* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 3.2 Equations of Lines:
Schrödinger equation wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Van der Waals equation wikipedia , lookup
Itô diffusion wikipedia , lookup
Exact solutions in general relativity wikipedia , lookup
Calculus of variations wikipedia , lookup
Schwarzschild geodesics wikipedia , lookup
Derivation of the Navier–Stokes equations wikipedia , lookup
Equation of state wikipedia , lookup
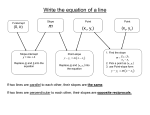
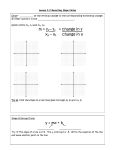
Section 3.2 Equations of Lines: • Standard Form: Ax + By = C where A, B, and C are numbers o 2x + 3y = 6 is a linear equation in standard form o x = 6 is a linear equation in standard form (B = 0) o y = 0 is a linear equation in standard form (A = 0) • Slope-intercept form: y = mx + b o m is the slope of the line o b is the y-intercept (where it crosses the y-axis) o y = 3x + 2 slope is 3/1 and y-intercept is (0, 2) “Rearranging the furniture”: • To go from standard form to slope intercept form: 2x + 3y = 6 3y = − 2x + 6 3y = − 2x + 6 2 y= − x+2 3 • Hop and swap the 2x to the other side It changes its sign and goes after the = Now divide by 3 to get y alone Now it’s in slope-intercept form To go from slope-intercept form to standard form: 5 x−2 6 6y = 5x – 12 –5 x + 6y = – 12 5 x – 6y = 12 = y Multiply everything by 6 (LCD) Hop and swap the 5x to the other side Be sure that the x-term goes first Make the x-term positive “If you don’t like a sign, change them all”