* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Esotropia Extropia
Visual impairment wikipedia , lookup
Contact lens wikipedia , lookup
Keratoconus wikipedia , lookup
Fundus photography wikipedia , lookup
Vision therapy wikipedia , lookup
Near-sightedness wikipedia , lookup
Blast-related ocular trauma wikipedia , lookup
Cataract surgery wikipedia , lookup
Diabetic retinopathy wikipedia , lookup
Visual impairment due to intracranial pressure wikipedia , lookup
Eyeglass prescription wikipedia , lookup
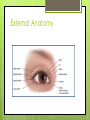
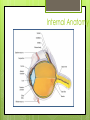
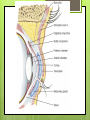
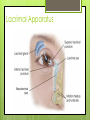
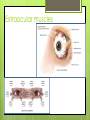
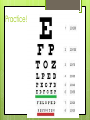
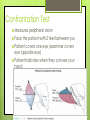
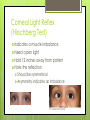
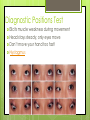
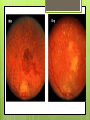
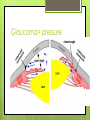
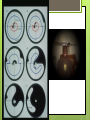
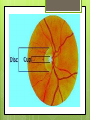
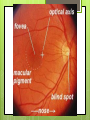
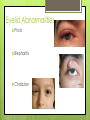
The Eyes! Chapter 14 Objectives Identify the internal & external anatomical features of the eye Describe the health history pertaining to the eyes Demonstrate the following techniques: Basic vision testing Extra ocular muscular functioning Pupillary response External eye inspection Fundoscopic exam More objectives Describe normal eye assessment findings Describe abnormal findings of the eye Discuss health promotion practices that are pertinent to the eyes Explain age-related changes in the eye Document findings of the eye assessment External Anatomy Internal Anatomy Lacrimal Apparatus Extraocular muscles Health History Vision Difficulty Pain Strabismus or diplopia Redness or swelling Watering or discharge History of Ocular problems Glaucoma Use of glasses/CL Self-care behaviors Talk the Talk OD = right eye OS = left eye Myopia = nearsighted Hyperopia = farsighted Presbyopia = “old man’s vision” Amblyopia = lazy eye Assessment techniques& Tools Snellen Eye Chart Confrontation Test Corneal Light Reflex Cover Test Diagnostic Positions Test Amsler Grid Pen light Opthalmoscope Snellen Eye Chart Measures visual acuity Distance Vision 20 feet from patient Cover one eye Documentation! Near Vision Jaeger Card 14 inches Cover one eye Practice! Confrontation Test Measures peripheral vision Face the patient with 2 feet between you Patient covers one eye (examiner covers eye opposite eye) Patient indicates when they can see your hand Corneal Light Reflex (Hirschberg Test) Indicates a muscle imbalance Need a pen light Hold 12 inches away from patient Note the reflection Should be symmetrical Asymmetry indicates an imbalance Cover Test Indicates a muscle imbalance Phoria vs tropia Patient stares at a fixed point Cover one eye at a time Normal = no movement in uncovered eye Abnormal= if the uncovered eye “jumps” it was not fixated on the point to begin with As you uncover the opposite eye, if it “jumps” it was not fixated Diagnostic Positions Test Elicits muscle weakness during movement Head stays steady; only eyes move Don’t move your hand too fast! Nystagmus Amsler Grid Detects Macular Degeneration If present, the disease will distort the lines on a grid Visual Loss with Macular Degeneration Glaucoma= pressure Inspection of External Structure General Eyebrows Eyeballs Exophthalmos Enophthalmos Conjunctiva & Sclera Scleral icterus Lacrimal Apparatus Inspection of Anterior Eyeball Structures Cornea & lens Arcus senilis Iris & pupil Anisocoria Pupillary light reflex Accommodation PERRLA Pupils Equal Round Reactive to light (with) Accommodation Inspect the Ocular Fundus Internal surface of the retina Tools & Process Opthalmoscope Diopter 0= normal vision - # = myopia + # = hyperopia Darken the room for dilation Have the patient focus Look thru the pupil Findings of the ocular fundus Red Reflex Opacities Optic disk Color : creamy yellow-orange to pink Shape: Round or oval Margins: Distinct & sharply demarcated Cup-disc ratio: Brighter area in centershould not exceed ½ of the diameter Ocular Fundus Continued Retinal vessels Number Color A:V ratio Caliber A-V crossing Tortuosity Pulsations Macula Same size as the disc Darker than the disc, but color is even Asymmetric Corneal Light Reflex Esotropia Extropia Eyelid Abnormalities Ptosis Blepharitis Chalazion Pupil Abnormalities Anisocoria Monocular Mydriasis Miosis Blindness Conjunctivitis Subconjunctival Cataracts hemorrhage