* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download White Dwarfs and the age of the Universe
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Orion (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Crab Nebula wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
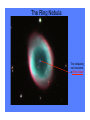
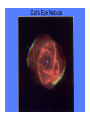
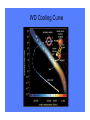
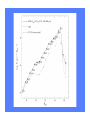
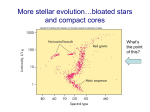
White Dwarfs and the age of the Universe The Ring Nebula The collapsing core becomes a White Dwarf The Hourglass Nebula Cat’s Eye Nebula Twin Jet Nebula How old are these baked potatoes? how to make a baked potato • rub with oil; sprinkle with salt and pepper • bake at 450 F for 1 hour • done when internal temperature = 210 F baked potato physics • Cools off: 210 F to 70 F • Time required: 2 hours, 20 min • Size of potato: did not change change in temperature -140 degrees in 140 minutes rate of change -1 degree per minute Another baked potato rate of change: -1 degree per minute Starting temperature: 210 F Current temperature: 150 F How ‘old’ is it? [how long since in oven?] change in temperature from starting point -60 degrees rate of change -1 degree per minute cooling age 60 minutes Now you can tell me the ‘age’ of any baked potato! White Dwarfs are the baked potatoes of the astrophysical world: • No heat source (cool off) • Don’t change size as they cool Canis Minor Orion Canis Major Sirius and Canis Major 1840s: Friedrich Bessell discovers odd motion of Sirius 1862: Alvan Clark discovers Sirius B Sirius and Sirius B How small can a star be? X-ray image visible light image Hot and faint 1915: Walter Adams measures temperature and size of Sirius B Sirius • d = 2.64 parsecs • T = 9,900 K • 23 times brighter than Sun Sirius B • d = 2.64 parsecs • T = 25,200 K • 34 times fainter than Sun what factors control the settings at which your pot of water will boil? from which burner (all on ‘high’) do you get the most energy? Temperature and surface area determine total energy output What is the size of Sirius B? we know temperature we know total energy output we can figure out size • four times hotter than the Sun (“hot”) • 34 times fainter than the Sun (“faint”) • 100 times smaller than the Sun (“small”) diameter of Sirius B = 99% of the diameter of Earth (Sirius is 1.7 times bigger in diameter than Sun) The Stellar Womb Stars are born deep in dark clouds: – very cold (- 400° F) – dark because visible light cannot penetrate The Orion Nebula The Trapezium Cluster Orion the role of gravity • mass attracts other mass • all parts of star gravitationally attract all other parts of star • result: all objects squeeze themselves how does force of gravity change as star squeezes itself? INCREASES SMALLER INCREASES Stellar Gestation • protostar shrinks • heats up • radiates away the excess heat • gets smaller, denser, hotter M16 When will protostars stop shrinking? Hubble’s nebula McNeil’s nebula A Star is Born Pleiades the birth of white dwarfs • they start off as hot (150,000 K), exposed cores of planetary nebulae • they generate no new energy • they cannot shrink (size determined by degeneracy pressure and mass/gravity) the fate of white dwarfs • WD is hot • Emits light from surface • surface is small, cools off slowly • cooling rate depends only on temperature (since size can’t change) • as WD cools off, rate of cooling goes down dramatically WD Cooling Curve properties of the oldest WDs • the coolest and faintest ones are the oldest • if we know the temperature and luminosity of a white dwarf, we know its size • if we know temperature, luminosity, and size now, we know the rate at which it is cooling today how old are the oldest WDs? • from the above we can ‘run the movie backwards’ and calculate how warm the white dwarf was last year and the year before and 1,000 years ago and 1 million years ago ... • from these calculations, we can determine how long it has been a white dwarf Ages of WDs in NGC 6397: 11.5 billion years Ages of WDs in M4: 12.1 billion years could we have missed fainter WDs? • newest, biggest telescopes can detect stars as faint as 70,000 times fainter than Sun • only one has been found • WD 0346+246 • 80 light years from Sun • 30,000 – 70,000 fainter than Sun • T = 3,820 degrees (K) → age as WD = 12.7 billion years