* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Figurative Language and Sound Devices Hyperbole: An
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
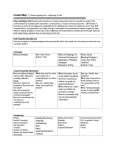
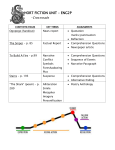
6th GRADE GMAS REVIEW SHEET STORY ELEMENT Protagonist Antagonists Settings Plot Climax DESCRIPTION The main character of a story Forces that work against the protagonist: nature, other characters, settings, inner thoughts Where and when a story takes place The events in a story—what happens to the protagonist makes up the plot. The high point of a story that occurs near the end of the story. Denouement A return to normalcy for the story that occurs after the climax. Conflicts Tensions between characters or between a character and the settings or character and inner thoughts. Problems Challenges the protagonist faces that he or she tries to resolve. Resolution The outcome or outcomes of trying to solve problems and deal with conflict. Themes Ideas from a story that can be generalized to apply outside the story – the lesson. Central Idea A theme that’s threaded through the entire piece Figurative Language and Sound Devices Hyperbole: An exaggeration (That building can touch the clouds.) Idiom: An expression that cannot be understood from the individual meanings of its elements, as in kick the bucket or under the weather. Irony: The opposite of what is meant. Metaphor: A comparison of two unlike things that suggests a similarity between the two items. (Love is a rose.) Personification: Making an inanimate object or animal act like a person Puns: A word or words, which are formed or sounded alike, but have different meaning; to have more than one possible meaning. (Using that pencil is pointless.) Simile: A comparison using "like" or "as" (She sings like an angel.) Alliteration: Repeated consonant sounds at the beginning of several words in a phrase (Robbie saw rabbits resting by roses.) Onomatopoeia: Words that sound like what they are. (POP! BAM! Slosh) Author’s Purpose Entertain – Make the reader feel an emotion Inform – Teach/Educate the reader about something Persuade – Convince the reader to believe something When we read, it is important for us to understand why the piece was written. Narrator/Author’s Point of View FIRST PERSON - A character within the story recounts/retells his or her own experiences or impressions. • Lets the reader know only what that character knows. • Uses the pronouns: I, me, my, mine, we, our, ours. SECOND PERSON - The story or the piece of writing is from the perspective of “you.” • Uncommon form of writing. • Used mainly with instruction manuals, recipes, giving directions, and poetry. • Uses the pronouns: you, yours. THIRD PERSON OBJECTIVE - The narrator remains a detached observer, telling only the stories action and dialogue. • Lets the reader know only what is seen and heard, not what characters think or feel. • Uses the pronouns: he, she, it, they THIRD PERSON LIMITED - The narrator tells the story from the viewpoint of one character in the story. • Lets the reader know what one character thinks, sees, knows, hears, and feels. • Uses the pronouns: he, she, it, they THIRD PERSON OMNISCIENT - The narrator has unlimited knowledge and can describe every character’s thoughts and interpret their behaviors. • Lets the reader know unlimited information about the characters. • Uses the pronouns: he, she, it, they Transition Words and Phrases to use in essays… Beginning (beginning of the second paragraph First, To begin with, The first reason, For one thing, To illustrate my point, You see, In fact, Obviously, Middle (the beginning of the third paragraph) Next, Obviously, Secondly, Second, The second reason, Once again, Additionally, In addition, Along with, Again, Likewise, Moreover, In the same manner, Similarly, End (the beginning of the fourth paragraph) Next, Lastly, Finally, The last reason, The final reason, Once again, Conclusion (the final paragraph) In conclusion, Thus, Therefore, As a result, To summarize, Finally, Consequently, By this time To sum up, Now that Evidenced based writing: The text says, the author states, as mentioned in the text, the author suggests in the text, an example from the text, etc. Constructed response – Fully answer the question after restating the question; use evidence from the text to support your answer. Your essay needs a(n)… Introduction – Grabber, and THESIS (Ex - There are three reasons that illustrate this point: 1) __ 2) __, and 3)__.) Body Paragraph 1 – Topic sentence – Point one from thesis statement, and supporting detail sentences Body Paragraph 2 – Topic sentence – Point two from thesis statement, and supporting detail sentences Body Paragraph 3 – Topic sentence – Point three from thesis statement, and supporting detail sentences Conclusion – Restate thesis a different way and leave the reader with something to think about Pronouns take the place of nouns or other pronouns. The antecedent is the word that is being replaced by the pronoun. Pronouns and antecedents must AGREE in number (singular/plural) and gender (male/female). Intensive and reflexive pronouns always end in self or selves. Commas are used to separate items in a series, and to set off information in a sentence that is not necessary, or after a subordinate (dependent) clause that begins a sentence. Remember dependent clauses start with trigger words. Where you naturally want to pause in a sentence is usually where a comma should go. You must use a comma and a conjunction when joining complete sentences together. Genres of Literature Nonfiction - This is Informational text dealing with an actual, real-life subject. This genre of literature offers opinions or conjectures on facts and reality. This includes biographies, history, essays, speech, and narrative nonfiction. Nonfiction is the opposite of fiction. Narrative Nonfiction is information based on fact that is presented in a format which tells a story. Essays are a short literary composition that reflects the author’s outlook or point. A short literary composition on a particular theme or subject, usually in prose and generally analytic, speculative, or interpretative. A Biography is a written account of another person’s life. An Autobiography gives the history of a person’s life, written or told by that person. Often written in Narrative form of their person’s life. A memoir (from French: mémoire: memoria, meaning memory or reminiscence) is a collection of memories that an individual writes about moments or events, both public or private, that took place in the subject's life. Speech is the faculty or power of speaking; oral communication; ability to express one’s thoughts and emotions by speech, sounds, and gesture. Generally delivered in the form of an address or discourse. ---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------Fiction - The genre of Fiction can be defined as narrative literary works whose content is produced by the imagination and is not necessarily based on fact. In fiction something is feigned, invented, or imagined; a made-up story. Drama is the genre of literature that’s subject for compositions is dramatic art in the way it is represented. This genre is stories composed in verse or prose, usually for theatrical performance, where conflicts and emotion are expressed through dialogue and action. This usually written in script format. Poetry is verse and rhythmic writing with imagery that evokes an emotional response from the reader. The art of poetry is rhythmical in composition, written or spoken. This genre of literature is for exciting pleasure by beautiful, imaginative, or elevated thoughts. It is often composed of stanzas. (Sections). Fantasy is the forming of mental images with strange or other worldly settings or characters; fiction which invites suspension of reality. Humor is the faculty of perceiving what is amusing or comical. Fiction full of fun, fancy, and excitement which meant to entertain. This genre of literature can actually be seen and contained within all genres. A Fable is a story about supernatural or extraordinary people usually in the form of narration that demonstrates a useful truth. In Fables, animals often speak as humans that are legendary and supernatural tales. Fairy Tales or wonder tales are a kind of folktale or fable. Sometimes the stories are about fairies or other magical creatures, usually for children. Science Fiction is a story based on impact of potential science, either actual or imagined. Science fiction is one of the genres of literature that is set in the future or on other planets. Short Story is fiction of such briefness that is not able to support any subplots. Realistic Fiction is a story that can actually happen and is true to real life. Folklore are songs, stories, myths, and proverbs of a person of “folk” that was handed down by word of mouth. Folklore is a genre of literature that is widely held, but false and based on unsubstantiated beliefs. Historical Fiction is a story with fictional characters and events in a historical setting. Horror is an overwhelming and painful feeling caused by literature that is frightfully shocking, terrifying, or revolting. Fiction in which events evoke a feeling of dread in both the characters and the reader. A Tall Tale is a humorous story with blatant exaggerations, swaggering heroes who do the impossible with nonchalance (like it is no big deal for them). Paul Bunyan, Pecos Bill, Sally Ann Thunder Ann Whirlwind Legend is a story that is sometimes of a national or folk hero. Legend is based on fact but also includes imaginative material. Johnny Appleseed Mystery is a genre of fiction that deals with the solution of a crime or the unraveling of secrets. Anything that is kept secret or remains unexplained or unknown. Mythology is a type of legend or traditional narrative. This is often based in part on historical events, that reveals human behavior and natural phenomena by its symbolism; often pertaining to the actions of the gods. A body of myths, as that of a particular people or that relating to a particular person. Greek and Roman Mythology Fiction in Verse is full-length novels with plot, subplots, themes, with major and minor characters. Fiction in verse is one of the genres of literature in which the narrative (story) is usually presented in blank verse form (poetry). Novel written in the form of poetry.