* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tektronix PG 502 Pulse Generator
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Chirp spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Solar micro-inverter wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear electromagnetic pulse wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Electromagnetic compatibility wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Time-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Tektronix analog oscilloscopes wikipedia , lookup
Chirp compression wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
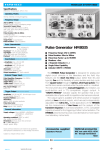
Tektronix PG 502 Pulse Generator The Tektronix PG 502 is a 250 MHz Pulse Generator that is one of many Tektronix 500 series modular test instruments designed to be used in any of the TM 500 series Power Supply Mainframes containing one to six module slots. There were two versions of the PG 502 as shown below in a TM 503 mainframe. These two versions both have the same specifications and operation. They are manually set pulse generators with rise and fall times of less than 1 ns. These systems are all analog circuitry with the front panel controls varying the parameters of the internal timing circuits to set the pulse repletion rate and pulse width. You must be careful to keep the repetition rate longer than the pulse width to avoid unpredictable output results. The output level is set by two concentric knobs, the outer one for the negative pulse level and the inner knob for the positive level. Note that the two concentric knobs are mechanically interlocked to limit the differential between the high and low levels while also allowing a DC offset. In order to be sure how the pulse generator is set, adjust it while connected to an oscilloscope which will show you what is actually happening. To generate pulses from zero to a positive voltage, use the outer knob to set the bottom of the pulse to zero and the inner knob to set the pulse to the desired positive voltage. To generate pulses from zero to a negative voltage, use the inner knob to set the top of the pulse to zero and the outer knob to set the pulse to the desired negative voltage. To set up a pulse train, first set the repetition rate slower than needed, then set the pulse width, then correct the repetition rate. If the generator is connected to something higher than a 50Ω load, the output will be higher than with the expected 50Ω termination. If the oscilloscope is 1MΩ input only, you can use a 50Ω termination at the scope input to provide the correct load. There is also a back termination button next to the output connector. Pulling this knob will insert extra series resistance in series with the output which will damp reflected signals, generally producing a cleaner output, but also cutting the output voltage in half. The output impedance remains 50Ω regardless of the back termination setting.