* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Batteries and EMF
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
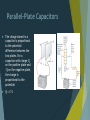
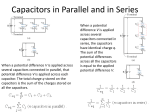
Capacitors and batteries Firdiana Sanjaya(4201414050) Ana Alina(4201414095) Definition of Capacitance The capacitance C of a capacitor is defined as the ratio of the magnitude of the charge on either conductor to the magnitude of the potential difference between the conductors: Capacitance has SI units of coulombs per volt. The SI unit of capacitance is the farad (F), which was named in honor of Michael Faraday Capacitors: devices for storing charge Parallel-Plate Capacitors The charge stored in a capacitor is proportional to the potential difference between the two plates. For a capacitor with charge Q on the positive plate and -Q on the negative plate, the charge is proportional to the potential: Q=CV Parallel-Plate Capacitors Type equation here. The Spherical Capacitor Capacitors with Dielectrics A dielectric is a nonconducting material, such as rubber, glass, or waxed paper. When a dielectric is inserted between the plates of a capacitor, the capacitance increases. If the dielectric completely fills the space between the plates, the capacitance increases by a dimensionless factor k, which is called the dielectric constant of the material. Combinations of Capacitors Series Combination 𝑄𝑆 = 𝑄1 = 𝑄2 = 𝑄3 =… 𝑉𝑆 = 𝑉1 + 𝑉2 + 𝑉3 +… 1 𝐶𝑠 1 1 1 1 2 3 = 𝐶 + 𝐶 + 𝐶 +… Combinations of Capacitors Parallel Combination 𝑄𝑝 = 𝑄1 + 𝑄2 + 𝑄3 +… 𝑉𝑝 = 𝑉1 = 𝑉2 = 𝑉3 =… 𝐶𝑝 = 𝐶1 + 𝐶2 + 𝐶3 +… Energy stored in a capacitor When a capacitor is being charge,positive charge is transferred from the negatively charged conductor to the positively charged condustor.Work must therefore be done to charge a capacitor. Energy stored in a capacitor 𝑉= 𝑄 𝐶 𝑄 = 𝐶𝑉 Batteries and EMF Batteries are capacitors that very good at storing charge for short time periods, and they can be charged and recharged very quickly. A battery consists of two electrodes, the anode (negative) and cathode (positive. Usually these are two dissimilar metals such as copper and zinc. These are immersed in a solution (sometimes an acid solution). A chemical reaction results in a potential difference between the two terminals. The voltage of a battery is also known as the emf, the electromotive force. Emf can be thought of as the pressure that causes charges to flow through a circuit the battery is part of. A flow of charge is known as a current. Batteries put out direct current. Current and Drift velocity Current (I) is measured in amperes (A), and is the amount of charge flowing per second. I = q / t The flow of positive charge in one direction is equivalent to the flow of negative charge in the opposite direction. The direction of the drift velocity is opposite to the electric field. In a typical case, the drift velocity of electrons is about 1 mm / s. The electric field, on the other hand, propagates much faster than this, more like 108 m / s. THANKS