* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download time of completion
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
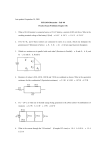
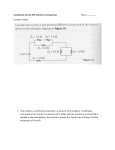
TIME OF COMPLETION_______________ NAME_____SOLUTIONS________________________ DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCES PHYS 2212, Exam 1 Version 1 Total Weight: 100 points Section 1 March 17, 2014 1. Check your examination for completeness prior to starting. There are a total of eleven (11) problems on nine (9) pages. 2. Authorized references include your calculator with calculator handbook, and the Reference Data Pamphlet (provided by your instructor). 3. You will have 75 minutes to complete the examination. 4. The total weight of the examination is 150 points. 5. There are six (6) multiple choice and five (5) calculation problems. Work five (5) multiple choice and four (4) calculation problems. Show all work; partial credit will be given for correct work shown. 6. If you have any questions during the examination, see your instructor who will be located in the classroom. 7. Start: Stop: 3:35 p.m. 4:50 p. m. PROBLEM POINTS 1-6 30 7 30 8 30 9 30 10 30 11 30 TOTAL PERCENTAGE CREDIT 1. Consider three resistors with unequal resistances connected in parallel to a battery. Which of the following statements are true? Check all that apply. a. The equivalent resistance of the combination of resistors is greater than the resistance of any one of the three resistors. b. The current flowing through each of the resistors is the same and is equal to the current supplied by the battery. c. The equivalent resistance of the combination of resistors is less than the resistance of any one of the three resistors. d. The algebraic sum of the currents flowing through each of the three resistors is equal to the current supplied by the battery. e. The algebraic sum of the voltages across the three resistors is equal to the voltage supplied by the battery. f. The voltage across each of the resistors is the same and is equal in magnitude to the voltage of the battery. 2. Consider two copper wires with the same cross-sectional area. Wire A is twice as long as wire B. How do the resistivities and resistances of the two wires compare? Check all that apply. a. Wire A has twice the resistance of wire B. b. Wire A and wire B have the same resistivity. c. Wire A has twice the resistivity of wire B. d. Wire B has twice the resistance of wire A. e. Wire A and wire B have the same resistance. f. Wire B has twice the resistivity of wire A. 3. When a potential difference of 10 V is placed across a certain solid cylindrical resistor, the current through it is 2 A. If the diameter of this resistor is now tripled, the current will be a. 3 A. b. 2/3 A. c. 2/9 A. d. 18 A. e. 2 A. 4. Consider two capacitors with unequal capacitance connected in series to a battery. Which of the following statements are true? Check all that apply. a. The sum of the charges stored on each capacitor is equal to the charge supplied by the battery. b. The voltage across each of the capacitors is the same. c. The equivalent capacitance of the combination of the two capacitors is greater than the capacitance of either of the capacitors. d. The charge stored on each of the capacitors is the same. e. The equivalent capacitance of the combination of the two capacitors is less than the capacitance of either of the capacitors. f. The algebraic sum of the voltages across the two capacitors is equal to the voltage supplied by the battery. 5. Which of the following statements are true? Check all that apply. a. The potential energy of a test charge increases as it moves along an equipotential surface. b. The potential energy of a test charge decreases as it moves along an equipotential surface. c. An equipotential surface is a three-dimensional surface on which the electric potential is the same at every point. d. Electric field lines and equipotential surfaces are always mutually perpendicular. 6. Five point charges q and four Gaussian surfaces S are represented in the figure shown. Through which of the Gaussian surfaces are the total electric flux zero? Check all that apply. a. S3 b. The total electric flux is not zero through any of the Gaussian surfaces. c. S2 d. S1 e. S4 7. Four capacitors are connected across a 90-V voltage source as shown in the figure. a. What is the charge on the 4.0-μF capacitor? 1 / C12 1 / C1 1 / C 2 3 / 4 F 1 C12 = 1.33F Q2 Q12 C12 V12 120 C b. What is the charge on a 2.0-μF capacitor? Q1 Q12 C12 V12 120 C c. What is the charge on the 3.0-μF capacitor? 1 / C34 1 / C3 1 / C 4 1 / 2 F 1 C34 = 2.00F Q3 Q34 C34 V34 180 C d. What is the potential difference across the 6.0-μF capacitor? V4 Q4 180 C 30.0 V C 4 6.00 F e. What is the equivalent capacitance of the combination? 1 / C12 1 / C1 1 / C 2 3 / 4 F 1 C12 = 1.33F 1 / C34 1 / C3 1 / C 4 1 / 2 F 1 C34 = 2.00F C1234=1.33 F + 2.00F = 3.33F 8. A +4.0 μC-point charge and a -4.0-μC point charge are placed as shown in the figure. a. What is the potential difference, VB – VA, between points A and B? VA ke Q1 Q k e 2 4.794 10 4 V r1 r2 VB k e Q1 Q k e 2 4.794 10 4 V r1 r2 V VB V A 9.59 10 4 V b. How much work is required to move a point charge of -2.0 C from point A to point B? W qV (2.00 10 6 C )(9.59 10 4 V ) 0.192 J 9. Three identical point charges q= +2.00 C are placed at each of three corners of a square of side 0.100 m. a. Find the magnitude of the net force on a point charge - 3q placed at the center of the square. F1 F2 F3 k e q(3q) 21.58 N l2 where l = 0.0707 m o F o F F Directions of the forces: 1 at 135 , 2 at 45 , and 3 at -45o, Adding three forces produces Ftot (15.25 N )i (15.25 N ) j with the magnitude of 21.58 N b. Find the direction of the net force on the point charge. Direction: 45o Easy check: because of the symmetry of the problem, the forces due to charge 1 and 3 cancel each other so total force must correspond to the force due to charge 2. 10.For the circuit shown in the figure, c. Find the equivalent resistance of the combination. 1 1 1 3 R12 R1 R2 16 R12=16/3 R123= R12 + R3=16/3 20 25.33 1 1 1 4 R45 R5 R4 6 R45=3/2 1 R12345 1 1 0.706 R123 R45 R12345=1.416 d. If the battery produces 120 V of potential difference what is the current in a 20.0 resistor? I3 V123 4.737 A R123 e. What is the potential difference across the 6.0 resistor? V 120 V 11. A portion of Nichrome wire of radius 3.90 mm is to be used in winding a heating coil. If the coil must draw a current of 9.50 A when a voltage of 120 V is applied across its ends, find the following. (Take the resistivity of nichrome to be1.50 10-6 Ω · m.) a. The required resistance of the coil. R V 12.63 I b. The length of wire you must use to wind the coil. R l TIME RA l A 402 m OF COMPLETION_______________ NAME__SOLUTION___________________________ DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL SCIENCES PHYS 2212, Exam 1 Version 2 Total Weight: 100 points Section 1 March 17, 2014 1. Check your examination for completeness prior to starting. There are a total of eleven (11) problems on nine (9) pages. 2.Authorized references include your calculator with calculator handbook, and the Reference Data Pamphlet (provided by your instructor). 3. You will have 75 minutes to complete the examination. 4. The total weight of the examination is 150 points. 5. There are six (6) multiple choice and five (5) calculation problems. Work five (5) multiple choice and four (4) calculation problems. Show all work; partial credit will be given for correct work shown. 6. If you have any questions during the examination, see your instructor who will be located in the classroom. 7. Start: Stop: 3:35 p.m. 4:50 p. m. PROBLEM POINTS 1-6 30 7 30 8 30 9 30 10 30 11 30 TOTAL PERCENTAGE CREDIT a. Consider three resistors with unequal resistances connected in series to a battery. Which of the following statements are true? Check all that apply. a. The equivalent resistance of the combination of resistors is greater than the resistance of any one of the three resistors. a. The current flowing through each of the resistors is the same. b. The equivalent resistance of the combination of resistors is less than the resistance of any one of the three resistors. c. The algebraic sum of the currents flowing through each of the three resistors is equal to the current supplied by the battery. d. The algebraic sum of the voltages across the three resistors is equal to the voltage supplied by the battery. e. The voltage across each of the resistors is the same and is equal in magnitude to the voltage of the battery. b. Consider two copper wires with the same cross-sectional area. Wire A is twice as long as wire B. How do the resistivities and resistances of the two wires compare? Check all that apply. a. Wire A has twice the resistance of wire B. b. Wire A and wire B have the same resistivity. c. Wire A has twice the resistivity of wire B. d. Wire B has twice the resistance of wire A. e. Wire A and wire B have the same resistance. f. Wire B has twice the resistivity of wire A. c. When a potential difference of 10 V is placed across a certain solid cylindrical resistor, the current through it is 2 A. If the diameter of this resistor is now tripled, the current will be a. 3 A. b. 2/3 A. c. 2/9 A. d. 18 A. e. 2 A. d. Consider two capacitors with unequal capacitance connected in parallel to a battery. Which of the following statements are true? Check all that apply. a. The sum of the charges stored on each capacitor is equal to the charge supplied by the battery. b. The voltage across each of the capacitors is the same. c. The equivalent capacitance of the combination of the two capacitors is greater than the capacitance of either of the capacitors. d. The charge stored on each of the capacitors is the same. e. The equivalent capacitance of the combination of the two capacitors is less than the capacitance of either of the capacitors. f. The algebraic sum of the voltages across the two capacitors is equal to the voltage supplied by the battery. e. Which of the following statements are true? Check all that apply. a. The potential energy of a test charge increases as it moves along an equipotential surface. b. The potential energy of a test charge decreases as it moves along an equipotential surface. c. PHYS 2212 Exam 1, Version 1 Spring 2014 An equipotential surface is a three-dimensional surface on which the electric potential is the same at every point. 14 d. Electric field lines and equipotential surfaces are always mutually perpendicular. f. Five point charges q and four Gaussian surfaces S are represented in the figure shown. Through which of the Gaussian surfaces are the total electric flux zero? Check all that apply. a. S3 b. The total electric flux is not zero through any of the Gaussian surfaces. c. S2 d. S1 e. S4 g. Four capacitors are connected across a 90-V voltage source as shown in the figure. PHYS 2212 Exam 1, Version 1 Spring 2014 15 1. What is the charge on the 6.0-μF capacitor? 1 / C34 1 / C3 1 / C 4 1 / 2 F 1 C34 = 2.00F Q4 Q34 C34 V34 180 C 2. What is the charge on a 2.0-μF capacitor? Q3 Q34 C34 V34 180 C 3. What is the charge on the 3.0-μF capacitor? 1 / C12 1 / C1 1 / C 2 3 / 4 F 1 C12 = 1.33F Q1 Q12 C12 V12 120 C 4. What is the potential difference across the 6.0-μF capacitor? PHYS 2212 Exam 1, Version 1 Spring 2014 16 V2 Q2 120 C 30.0 V C 2 4.00 F 5. What is the equivalent capacitance of the combination? 1 / C12 1 / C1 1 / C 2 3 / 4 F 1 C12 = 1.33F 1 / C34 1 / C3 1 / C 4 1 / 2 F 1 C34 = 2.00F C1234=1.33 F + 2.00F = 3.33F h. A +4.0 μC-point charge and a -4.0-μC point charge are placed as shown in the figure. a. What is the potential difference, VB – VA, between points A and B? VA ke Q1 Q k e 2 4.794 10 4 V r1 r2 PHYS 2212 Exam 1, Version 1 Spring 2014 17 VB k e Q1 Q k e 2 4.794 10 4 V r1 r2 V VB V A 9.59 10 4 V b. How much work is required to move a point charge of +3.0 C from point A to point B? W qV (3.00 10 6 C )(9.59 10 4 V ) 0.288 J 9. Three identical point charges q= +2.00 C are placed at each of three corners of a square of side 0.100 m. a. Find the magnitude of the net force on a point charge - 3q placed at the empty corner of the square. F1 F3 k e F2 k e q(3q) 10.79 N l2 where l = 0.100 m q(3q) 5.43 N l2 where l = 0.141 m o F o F F 1 2 Directions of the forces: at 90 , at 45 , and 3 at 0o, PHYS 2212 Exam 1, Version 1 Spring 2014 18 F ( 14 . 62 N ) i ( 14 . 62 N ) j with the magnitude of 20.68 N tot Adding three forces produces b. Find the direction of the net force on the point charge. Direction: 45o 10.For the circuit shown in the figure, c. Find the equivalent resistance of the combination. 1 1 1 3 R12 R1 R2 16 R12=16/3 R123= R12 + R3=16/3 20 25.33 1 1 1 4 R45 R5 R4 6 R45=3/2 1 R12345 1 1 0.706 R123 R45 R12345=1.416 PHYS 2212 Exam 1, Version 1 Spring 2014 19 d. If the battery produces 100 V of potential difference what is the current in a 20.0 resistor? I3 V123 3.95 A R123 e. What is the potential difference across the 2.0 resistor? 100 V 11. A portion of Nichrome wire of radius 2.90 mm is to be used in winding a heating coil. If the coil must draw a current of 8.50 A when a voltage of 120 V is applied across its ends, find the following. (Take the resistivity of nichrome to be1.50 10-6 Ω · m.) 5. R The required resistance of the coil. V 14.11 I 6. The length of wire you must use to wind the coil. R l RA l A 249 m PHYS 2212 Exam 1, Version 1 Spring 2014 20