* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 3
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
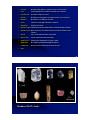
Geochemistry Periodic Table of the Elements Chemical Compound: Sodium Chloride (NaCl) Mineral: Halite (NaCl) What is a Mineral? •! •! •! •! Naturally occurring Inorganic Crystalline solid Definite chemical composition Diamond Silica Tetrahedron Quartz silicon dioxide (SiO2) Sheet silicates (e.g. micas) Unordered atoms (glass) Feldspars Micas Rock-forming silicates Halite Gold Pyrite Gypsum Calcite Hematite Physical Properties of Minerals •! Cleavage Breakage along planes of weakness in the crystal structure. •! Color Visible light spectrum radiation reflected from a mineral. •! Crystal Form Geometric shape of a crystal. •! Fracture Breakage not along planes of weakness in the crystral structure. •! Hardness Resistance to scratching or abrasion. •! Luster Character of the light reflected by a mineral. •! Magnetism Magnetic attraction. •! Reaction to HCl Chemical interaction of hydrochloric acid and calcium carbonate •! Specific Gravity Ratio of the mass of a mineral to that of an equal volume of water. (density) •! Streak Color of the mineral when it is powdered. •! Fluorescence Colour of mineral in ultraviolet light •! Radioactivity Measured by scintillometer or geiger counter •! Diaphaneity How light is transmitted through the mineral •! Conductivity Does the mineral conduct an electrical current? •! Taste 1 = talc 10 = diamond Hardness (Mohs Scale) Streak Colour Habit & Lustre Cleavage & Diaphaneity What is a Rock ? •! Naturally formed •! Consolidated material •! Composed of grains / crystals of one or more minerals Types of Rocks •! Igneous (formed from solidification of molten rock) •! Sedimentary (formed from: –! the lithification of any sediment, or –! precipitation from solution on Earth s surface, or –! consolidation of the remains of plants and animals •! Metamorphic (formed from changes induced by changes in pressure and/or temperature) Extr usive (volcanic) Intr usive (plutonic) Igneous Rocks Volcanic Plutonic Erosion and uplift