* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Urinary System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
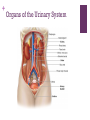
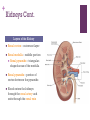
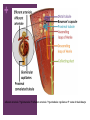
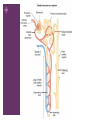
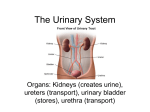
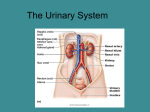
+ The Urinary System + Organs of the Urinary System + Kidneys Functions of the Kidneys Remove metabolic waste products from the blood Secrete hormone erythropoietin, which stimulates the bone marrow to produce red blood cells Secrete hormone renin which helps regulate blood pressure Characteristics Bean-shaped Retroperitoneal position Renal sinus – concave depression Hilum – where the renal artery, vein, and ureter enter Renal pelvis – area where urine is drained from the kidney Calyces – smaller tubes in which the renal pelvis divides + Kidneys Cont. Layers of the Kidney Renal cortex – outermost layer Renal medulla – middle portion Renal pyramids – triangularshaped areas of the medulla Renal pyramids – portion of cortex between the pyramids Blood enters the kidneys through the renal artery and exits through the renal vein + Nephrons Function and Parts Waste products are removed Each kidney has about 1M Renal Corpuscle Glomerulus Bowman’s capsule Blood filtration occurs Renal Tubule Proximal convoluted tubule Attached to Bowman’s capsule Loop of Henle Straighter tubule that curves back toward the renal corpuscle Distal Convoluted tubule Several combine to form collecting ducts Collecting ducts – deliver urine to the renal pelvis, which empties into the ureters + afferent arteriole glomerulus efferent arteriole peritubular capillaries veins of the kidneys + + Glomerular Filtration Takes place in the renal corpuscles (glomerulus) Blood that contains wastes is forced into the glomerulus – glomerular filtrate Depends on filtration pressure which is determined by blood pressure Tubular Reabsorption Second process Glomerular filtrate flows into the proximal convoluted tubule Where nutrients, water and ions are reabsorbed back into the bloodstream Water reabsorption depends on ADH and aldosterone (hormones) Tubular Secretion Third process Where substances (drugs, hydrogen ions, waste products) are excreted into the urine Urine Composition Water (mostly) Urea Uric Acid Trace amounts of amino acids Urine Formation + Ureters, Urinary Bladder, Urethra Ureters Two Carry urine from kidney to bladder Peristalsis propels urine toward the bladder Urinary Bladder Expandable organ that stores urine Up to 600 mL on average Detrusor muscle – contracts to push urine from the bladder to the urethra Urethra Tube that carries urine from bladder to the outside Shorter in females Micturition Process of urination Bladder distends with urine Stimulates stretch receptors in the bladder Parasympathetic nerves stimulate the detrusor muscle Sense the need to urinate Brain sends impulses to voluntarily contract the urethral sphincter to inhibit the need to urinate Voluntary decision to urinate relaxes sphincter Contraction of detrusor muscle and urine is expelled through the urethra