* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Assyrians
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
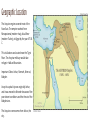
The Assyrians By: Brynnydd Hamilton and Alexandra Kiritsy Introduction Intro Assyria was one of the most advanced civilizations before it’s downfall in 612 B.C. Archaeologist Sir Max Mallowan discovered that the area where Assyria’s capital cities were had been inhabited since 5000 B.C, although the cities did not exist that early. Civilization Components Geographic Location The Assyrian region covered most of the Near East. The empire reached from Mesopotamia (modern Iraq), Asia Minor (modern Turkey), to Egypt by the year 675 B. C. This civilization was located near the Tigris River. The Assyrian military would take refuge in Hakkari Mountains. Important Cities: Ashur, Nineveh, Nimrud, Babylon Assyria’s capital city was originally Ashur, and it was moved to Nineveh because of the poor desert conditions and the threat of the Babylonians. The Assyrian name comes from Ashur, the city. Nineveh Sketch of Ashur Natural Resources The Assyrians controlled the Fertile Crescent, which provided them with fertile land for farming. They were also near the Tigris River. They grew crops such as wheat, barley, millet, melons, lentils, and other vegetables. The land was suited for herding and grazing. They had sheep, goats, donkeys, and water buffalo. The Assyrians had a large road system for trade. They continued to conquer because they need resources such as wood, iron, gold, metals, linens, ivory, and other treasures of foreign nations. During battles, the Assyrians were interested in obtaining horses for their own use. Beliefs/Value Systems Pagan gods Influenced by the Sumerians and Babylonians ● ● ● ● Ashur: Assyria’s National god, God of War Ishtar: Wife of Ashur, Goddess of Love and War Nergal: God of Plagues Geshtu-e: His blood was taken to create mankind More Beliefs: ● ● The god Ashur instructed the king to continuously extend the empire’s borders. If not, the apocalypse would occur. Honor the gods and king Language/Communication Systems The Assyrian language was an ancient Aramaic language, which belonged to a larger group of Semitic languages. It is often referred to as Ashuric. The modern language is called Neo-Assyrian. They wrote using cuneiform. Their writing was recorded on clay tablets. Ashurbanipal wanted the literary works of the empire brought to the capital city of Ashur for duplication, creating the first library of the world. Ashurbanipal then used several of these writings as omens for decision making. In the king’s palace in Nineveh, his artisans would paint graphic images on the walls of the palace depicting successful battle scenes. These included illustrations of people being impaled, beheaded, and cooked alive. When an emissary came from another land or kingdom to visit Assyria, they would be intimidated by what they saw. Societal Organizations Theocratic Government: God was recognized as the ruler, and the priests of Assyria were the primary leaders, and claimed to be interpreting his will. The king was considered to be the high priest. Imperial Administration: The nation of Assyria was split up into mini-nations that had their own rulers. These rulers all collaborated together. Hammurabi’s Code: Many Mesopotamian cultures followed Hammurabi’s Code, a brutal retribution-based code of 282 laws written by the Babylonian king Hammurabi. Their society was fairly similar to the Babylonian culture. Cultural Organization The religious figures were at the top of the Assyrian social hierarchy. Members of the higher class were given more privilege in the legal system than the members of the lower class. Hammurabi’ s Code provided very few provisions for the protection of slaves. Only boys were educated in the Assyrian culture. They attended schools called “tablet houses” which were generally attached to places of worship. Women had very few opportunities in Assyrian culture. They were regarded as property and had very little control of their fates. Monetary System and Trade The Assyrians used a variety of objects as money, including barley, lead, copper, tin, gold, or silver. Silver and barley were used as the primary money. Trading was carried out by the merchants, who were fairly high in the social hierarchy. Merchants would establish business in small trade towns, and instate a family member as the business owner, then return to one of the primary cities. Technological Advances and Cultural Arts Assyrian Technological Advances ● ● ● ● ● Use of iron Paved Roads Battering Rams Mathematics Two-wheeled chariots Cultural Arts ● ● ● ● ● Ziggurats Relief Sculptures Pottery Gold-smithing Locks and Keys Additional Investigation The Rise of Assyria Shamshi-Adad I, 1813 B.C.: He united the cities Ashur, Nineveh, Arbel, and Nimrud, which formed the center of Assyrian society, trading, and culture. He drove the Amorites and Hittites out of Mesopotamia, who were fierce nomadic tribes. They had been one of the main obstacles of the formation of Assyrian culture. The Fall of Assyria The Assyrians expanded beyond their road systems and lost control of the empire. The conquered peoples disliked the Assyrian rulers because of their intense tax and tribute demands. The later kings were weak rulers, who were not capable of keeping the empire in union. There were many revolts in the empire, and the army was defeated by these coalitions. In 612 B.C., the capital city of Nineveh was sacked by the Babylonians, Medes, and other enemies, leading to the downfall of the Assyrian Empire. Fall of Nineveh Influence/Effects First to use Imperial Administration system which is used by nations today Highest civilization of it’s time Civilized barbaric regions Old and New Testament Influenced the organization and techniques of the Persian army Over 3 million people today speak Neo-Assyrian Fun Facts The Assyrians were vicious, ruthless warriors. They ruled with terror, and they placed a great emphasis on the military. When the Assyrians defeated the Elamites, they beheaded the Elamite king. His head was returned to the Assyrian king. The king stabbed the head before hanging it on a tree and celebrating their victory. The Assyrians would take many prisoners of war. Ashurnasirpal II would have the captives skinned, and he would place those skins on the walls of the city. Ashurnasirpal II and his servants The Assyrians demanded tribute and tax from the conquered nations. If they refused or failed to do so, the Assyrians made sure that they would regret it. They would often send military force to collect the tribute. In 745 B.C., Tiglath-Pileser III made the first standing army and an armory, making the Assyrian military the most advanced in the world. The tallest members of the army used spears as their weapon. Other soldiers only had shields to protect the archers. All of the soldiers were issued iron helmets, leather boots, and iron breastplates. In 704 B.C., Sennacherib II attacked and destroyed Babylon. The Assyrian people disliked this decision because they respected the Babylonian culture. Esarhaddon killed his father, Sennacherib, by either stabbing him multiple times or crushing him with a giant statue. It was recorded on a clay tablet that Sennacherib had cursed Babylon for 70 years, but it was later discovered that the high priests were reading the tablet upside down. He had actually cursed Babylon for 11 years. When the Assyrians attacked Jerusalem and Lachish, they constructed large siege towers that were covered in leather. This made the towers fire resistant because the enemy would often shoot fire arrows. The Assyrians would also throw the heads of captives over the walls or impale the captives’ bodies on stakes to intimidate enemies during battle. “A mere friend will agree with you, but a real friend will argue” - Assyrian Proverb Sources Websites aina.org ancientassyria.weebly.com historyworld.net omniglot.com/writing/assyrianneoaramaic metmuseum.org everyculture.com britishmuseum.org encyclopedia.com/topic/Assyria worcesterjcc.org catherinecollegelibrary.net/classic bible-history.com Videos ancient.eu/assyria/ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jwqlnjgymKA (Military History: Ancient Assyria) jewishvirtuallibrary.org britannica.com/place/Assyria angelfire.com https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0a_F2y5e5Ls (Assyrian Empire) Photos http://www.knowledgequestmaps.com/images/Assyrian%20Empire.ldsc.jpg (Map of Ancient Assyria) https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/6/64/The_Palaces_at_Nimrud_Restored.jpeg (City of Nineveh) http://www.iraqiembassy.us/sites/default/files/photos/history_timeline_photo_04_1.jpg (Sketch of Ashur) https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/f/fc/Tigris_River_At_Diyarbakir.JPG (Tigris River) http://www.greenacres.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/04/blog-wheat.jpg (Wheat) https://s-media-cache-ak0.pinimg.com/736x/b5/de/3e/b5de3e9382826c74995b928ce44faf76.jpg (The god Ashur) http://www.aina.org/images/alphabet.gif (Assyrian Alphabet) http://historicconnections.webs.com/Assyrian%20Weding%20Contract.jpg (Cunieform Clay Tablet) http://www.metmuseum.org/toah/images/h2/h2_32.143.4.jpg (Image of Ashurnasirpal and servants) http://www.archeolog-home.com/medias/images/08020542.jpg (Assyrians in battle) https://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/c/cd/Britishmuseumassyrianrelieftwohorsemennimrud.jpg (Assyrians in battle) http://thumbs.dreamstime.com/x/acient-assyrian-art-5-8537822.jpg (Assyrians in battle) http://www.aanf.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/ashurnasirpal.jpg (Assyians in chariots) http://www.iccdc.us/wp-content/uploads/2014/06/Assyrian-Armor-238x300.jpg (Assyrian Soldiers) Photos (continued) https://c1.staticflickr.com/9/8010/7524445046_18a5efaf42_b.jpg (Assyrian Siege Towers) http://allaboutashur.yolasite.com/resources/p.png (Assyrian soldier and Lion) http://ahistoryblog.com/wp-content/uploads/2012/06/Fall-of-Nineveh.jpg (Fall of Nineveh and Assyrian Empire) Thanks! Contact us: Brynnydd Hamilton Alexandra Kiritsy Massachusetts Academy of Math and Science WPI Worcester, Massachusetts USA Planet Earth