* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 32
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
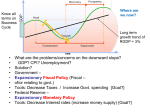
PRINCIPLES OF ECONOMICS Chapter 32 Macroeconomic Policy Around the World PowerPoint Image Slideshow Job fairs and job centers are often available to help match people to jobs. This fair took place in the U.S. (Hawaii), a highincome country with policies to keep unemployment levels in check. Unemployment is an issue that has different causes in different countries, and is especially severe in the low- and middle-income economies around the world. COUNTRY CLASSIFICATION Developing Countries: Nations in Africa, Asia (except Japan), and Latin America. Developed Countries: Nations in North America (except Mexico) and Western Europe plus Australia, Japan, and New Zealand. Transitional Countries: Nations of the former Soviet Union and Eastern Europe that are moving from socialism to capitalism. COUNTRY CLASSIFICATIONS Low income countries: Per capita income up to $1,025 Middle income countries: Per capita GDP $1,025 to $12,475 High income countries: Per capita GDP more than $12,475 COUNTRY CLASSIFICATIONS Low-income countries account for • less than 1% of global income • 18.5% of the world population Middle-income countries account for • 31.1% of global income • 69.5% of world population High-income countries account for • 68.3% of global income • 12% of the world’s population. COUNTRY CLASSIFICATION COUNTRY CLASSIFICATION There is a clear imbalance in the GDP across the world. North America, Australia, and Western Europe have the highest GDPs while large areas of the world have dramatically lower GDPs. GROWTH POLICIES OF HIGH INCOME COUNTRIES Japan’s Prime Minister used fiscal and monetary policies to stimulate his country’s economy, which has worked in only the short run. GROWTH POLICIES OF HIGH INCOME COUNTRIES • Have fiscal policy focus on investment in human capital, social capital, and technology • Keep inflation and unemployment low • Reform tax and spending structures • Keep independent central banks for steady growth of the money supply to support economic growth • Eliminate federal deficit and reduce national debt • Reduce over-consumption of food and fossil fuel GROWTH POLICIES OF MIDDLE INCOME COUNTRIES • Maintain high saving rates • Have fiscal policy focus on investment in human capital, social capital, and technology • Continue to emphasize export promotion • Reform tax structure • Continue to adopt “appropriate” technology • Reduce government control and rely more on market system 11 of 32 GROWTH POLICIES OF LOW INCOME COUNTRIES • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Alleviate poverty Sustain economic growth and income equality Provide civil liberty and freedom to choose Invest in human capital (education, nutrition, health) Control population growth (education, family planning) Invest in social capital (housing, electricity, drinking water, schools, transportation, communication) Provide more capital per worker hour Adopt appropriate technology Improve trust and honesty (eliminate corruption) Improve the socio-economic status of women Rely of democracy and market-orientation Achieve peace and harmony (no need for big military) Improve tax and spending structures Have independent central banks ECONOMIC CHALLENGES LOW INCOME COUNTRIES In low-income countries, all income is often spent on necessities for living and cannot be accumulated or invested in physical or human capital. The students in this photograph learn in an outside “classroom” void of not only technology, but even chairs and desks. POLITICAL CHALLENGES LOW INCOME COUNTRIES Low-income countries, like those in this chart, share common elements such as political factionalism, infighting, and corruption. TYPES OF UNEMPLOYMENT ACROSS COUNTRIES High income countries: • Mostly cyclical due to recessions Middle income countries • Mostly structural due to technological change Low income countries • Both cyclical and structural • Lack of job creation policy APPROPRIATE TECHNOLOGY Modern technologies, such as solar-power and Wi-Fi, enable education to be delivered to students even in remote parts of a country without electricity. These students in Ghana are sharing a laptop provided by a van with solar-power. Economic impacts on middle and low income countries • Slow economic growth • Declining exports • Reduced foreign investment and foreign aid inflow • Declining stock markets and rising capital outflow • Inability to pay back debt 13-16 GLOBAL FINANCIAL CRISIS GLOBAL FINANCIAL CRISIS The economic conditions in Greece have deteriorated from the Great Recession such that the government had to enact austerity measures, cutting wages and increasing taxes on its population. Massive protests are but one byproduct.