* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Population Dynamics
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
The Population Bomb wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Two-child policy wikipedia , lookup
Human overpopulation wikipedia , lookup
World population wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
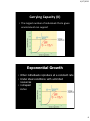
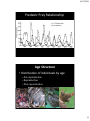
4/17/2015 (7) Science concepts. The student knows the relationship between carrying capacity & changes in populations and ecosystems. The student is expected to: (A) relate carrying capacity to population dynamics. (B) Calculate birth rates & exponential growth of populations. (C) Analyze & predict the effects of nonrenewable resource depletion. (D) Analyze & make predictions about the impact on populations of geographic locales due to disease, birth & death rates, urbanization, & natural events such as migration and seasonal changes. 1 4/17/2015 Levels of Biological Organization Biosphere Biome Ecosystem Community Population Organism Species Population Group of individuals of the same species occupying the same area at the same time Population 2 4/17/2015 Population density is the number of individuals that live in a defined area. • Population density is a measurement of the number of individuals living in a defined space. • Ex: 100 coyotes per square mile We took a sampling of deer & counted 200 deer over 10 square miles. What would be this deer population’s density? 200/10 = 20 deer per square mile Geographic DISTRIBUTION shows what regions of the world organisms are found in. 3 4/17/2015 Geographic DISPERSION of a population shows how individuals in a population are spaced. Clumped dispersion • Population dispersion refers to how a population is spread in an area. Uniform dispersion Random dispersion • There are three types of dispersion. – clumped 4 4/17/2015 • There are three types of dispersion. – uniform • There are three types of dispersion. – random 5 4/17/2015 Test Review Test on Wednesday Study: Journal notes Texas Ecoregions (Pineywoods – Edwards Plateau) Quizzes Chapter 14 worksheets Population Growth Rate • • • • + Natality = births (b) - Mortality = deaths (d) + Immigration = moving in (i) - Emigration = moving out (e) 6 4/17/2015 Population Growth Recruitment Losses Natality Immigration Mortality Emigration (birth rate) (in) (death rate) (out) Population Graph 7 4/17/2015 Carrying Capacity (K) • The largest number of individuals that a given environment can support Exponential Growth • When individuals reproduce at a constant rate • Under ideal conditions with unlimited resources • J-shaped curve 8 4/17/2015 Logistic Growth • When growth slows or stops after a period of exponential growth • As resources become less available • S-shaped curve Limits to Growth • Limiting Factor • Factor that causes population growth to decrease Write the following on the separate colors: • Density-Dependent Limiting Factor – Depends on population size • Density-Independent Limiting Factor – Affects all populations in similar ways, regardless of population size 9 4/17/2015 Limiting Factors Density Dependent Competition Predation (Hunting) Density Independent Unusual Weather Natural Disasters Parasitism Seasonal Cycles Disease Human Activity – damming rivers, clear-cutting, Biotic Potential • The size that a population would reach if all offspring were to survive – Ideal conditions – No limiting factors • Populations vary in their capacity for growth. When environmental factors are optimal, populations grow. Maximum Natality – Minimum Mortality 10 4/17/2015 Predator Prey Relationship Age Structure • Distribution of individuals by age – Pre-reproductive – Reproductive – Post-reproductive 11 4/17/2015 K-Selected • Stable populations • Remain at/near Carrying Capacity = Logistic Growth • Late successional species = Climax Species Life Strategies R-Selected • HIGH population growth rates = Exponential Growth (biotic potential) • Population greatly fluctuates above/below Carrying Capacity • Early successional species = Pioneer Species 12 4/17/2015 General Characteristics R-Selected K-Selected Organism Size Small Large Low High (little or no parental care) (much parental care) # of Offspring Produced Many (quantity) Few (quality) Timing of Maturation (Reproductive Age) Early Late Life Expectancy Short Long Exponential Logistic (J curve) (S curve) Reproductive Rates Type of Growth Curve Niche Generalists Specialists (adapt quickly to changes) (stable habitats) Pests (invasive) T/E Species Species Type K-Selected R-Selected 13 4/17/2015 14