* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Align assessment questions
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
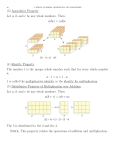
Grade 3 Unit 1: Properties of Mult. /Div. & Solving; Problem Solving with Units 2-5 and 10 Standards OA.1- Interpret products of whole numbers, e.g. interpret 5 x 7 as the total number of objects in five groups of seven objects each. For example, describe a context in which a total number of objects can be expressed as five times seven. OA.2- Interpret whole number quotients of whole numbers , e.g., interpret 56 ÷ 8 as the number of objects in each share when 56 objects are partitioned equally into 8 shares, or as a number of shares when 56 objects are partitioned into equal shares of 8 objects for each. For example, describe a context in which a number of shares or a number of groups can be expressed as 56 ÷ 8. OA.3- Use multiplication and division within 100 to solve word problems in situations involving equal groups, arrays, and measurement quantities, e.g. by using drawings and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem. OA.4- Determine the unknown whole number in a multiplication or division equation relating three whole numbers. For example, determine the unknown number that makes the equation true in each of the equations. 8 x ? = 48, 5 = __ ÷3, 6 x6 = ?. OA.5 – Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide. Examples, if 6 x4 =24 is known, the 4 x6=24 is also known. (Commutative property of multiplication) 3x5x2 can be found by 3 x 5 =15, then 15 x 2 =30, or by 5 x 2=10, then 3 x 10=30. (Associative property of multiplication) Knowing that 8x5=40 and 8x2=16, one can find 8x7 as 8 x(5+2) = (8x5) + (8x2) = 40 +16 = 56. (Distributive property.) OA.6 - Understand division as an unknown-factor problem. For example, find 32 ÷ 8 by finding the number that makes 32 when multiplied by 8. OA.7 – Fluently multiply and divide within 100, using strategies such as the relationship between multiplication and division (e.g. knowing that 8x5=40, one knows 40 ÷ 5 = 8) or properties of operations. By the end of Grade 3, know from memory all products of two one-digit numbers. OA. 8 – Solve two step problems using the four operations. Represent these problems using equations with a letter standing for the unknown quantity. Assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies including rounding. Revised July 21, 2014 Align assessment questions (to be completed by Coaches) Unit Objectives OA. 1 I can interpret products in multiplication (e.g. 50=5x10 can be interpreted as 5 groups of 10, an array with 5 rows and 10 columns, the area of a 5-by-10 rectangle, 5 rows of 10 objects). OA.2 I can explain division as a set of objects partitioned into equal number of shares. I can identify parts of division equations (dividend, divisor, and quotient) I can interpret quotients in division (e.g., 50/10=5 can be 5 groups with 10 items in each group or 10 groups with 5 items in each group.) OA.3 I can determine when to multiply and divide in word problems. I can represent multiplication and division word problems using drawings, and equations with unknowns in all positions. I can solve word problems involving equal groups, arrays, and measurement quantities using drawings and equations. OA.4 I can determine the unknown number in multiplication and division problems such as in the following: 8x9 = ____ 8x ___= 48 ___x3=27 28÷7=____ ___÷6=3 35÷____=5 Revised July 21, 2014 OA.5 I can explain the commutative, associative, and distributive property of multiplication. I can apply the commutative, associative, and distributive properties to decompose, regroup, and/or reorder factors to make it easier to multiply two or more factors. I can explain how the operation properties can and cannot apply to division and use those properties that can apply to make it easier to find the quotient. OA.6 I can explain the relationship between multiplication and division. I can turn a division problem into a multiplication problem with an unknown factor. OA.7 I can multiply any two numbers with a product within 100 with ease by picking and using strategies that will get to the answer fairly quickly. I can divide whole numbers with a divisor within 100 and with a whole number quotient with ease by picking and using strategies that will get to the answer fairly quickly. I can instantly recall from memory the product of any two one-digit numbers. OA.8 I can choose the correct operation to perform the first computation, and choose the correct operation to perform the second computation in order to solve two-step word problems. I can write equations using a letter for the unknown number. I can decide if my answers are reasonable using mental math and estimation strategies including rounding. Revised July 21, 2014 Essential Questions: OA. 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 In what ways can operations affect numbers? How can different strategies be helpful when solving a problem? Vocabulary Multiplication Product Dividend Quotient equation associative property order of operations rounding equal groups divide multiply parentheses row unit Materials At least 18 counters per student White boards Markers erasers Revised July 21, 2014 factor division divisor array commutative property distributive property estimation column distribute fact number of groups rotate size of groups unknown Assessments Unit 1 District Assessment (Use Eureka Math Module 1 Assessment) Math Tasks Revised July 21, 2014 Revised July 21, 2014 Revised July 21, 2014