIEW By the end of this lesson students will have a basic understanding of the physical structure of a plant. CURRICULUM CONNECTIONS Science and Technology, Grade 1, Understanding Life Systems – The Needs and Characteristics of Living Things 2.3 investigate and compare the physical characteristics of a variety of plants and animals, including humans (e.g., some plants produce flowers and some do not; most plants have roots; some animals have two legs, while others have four; all animals have sense organs) 2.4 investigate the physical characteristics of plants (e.g., basic parts, size, shape, colour) and explain how they help the plant meet its basic needs (e.g., roots anchor the plant and help provide the plant with food and water; some plants have brightly coloured flowers to attract bees), using a variety of methods and resources LESSON GOALS Identify the basic parts of a plant Explain the basic function of each part of the plant MATERIALS A Seed Is Sleepy by Dianne Hutts The Tiny Seed by Eric Carle From Seed to Plant by Gail Gibbons (book and video on internet) Internet access Worksheets (Included) TEACHING AND LEARNING STRATEGIES Read a Seed is Sleepy by Dianne Hutts or The Tiny Seed by Eric Carle. A Seed is Sleepy introduces students to a variety of seeds and plant facts. The Tiny Seed is a good visual introduction to the life of plants. Use the worksheet PARTS OF A PLANT to have students learn to write the parts of a plant (roots, stem, leaves, flower, seed). Have them colour the flower. Discuss as a larger class what each part of the plant does. (Every plant starts as a tiny seed. When the seed grows, the roots form to help anchor the plant in the soil and helps the plants get it nutrients/food/energy/water from the soil. The leaves help the plant get its food from the Sun. Some plants have flowers). The book and video From Seed to Plant by Gail Gibbons is a great way to learn about the parts of a plant and how it grows. You can find the video at www.teachertube.com/video/from-seed-to-plant-115357 Have students use the worksheet Tell Me About A Plant to create a few sentences about plants. PLANT PARTS FLOWER SEED STEM ROOT LEAF LEAVES STEM ROOTS FLOWER LESSON 3: THE NEEDS OF PLANTS LESSON OVERVIEW In this lesson students will investigate the needs of plants. They will be able to demonstrate an understanding of the basic needs of plants: sunlight, water, air, soil and nutrients. They will also have investigated how plants are an integral part of the environment and that humans play a large role in maintaining the health and growth of plants. MATERIALS The Curious Garden by Peter Brown The Carrot Seed by Ruth Krausse Blackboard and chalk Worksheets (included) Art Supplies LESSON GOALS Identify the basic needs of plants Identify the role of humans in maintaining the health and growth of plants CURRICULUM CONNECTIONS Science and Technology, Grade 1, Understanding Life Systems – The Needs and Characteristics of Living Things. 1.1 identify personal action that they themselves can take to help maintain a healthy environment for living things, including humans 3.1 identify environment as the area in which something or someone exists or lives 3.5 describe how showing care and respect for all living things helps to maintain a healthy environment 3.1 investigate the physical characteristics of plants (e.g., basic parts, size, shape, colour) and explain how they help the plant meet its basic needs (e.g., roots anchor the plant and help provide the plant with food and water; some plants have brightly coloured flowers to attract bees) TEACHING AND LEARNING STRATEGIES Ask students, What things do plants need to grow? Write the responses down on the board. (For example, sunlight, air, soil, nutrients from the soil, and water). Plants make their own food for energy. This energy is what fuels the plant's growth. The necessary ingredients plants need to make food are sunlight which is absorbed through the plants leaves, water which is taken into the plant by being absorbed by its roots, good soil that contains minerals plants need for nutrients. These minerals dissolve into the water in the ground. This is the same water that is taken in by the roots. Air is taken in through the plants leaves. How are the needs of plants similar to other living things? Use the worksheet The Needs of Plants to consolidate learning. Read The Curious Garden by Peter Brown or The Carrot Seed by Ruth Krausse to begin a discussion about the role of humans in protecting plants and the environment and the interdependence between plants and humans. What things do you do to help the environment? Brainstorm with the students about all the different things they do and the class does to help maintain a healthy environment (recycling, walking to school, riding a bike, taking public transit, not littering, growing a garden). THE NEEDS OF PLANTS _____________________________ ______________________________________ _____________________________ __________________________________________________________________ SUNLIGHT AIR WATER SOIL AND NUTRIENTS