* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Coronary Circulation
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
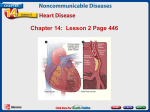
Coronary Circulation when blood supply to a region of the myocardium is reduced or cut off for a prolonged period that part of the heart will be damaged or die – called a myocardial infarction, a.k.a. heart attack the system of vessels that supply blood to the heart is called coronary circulation – it is supplied to the heart by 2 main arteries, the right and left coronary arteries these arteries branch off the aorta, which then divided multiple times, supplying all regions of the myocardium with oxygenated rich blood these arteries continue to branch into smaller vessels called arterioles – then they become even smaller in diameter, one-celled thick vessels called capillaries in the capillaries oxygen, carbon dioxide and nutrients are exchanged between the blood and myocardium these vessels eventually become larger called coronary venules – as blood moves through these venules they become together to form larger vessels called coronary veins all of the coronary veins come together to form the coronary sinus – which drains the right atrium of the heart – this completes coronary circulation Cardiac Cycle defined as a series of events that occurs through one heart beat during this cycle there is both a relaxation (diastole), where the heart is filling with blood, and a phase of contraction (systole), where the heart contracts and ejects the blood systolic blood pressure – pressure in the arteries during the contraction phase (i.e. 120mmHg) diastolic blood pressure – pressure in the arteries during the relaxation phase (i.e. 80 mmHg) normal blood pressure reading 120/80 mmHg Blood main role: transport medium for oxygen, carbon dioxide and nutrients made up of 2 main components: plasma and blood cells plasma: fluid component – composed mostly of water and other dissolved substances such as nutrients, proteins and gases 55% of blood blood cells: RBC called erythrocytes – 45% of blood transport oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood contains hemoglobin that binds oxygen and carbon dioxide – it gives the blood the ability to transport and deliver oxygen to the tissues and remove carbon dioxide to the lungs WBC called leukocytes – less than 1% of blood important for the body’s immune system – protecting the body from disease and helps to regulate blood clotting