* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 11 Mountain Building
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
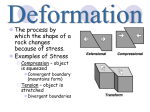
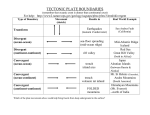
Chapter 11 Mountain Building: Section 11.1 Forces in Earth’s Crust: • Earth has 14 ___________________ over 8000 meters (~14,250 ft.) Deformation of Rock: • ________________________ – any change in the original shape and/or size of a rock body. Every rock, no matter how strong, has a point which it will bend or break. • Most deformation occurs at _________________________ where rocks are subjected to stress and strain. • _______________________ – the force per unit area acting on a solid. Rocks begin to fold, flow, or fracture when subjected to stress greater than their own strength. • _______________________ – the change in shape or volume or a rock due to stress. Types of Stress: • ________________________ • ________________________ • ________________________ Principle of Isostasy: • __________________________ – concept of floating crust in gravitational balance. • __________________________ – the process of establishing a new level of gravitational balance. Newly formed mountains sink deep into the crust due to their ______________________________. As mountains weather and erode away they become lighter, and the crust rises in response. This is an example of an ________________________________. Section 11.2 Folds, Faults, and Mountains: • During mountain building, __________________________________________ often bend flat-lying sedimentary and volcanic rocks into wavelike ripples called folds. • There are three types of folds – 1. ____________________ 2. ____________________ 3. ____________________ • The Appalachian and Himalayan Mountains are ______________________________. Types of Folds: 1._________________________ -- Upward fold of rock – an arch 2._________________________ -- Downward fold in rock – a trough 3._________________________ -- Step-like Fold Types of Faults: • _______________________– rock surface immediately above the fault. • _______________________ – the rock surface below the fault. • The major types of faults are normal faults, reverse faults, thrust faults, and strike-slip faults. • _______________________– occur due to tensional stress. The hanging wall block moves down relative to the footwall. Found at divergent boundaries. Angles are often 60 0 • _______________________ – result from compressional stress. The hanging wall block moves up relative to the footwall. High angle faults > 450. Convergent boundary • _______________________– reverse faults with angles less than 450. The hanging wall goes up an over the footwall. Convergent boundary • _______________________– produced by shearing stress at transform boundaries. The movement is horizontal and parallel to the trend, or strike, of the fault. Types of Mountains: • The major types of mountains include volcanic mountains, folded mountains, fault-block mountains, and dome mountains. • ____________________________ – processes involved in mountain building. • ____________________________ – several mountains of similar shape, age, and structure. The Clinch Mountain Range is in this area. • ____________________________ – group of mountain ranges in the same region. We live in the Appalachian system. • ____________________________ – caused by compressional forces found at convergent boundaries that fold rock at reverse and thrust faults. The Appalachian Mountains, the Himalayan Mountains, and the Alps are some examples of folded mountains. • ____________________________ – vents in the Earth’s crust that allow magma to come to the surface. • _____________________________ – form as large blocks of crust are uplifted and tilted along normal faults. • _____________________________ – block of crust that drops down due to normal faulting. It creates the valley floor. • _____________________________ – blocks of crust that border the graben that stay uplifted creating the mountains. Landforms: • Up-and-down movements of the crust can produce a variety of landforms, including plateaus, domes, and basins. • _____________________________ – broad, flat area of land uplifted to a relatively high elevation. The Colorado Plateau is cut by the Grand Canyon. • _____________________________ – broad upwarped areas of land caused by laccoliths. The Black Hills of South Dakota are an example. • _____________________________ – downwarped structures in the crust caused by plate motions causing the crust to bend downward. Section 11.3 Mountains and Plates Convergent Boundary Mountains: Convergent Boundary Mountains: ____________________________________________ – when two oceanic plates collide, one will subduct beneath the other resulting in a deep ocean trench and a volcanic island arc. An example is the Aleutian Islands of Alaska. _____________________________________________ – when they converge it can produce inland volcanic mountains along with some folded mountains. Examples include the Cascade Range, the Andes of South America, and the Coastal Range on the West Coast of the United States. _____________________________________________ – when two continental plates collide folded mountains are formed. Examples include the Appalachians and the Himalayas. Divergent Boundary Mountains: • Most mountains are formed at convergent boundaries, but some are formed at divergent boundaries along the mid-ocean ridges. They are _____________________________________ made of volcanic rock. Non-Boundary Mountains: • Some mountains do not form at plate boundaries. These are _____________________________ that form at a hot spot, a weak area in the Earth’s crust. Fault-block mountains and upwarped(domed) mountains can also form a long way from plate boundaries Continental Accretion: • ________________________________ – this process enlarges continental landmasses and forms mountains along the edges of continents. Pieces of crust that collide with the continent become stuck or embedded in the continental crust. • ________________________________ – accreted crustal blocks.