* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Byzantine Empire - Moore Public Schools
History of the East–West Schism wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine literature wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Isaurian dynasty wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Heraclian dynasty wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Angelos dynasty wikipedia , lookup
Constantinople wikipedia , lookup
Emirate of Crete wikipedia , lookup
History of the Byzantine Empire wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Papacy wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Empire under the Komnenos dynasty wikipedia , lookup
State church of the Roman Empire wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine Greeks wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine dress wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine–Arab wars (780–1180) wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine economy wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine music wikipedia , lookup
Byzantine art wikipedia , lookup
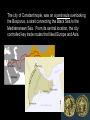
The Byzantine Empire Essential Vocabulary: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Byzantine Empire Justinian Constantine Germanic invaders Visigoth Kingdom Frankish Kingdom Peninsula Autocrat 9. Justinian’s Code 10. Hagia Sophia 11. Icons 12. Mosaics 13. Schism 14. Ottoman Empire 15. Cyrillic alphabet 16. Czar http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VWa8vOjmiMs The Byzantine Empire The Roman empire, divided in the late AD200’s, was weakened by internal and external forces. Power shifted to the East, as Germanic invaders weakened the western half of the once great Roman empire. By 330, the emperor Constantine, had built a new capital city in Constantinople on the site of the Greek city Byzantium. The Byzantine empire arose from this site. The Byzantine Empire During the Reign of Justinian At its height, the Byzantine empire covered an area from Rome through southeastern Europe and Asia Minor, down to Egypt and across North Africa. The city of Constantinople, was on a peninsula overlooking the Bosporus, a strait connecting the Black Sea to the Mediterranean Sea. From its central location, the city controlled key trade routes that liked Europe and Asia. The Byzantine empire reached its peak under the emperor Justinian. Justinian was a autocratic ruler, or single ruler with complete authority. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D50IUZPGPqg Emperor Justinian became known for his collection of ancient laws known as Justinian’s Code. This written set of laws became the basis today’s international laws. • Justinian blended Greek, Roman, Persian and Middle Eastern architecture • The best known structure is the Church of Hagia Sophia whose name means “Holy Wisdom” In the area of art, the Byzantine empire made great contributions. Icons were images of Jesus, the Virgin Mary and others. These icons were supposed the create the sense that the holy person was actually present. Byzantine artists also developed Mosaics, pictures or designs formed by inlaid pieces of stone or other materials. Mosaics often displayed religious themes. In 1054, permanent split or schism occurred between the Orthodox Christian Church in the East and the Roman Catholic Church in the West. End of the Byzantine Empire • The Byzantine Empire finally fell in 1453, after an Ottoman Turkish army stormed Constantinople during the reign of Constantine XI. Decline of the Byzantine Empire • Utilize map book page 46 1. What time period did the Byzantine Empire exist? 2. What year did Constantinople get captured by the Ottoman Turks? 3. Why did the Byzantine Empire have so many enemies like the Arabs and the Turks? Roman Catholicism v. Eastern Schism – 1054 AD Orthodox • Roman Catholicism – In West Centered in Rome Priests were celibate Latin used in services Supported use of icons Headed by Pope Becomes Roman Catholic Church • Eastern Orthodox – In East Centered in Constantinople Priests could marry Greek used in services Forbid use of icons Headed by Patriarch Becomes Eastern Orthodox Church Patriarch POPE Byzantine missionaries carried Orthodox Christianity to Russia and other Eastern European nations. The decline of the Byzantine empire came with the onset of invading armies. The final blow came at the hands of the Ottoman empire in 1453. Byzantine Contributions The Byzantine empire hoped to preserve Greek and Roman culture and also strongly influenced the first Russian state. As Russia traded with the Byzantine empire, the Byzantines influenced both Russian and eastern European development. • The Byzantine empire had its influence in the development of history. Emerging out of the once strong Roman empire, the Byzantines develop a written set of law and strongly influence art and architecture of the time. • The Byzantine empire preserved the Greek, Roman and Persian achievements as well as influencing the development of Russia and Eastern Europe. The Byzantines gave Russia a written language. Two Byzantine missionaries adapted the Greek alphabet This new system, called the Cyrillic alphabet is still used in Russia today. Cyrillic Alphabet spread Christianity • Byzantine monks traditionally spread Christianity. • Most famous was Cyril, traveled Slavic regions of Eastern Europe. • Gained followers and made major contribution of Cyrillic alphabet. • Most Slavs were illiterate so he designed an alphabet based on Greek and their language. • Cyrillic alphabet – based loosely on Greek alphabet; still used in parts of Europe Another Byzantine influence on Russia was that of an autocratic ruler. Autocratic rulers in Russia were known as czars. Czar is the Russian word for Caesar. Personal Reflection: • How do you think the split in the church may affect the long term cultural differences in the east and the west?