* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 8.9 Types of Energy Wednesday, February 3rd, 2016, EQ#12 Block
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
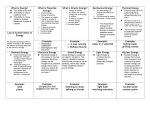
8.9 Types of Energy Wednesday, February 3rd, 2016, EQ#12 Block#1 EQ: What is the difference among Thermal Energy, Heat, and Temperature? Thermal energy: the total kinetic energy of all the moving particles in an object Temperature: the average kinetic energy of all the moving particles in an object Heat: the transfer of thermal energy from one object to another object AA: A ball with a mass of 4 kg rolls across the floor with a speed of 4 m/s. A) Find KE. Now the ball doubles its speed. B) What is the new KE? KE = 1/2mv2 KE = ½ x 4 x 42 KE = 32 [J] KE = 1/2mv2 KE = ½ x 4 x 82 KE = 2 x 64 KE = 128 [J] Potential Energy: Energy that is stored for use at a later time 1. Gravitational PE Energy that is stored by raising objects to a higher height Example: a can on a shelf, a roller coaster at the top of a hill 2. Chemical PE Energy that is stored at the molecule level Example: food, gasoline, wood, and plants 3. Electrical PE Energy stored in the collection of like charges Example: a battery, clouds in a thunderstorm 4. Nuclear PE Energy that is stored inside the nucleus of an atom Example: nuclear bomb, nuclear power plant 5. Elastic PE Energy that is stored in stretching or compressing things Examples: hair tie, rubber band, spring, sneakers Kinetic Energy: the energy of motion 1. Mechanical KE When one moving object causes a second object to move Example: hammer and nail, screw and screwdriver 2. Acoustic KE Motion of molecules bumping into other molecules carrying sound Example: anything that makes sound 3. Electrical KE The energy of charge in motion Example: electricity, lightening 4. Radiant KE The movement of light and radiation Light is a form of radiation Example: radio, infrared, visible, ultraviolet (UV), X-rays, and gamma rays 5. Thermal KE The movement and collision of atoms in an object Thermal energy: the total kinetic energy of all the moving particles in an object Temperature: the average kinetic energy of all the moving particles in an object Heat: the transfer of thermal energy from one object to another object Conservation of Energy Law: Allowed to do: A. Transform energy into a different type of energy B. Transfer energy from one object to another object Cannot do: A. Create new energy B. Destroy energy *Total amount of energy in the universe is constant! Thursday, February 4th, 2016, EQ#12 Block#2 EQ: What two things can you do and can you not do according to the Conservation of Energy Law? Allowed to do: Transform energy into a different type of energy Transfer energy from one object to another object Cannot do: Create new energy Destroy energy AA: What is the difference between chemical PE and nuclear PE? Which one has more energy? Chemical PE is store at the molecule level and nuclear PE is stored in the nucleus of an atom. The nuclear PE has more energy.