* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AST 443
Nebular hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Type II supernova wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
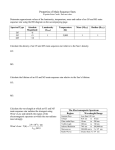
AST 443 Ch - 20 Problems 5. The Sun will reside on the main sequence for 1010 years. If the luminosity of a main-sequence star is proportional to the fourth power of the star’s mass, what mass star is just now leaving the main sequence in a cluster that formed (a) 400 million years ago, (b) 2 billion years ago? 8. Calculate the average density of a red-giant core of 0.25 solar-mass and radius 15,000 km. Compare this with the average density of the giant’s envelope, if it has a 0.5 solar-mass and its radius is 0.5 A.U. Compare each with the central density of the Sun. 9. A 15-solar-mass blue supergiant with a surface temperature of 20,000 K becomes a red supergiant with the same total luminosity and a temperature of 4000 K. By what factor does its radius change?