* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CHAPTER ONE: Tools of Geometry Page 1 of 12
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Analytic geometry wikipedia , lookup
Lie sphere geometry wikipedia , lookup
Cartesian coordinate system wikipedia , lookup
Duality (projective geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Geometrization conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Compass-and-straightedge construction wikipedia , lookup
History of geometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
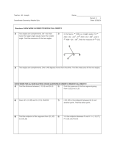
CHAPTER ONE: Tools of Geometry Page 1 of 12 (1-1) Nets and Drawings for Visualizing Geometry Given a standard six-sided die, what would it look like if I flattened it? What about this solid? ... or this one? A __________________ is a two-dimensional diagram that you can fold to form a three-dimensional figure. A net shows __________________ of the surfaces of a figure in one view. (1-2) Points, Lines, and Planes undefined term = a term whose meaning is accepted _____________________________ a definition Our undefined terms: _______________ , _______________, & _______________ CHAPTER ONE: Tools of Geometry Page 2 of 12 Naming Them: _________________________ is the set of all points in three dimensions. A SEGMENT (or line segment) is part of a line that consists of _________________________ and _______________ of the points in between them. A _______________ is part of a line that consists of one endpoint and all of the points of the line on one side of the endpoint. _________________________ are two rays that share an endpoint and form a _______________. CHAPTER ONE: Tools of Geometry Page 3 of 12 A _________________________ or _________________________ is an accepted statement of fact. Postulate 1-1: Through any two points there is _____________________________________. Postulate 1-2: If two distinct lines intersect, then they intersect in _____________________________________. Postulate 1-3: If two distinct planes intersect, then they intersect in ____________________________________. Postulate 1-4: Through any three non-collinear points, there is ____________________________________________ . (1-3) Measuring Segments Postulate 1-6 (Segment Addition Postulate): If three points A,B, and C are collinear and B is between A and C, then ___________________________ Distance (on a number line): Given two points A and B on a number line, the distance between them, d, is ______________________ The distance between A and B can also be written as ____________ CHAPTER ONE: Tools of Geometry Page 4 of 12 Given a number line where… G = ____________and J = ____________, find GJ. P = ____________ and Q = ____________, find PQ. Given EG where EF = ____________ and FG = ____________. If EG = 59, find x, EF, FG, and EG Equality vs Congruence: Two objects are ______________________if they have the same ______________________. Two objects are ______________________if they are the same ______________________. Equal Segments vs Congruent Segments Equality: _______________________ Congruence: _______________________ CHAPTER ONE: Tools of Geometry Page 5 of 12 The ______________________of a segment is the point that divides the segment into two congruent segments. The point, line, ray, or other segment that intersects a given segment at its midpoint is a ______________________for that segment. BE CAREFUL HERE! The midpoint is a ________________, while a bisector ____________________ the midpoint. Q is the midpoint of PR. If PQ = ____________ and QR = ____________, find x, PQ, QR, and PR. (1-4) Measuring Angles An ___________________ is formed by two rays with the same endpoint. The rays are the ___________________ of the angle, and the endpoint is the ___________________ of the angle. SIDES: ___________ and ___________ VERTEX: ___________ CHAPTER ONE: Tools of Geometry Page 6 of 12 Naming Angles: 1 => ___________ 2 => ___________ ___________ ___________ ___________ 3 => ___________ ___________ The ______________________________ of an angle is the region containing all the points between the two sides of the angle; the ______________________________ of an angle is the region containing all of the points outside of the angle. Types of Angles: ___________________ angles measure between 0 & 90 degrees. ___________________ angles measure 90 degrees. ___________________ angles measure between 90 & 180 degrees. ___________________ angles measure 180 degrees. Equal Angles vs Congruent Angles Equality: _______________________ Congruence: _______________________ CHAPTER ONE: Tools of Geometry Page 7 of 12 Postulate 1-8 (Angle Addition Postulate): If point B is in the interior of AOC, then ________________________________________ DEF is a straight angle. Find m DEC and m CEF. (1-5) Exploring Angle Pairs ______________________________ angles are two coplanar angles with a common side, a common vertex, and no other points in common. ______________________________ angles are two angles whose sides are opposite rays. A little easier... Vertical Angles are formed when __________________________________________________ intersect. CHAPTER ONE: Tools of Geometry Page 8 of 12 ______________________________ angles are two angles whose measures have a sum of 90 degrees. Each angle is called the ______________________________ of the other. ______________________________ angles are two angles whose measures have a sum of 180 degrees. Each angle is called the ______________________________ of the other. A _____________________________________________ is a pair of adjacent angles whose noncommon sides are opposite rays. The angles of a linear pair form a straight angle. Postulate 1-9 (Linear Pair Postulate): If two angles form a linear pair, then they are _________________________________________. An _____________________________________________ is a ray or segment that divides an angle into two congruent angles. CHAPTER ONE: Tools of Geometry Page 9 of 12 XP bisects MXE. If m PXM = ___________, find m PXE and m EXM. (1-6) Basic Constructions – moved to Chapter 2 (1-7) Midpoint and Distance in the Coordinate Plane On a NUMBER LINE, the coordinate of the midpoint is the _______________ of the coordinates of the endpoints. Given points A and B on a number line, the midpoint M of AB is M = On the COORDINATE PLANE, the x-coordinate of the midpoint is the ______________________ of the x-coordinates and the y-coordinate of the midpoint is the _____________________of the y-coordinates. Given two points on the coordinate plane, A(x1, y1) and B(x2, y2), the midpoint M of AB is M = Given P = ___________ and Q = ___________; find M, the midpoint of PQ. CHAPTER ONE: Tools of Geometry Given F = ___________ and G = ___________ ; find M, the midpoint of FG. Given AB with midpoint M. If A = ___________ and M = ___________, find B, the OTHER ENDPOINT. DISTANCE FORMULA: The distance between two points, A(x1, y1) and B(x2, y2), is d = If L = ___________ and M = ___________, find LM. If S = ___________ and T = ___________, find ST. Page 10 of 12 CHAPTER ONE: Tools of Geometry Page 11 of 12 (1-8) Perimeter, Circumference, and Area The ___________________________________ of a polygon is the sum of the lengths of its sides. The ____________________________ of a polygon is the number of square units that it encloses. For a SQUARE: perimeter = ___________ area = ___________ For a RECTANGLE: perimeter = ___________ area = ___________ For a TRIANGLE: perimeter = ___________ area = ___________ CHAPTER ONE: Tools of Geometry For a CIRCLE: Page 12 of 12 perimeter ( ___________________________________ ) = ___________ area =___________ Postulate 1-10 (Area Addition Postulate): The area of a region is the ___________ of its non-overlapping parts. Find the area of the pictured shape: Find the area of the shaded region