* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earth And the Sun
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
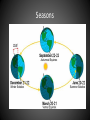
Earth and the Sun Earth Science 2013 Astronomy • Definition: The study of the planets,[------ moon, stars, and other objects in space Sun • • • • The Sun is the center of our Solar System There are 8 planets in our solar system We are 92 million miles from the Sun The Sun is responsible for all the energy we receive on Earth Earth • The planet we live on • Only Planet with life(that we know of…) • Third planet from the Sun Earth • The Earth is an inner planet – Small in size – Few or no moons(only one) – No rings Earth’s Movements • • • • Rotation: One spin on its axis Takes about 24 hours to rotate once This rotation causes DAY and NIGHT Sun always rises in the EAST and sets in the WEST Earth’s Movements • Revolution (orbit): One lap around the Sun • This takes about 365 days or one year to complete • The path is not quite a circle; its more of an oval shape Calendars • Calendars mark time on earth in 24 hour days and 365 days per year • The Egyptian astronomers counted the days between the appearance of the star Sirius and found an average of 365 days between appearances. • So the Egyptians came up with one of the first Calendars! Leap Years • The path of the Earth around the Sun actually takes 365 ¼ day to complete. • Every fourth year we add up the extra time ¼ + ¼ + ¼ + ¼ = one extra day • This day is added to the calendar every 4 years on February 29 • Leap Years: 2004, 2008, 2012, 2016, 2020, 2024, 2028, etc Earth’s Tilt • Earth has seasons because the axis is tilted as it moves around the Sun • WE ARE IN THE NORTHERN HEMISPHERE • When the Northern Hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun, we get the most sunlight = summer • When the Northern hemisphere is tilted away from the Sun, we get the least sunlight = winter Seasons Seasons • Most places on Earth have 4 distinct seasons: Winter, Spring, Summer, and Fall • The length of each season depends on its location on the Earth and how the sunlight hits the Earth • The uneven heating of the Earth creates three different climates: tropical, temperate, and polar Season’s interactive • Click here Four Seasons • Winter Solstice – Starts around December 21 – Northern Hemisphere is tilted away from the Sun – The rays from the Sun are the weakest – Shortest day of the year in Northern Hemisphere; longest day of the year in the Southern Hemisphere – Marks the beginning of winter Four Seasons Four Seasons • Autumnal Equinox – Starts around September 22 – The Suns is directly over the equator creating an equal amount of daytime and nighttime – Marks the beginning of Fall Four Seasons • Spring Equinox – Starts around March 21 – The Suns is directly over the equator creating an equal amount of daytime and nighttime – Marks the beginning of summer Four Seasons Four Seasons • Summer Solstice – Starts around June 21 – Northern Hemisphere is tilted towards the Sun – The rays from the Sun are the strongest – Longest day of the year in Northern Hemisphere; shortest day of the year in the Southern Hemisphere – Marks the beginning of the summer Climate Zones The Moon • The Moon takes 27.3 days to revolve around the Earth • The Moon takes 27.3 days to rotate on its axis • Therefore, we only ever see one side of the moon Lunar Landing Sites