* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download y -y =h
Survey
Document related concepts
Theoretical and experimental justification for the Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
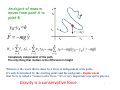
An object of mass m moves from point A to point B yB-yA=h y yB yA B A xA xB x Completely independent of the path The only thing that matters is the difference in height Whenever the work that is done by a force is independent of its path-it's only determined by the starting point and the end point-- displacement that force is called a "conservative force." It's a very important concept in physics. Gravity is a conservative force. 1 An object of mass m moves from point A to point B yB-yA=h y yB yA B A xA xB x Work energy theorem mgy is called gravitational potential energy denoted by U 2 The sum of potential energy at point B and the kinetic energy at point B is the same as the potential energy at A and the kinetic energy at point A. One can be converted into the other and it can be converted back. Kinetic energy can be converted back to potential energy, and potential energy can be converted back, but the sum of them‐which we call "mechanical energy“ is conserved. Mechanical energy is only conserved if the force is a conservative force. Amazing result and a very useful tool ! 3 Conservation of Mechanical Energy Definition of mechanical energy: Using this definition and considering only conservative forces, we find: Or equivalently: The Work Done by Conservative Forces Gravity example If we pick up a ball and put it on the shelf, we have done positive work on the ball. We can get that energy back if the ball falls back off the shelf; in the meantime, we say the energy is stored as potential energy. 5 Clicker Two paths lead to the top of a big hill. One is steep and direct, while the other is twice as long but less steep. How much more potential energy would you gain if you take the longer path? a) the same b) twice as much c) four times as much d) half as much e) you gain no PE in either case 6 Initial Potential Energy Initial total energy energy is conserved energy is conserved energy is conserved Final total energy Final =Initial 7 Clicker a b c d) same speed for all ramps Three balls of equal mass start from rest and roll down different ramps. All ramps have the same height. Which ball has the greater speed at the bottom of its ramp? 8 A, vA=0 D, vD h B, vB R 2R y y x Point B: Point D: y=0, U=0 C, vc=max velocity let y be a variable for every point (1) However there is an addition condition for point D for the ball to stay on the track (2) (1) Substitute equation (2) for vD Min criteria Solve for h d Assuming m2 to be larger, the system will accelerate in the direction indicated. Since the acceleration is same for both masses, they can be treated as a system with total mass m2+m1 Net force on the two mass system is the difference in the masses Equation of motion can be written as Kinematic equation From chapter 2 10 Conservation of Energy Potential Energy terms Kinetic Energy terms d s d Put everything together Same solution using Newton’s 2nd law 11