* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Click here to view the PowerPoint Presentation
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
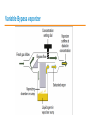
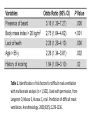
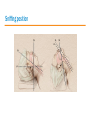
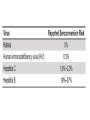
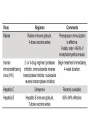
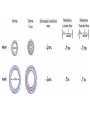
Anesthesiology Continuing Education (ACE) Joel O. Johnson, MD, PhD Co-editor in Chief asahq.org 2 Disclosure - Co-editor in Chief for Anesthesiology Continuing Education Objectives - Understand the goals of the ACE product in furthering education - Appreciate the types of questions included in ACE - Gauge the benefit that the ACE product will have on your individual learning goals Question writing - Each item is researched and written by an expert anesthesiologist - The item is reviewed and edited by the co-editorsin-chief - Each question and it’s content is discussed by the ACE Editorial Board at quarterly meetings - 100 questions are chosen for publication semiannually, after a final review for content and educational value Content - “Walking Around Knowledge” - Concise explanations - Illustrations, Figures and Tables - References including one textbook and at least one published paper Publication - Electronic, web-based - Booklet Audience Response and Participation - Please take out your mobile device/laptop. - Go to www.pollev.com/ - The polling questions will appear in your browser. 8 Cardiac A patient scheduled for surgery has a preoperative electrocardiogram (ECG) Which of the following rhythms is MOST likely to develop in this patient? a) Second-degree atrioventricular block b) Supraventricular tachycardia c) Pulseless electrical activity d) Ventricular fibrillation Delta waves in an ECG are associated with the presence of a myocardial accessory conducting pathway. Wolff–Parkinson– White (WPW) pattern on an ECG consists of a delta wave and a short P-R interval due to an accessory pathway in the conducting system of the heart. Some patients with a WPW pattern on ECG may develop WPW syndrome, which includes the presence of dysrhythmias, most commonly tachydysrhythmias such as supraventricular tachycardia (SVT). Neither second-degree atrioventricular block nor pulseless electrical activity is commonly associated with WPW syndrome. Although ventricular fibrillation has been reported in patients with WPW syndrome, it is not the most common dysrhythmia in this patient population. Anesthesia Machine Which of the following properties of desflurane MOST likely necessitates the unique construction of the agent-specific desflurane vaporizer? a) b) c) d) Low blood–gas solubility High boiling point Low molecular weight High vapor pressure. Vapor Pressure (°C) Boiling Point (°C) MAC Blood:Gas Partition Coefficient Desflurane Isoflurane Halothane Enflurane 664 238 243 175 22.8 48.5 50.2 56.5 6.0 1.28 0.75 1.58 0.43 1.4 2.3 1.9 Sevoflurane 157 58.5 2.05 0.68 Agent Variable Bypass vaporizer Desflurane vaporizer Effects of Aging (Geriatrics) Which of the following is MOST likely to be decreased as a consequence of aging? a) b) c) d) Total lung capacity Residual volume Vital capacity Closing capacity Closing capacity increases with age Pharmacology Which of the following statements about egg allergies is MOST likely true? a) Propofol contains the allergen egg white ovalbumin. b) Parenteral nutrition with fat emulsion containing egg lecithin is contraindicated in egg allergic patients. c) Egg allergy is more common in the adult population than in the pediatric population. d) Previous anaphylaxis to eggs is considered a contraindication to propofol. Explanation It is likely that rare reports of allergic reactions to propofol are due to interactions with the propofol molecule itself, involving the phenol ring or isopropyl side chains. In particular, prior exposure to cosmetic and dermatological products containing isopropyl side chains may have cross-sensitized the patient, particularly in atopic individuals. Morbid obesity Which of the following drugs is BEST dosed on total body weight in a morbidly obese patient? a) b) c) d) Succinylcholine Rocuronium Vecuronium Cisatracurium Mask ventilation Which of the following is MOST predictive of difficult mask ventilation? a) b) c) d) Lack of teeth Body mass index greater than 26 kg/m2 Presence of a beard History of snoring Table 1. Identification of risk factors for difficult mask ventilation with multivariate analysis (n = 1,502). Used with permission, from Langeron O, Masso E, Huraux C, et al. Prediction of difficult mask ventilation. Anesthesiology. 2000;92(5):1229-1236. Intubation In the properly executed ramped or head-elevated laryngoscopy position (HELP), which of the following is MOST likely true? a) The cervical spine is in an extended position with respect to the thoracic spine. b) The head is in a flexed position with respect to the cervical spine. c) The external auditory meatus is in the same plane as the sternal notch. d) The oral axis is perpendicular to the pharyngeal axis. Sniffing position HELP (head elevated) Intraoperative Complications The reported risk of perioperative venous gas embolism (VGE) is HIGHEST during which of the following procedures? a) b) c) d) Cesarean delivery Central line placement Stereotactic brain biopsy Laparoscopy Procedure Hysteroscopy Cesarean delivery Reported Risk 85%‒98% 30%‒97% Craniofacial procedures 66%‒83% Sitting craniotomy Uterine myomectomy 10%‒80% 40%‒70% Hepatic resection/surgery 44%‒68% Total hip arthroplasty 57% Operative hysteroscopy 10%‒50% Stereotactic brain biopsy 8%‒14% Deep brain stimulator implant 4.5% Laparoscopy Central line placement <0.6% 0.2%‒1% Rare (case reports) of VGE Procedure Mechanism Intestinal endoscopy Air/CO2 under pressure Vitrectomy Entrainment through the central retinal vein Spine surgery Venous entrainment when the operative site is ≥ 5 cm above the level of the right ventricle Shoulder arthroscopy Entrainment of residual air in saline irrigation bags Gravity driven or pressurized venous entry of air Infusions Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography Transurethral resection of the prostate Contrast injector in imaging studies Intravenous infusion bags Forced air via the endoscope after a Kasai procedure Risk The HIGHEST risk of seroconversion from a needlestick injury is from a patient infected with which of the following? a) Rabies b) Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) c) Hepatitis C d) Hepatitis B Pediatrics Postextubation croup in pediatric patients is MOST likely to be associated with: a) an audible leak at a peak inspiratory pressure of 20 cm H2O. b) supine position. c) patient age of 5 or 6 years. d) a recent history of croup Summary The benefits associated with the Anesthesiology Continuing Education product are: • Refreshes the participants knowledge • Introduces new concepts that are built on existing knowledge • Provides continuing education that translates into useful clinical information A 40-year-old patient in the postanesthesia care unit after laparoscopic cholecystectomy develops new-onset atrial fibrillation (AF). Vital signs include a heart rate of 135 beats/min and noninvasive blood pressure of 140/66. The patient is awake and oriented. What is the recommended initial next step? (A) (B) (C) (D) Heart rate control Echocardiogram Electrical cardioversion Anticoagulation Which of the following is MOST likely to be associated with an increased risk of postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV)? (A) (B) (C) (D) Age greater than 75 years History of smoking cigarettes Male sex Longer duration of anesthesia A 52-year-old woman with mitral valve stenosis presents for a cholecystectomy. Her preoperative electrocardiogram reveals normal sinus rhythm at 90 beats/min. Which of the following represents the BEST perioperative management strategy? (A) β-Receptor blockade (B) Infective endocarditis prophylaxis (C) Anticoagulation (D) Nitroglycerin Exposure to which of the following is MOST likely to deactivate the color indicator in soda lime absorbent? (A)Fluorescent lights (B)Compound A (C)Water (D)Heat Each of the following medications is capable of causing burst suppression on the electroencephalogram (EEG) EXCEPT (A) midazolam. (B) pentobarbital. (C) sevoflurane. (D) sufentanil. If an E-cylinder is providing 4 L/min flow of oxygen and the cylinder pressure gauge reads 600 psig, the cylinder will MOST likely become empty in (A) 90 minutes. (B) 60 minutes. (C) 45 minutes. (D) 15 minutes. Which of the following estimates of the total blood volume for a 1.8-kg premature neonate is MOST accurate? (A) 125 mL (B) 150 mL (C) 175 mL (D) 240 mL Questions?





















































![Wolfe Parkinson White [WPW] Syndrome in Women](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001611315_1-d98292e77d672846b89791f3e725d964-150x150.png)