* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Summary – What you should know
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
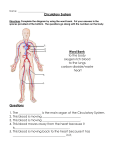
Calderglen High School Science Department Cells and the Human Body What I should know and be able to do Name_______________________________________ Class________________________________________ 1 What I should know or be able to do Cells The parts of an animal cell Cytoplasm—site of cell reactions Nucleus—controls cell activites Cell membrane— controls entry and exit from the cell Parts of the microscope A stain helps to show up the parts of a cell Specialised cells— nerve cells, Red blood cells Body Systems The human body is made of systems Each system is in turn made up of organs Some systems are the digestive, muscular, circulatory, and nervous and respiratory systems. State the name of one organ each from the digestive, muscular, circulatory, nervous and respiratory systems Give the functions of the digestive, muscular, circulatory, nervous and respiratory systems The Heart The heart is made of muscle The heart pumps blood around the body The ribcage helps to protect the heart The heart has 4 chambers Valves stop the blood flowing in the wrong direction A vein called the vena cava returns blood to the heart An artery called the aorta takes blood away from the heart The left side of the heart contains oxygenated blood The right side of the heart contains deoxygenated blood A stethoscope is used to listen to the heartbeat I can explain how to listen to a person’s heart using a stethoscope The heart rate and the pulse rate have the same value The heart rate changes with activity 2 I know about arteries, capillaries and veins A sphygmomanometer is used to measure blood pressure I can explain how to measure blood pressure using a digital sphygmomanometer Blood pressure is caused by the pressure of the blood from the heart entering the arteries The Lungs The lungs are protected by the ribcage The lungs take in oxygen from the air and give out carbon dioxide The windpipe takes the air into and out of the lungs The bronchi link the windpipe to the lungs In the air sacs, oxygen leaves the lungs and enters the blood and carbon dioxide enters the lungs from the blood The diaphragm helps to move air into and out of the lungs Teeth Four types of tooth are incisors (for biting food), canines, premolars and molars (for grinding food). The parts of a tooth are an outer layer of hard wearing enamel, dentine and a pulp cavity with nerves and blood vessels Know the position of the different kinds of teeth in the mouth Plaque is a layer of bacteria that forms over teeth Plaque forms acid from sugary food Acid destroys tooth enamel, causing cavities Know how to keep your teeth healthy Reproduction Male sex cell is a sperm The female sex cell is an egg (ovum) Sperm are produced in the testes Eggs are produced in the ovary Know the structure of the male and female sex organs including the site of fertilisation (oviduct) 3 Know the structure and function of the uterus containing an embryo including amniotic fluid, umbilical cord and placenta. Know both useful substances (food and oxygen) and harmful substances (alcohol, heroin and products from cigarette smoke) that cross the placenta from mother to baby. Chromosomes contain genes. They are long coiled strands of DNA. Other things I have learned in this topic: Health To value and look after my health How a person can avoid having heart attack How to look after my teeth Skills I may have developed in this topic : Practical skills Making hypothesis Planning experiments Setting up and carrying out experiments Drawing conclusions from experimental results Evaluating the fairness and validity of practical work Drawing tables Drawing Line Graphs Working as part of a team Contributing to group/team discussions Simple arithmetic calculations Notes 4