* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Building electrical circuits
Nanogenerator wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Transistor–transistor logic wikipedia , lookup
Operational amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Radio transmitter design wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Printed circuit board wikipedia , lookup
Electrical engineering wikipedia , lookup
Valve RF amplifier wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Index of electronics articles wikipedia , lookup
Surface-mount technology wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
RLC circuit wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
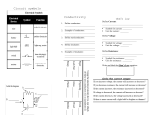
MODERN LIVING AND ENERGY - SECTION 3 BUILDING ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS BOOK 1 MODERN LIVING & ENERGY SECTION 3 BUILDING ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS 2 MODERN LIVING AND ENERGY - SECTION 3 BUILDING ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS SYMBOLS It is important to know the symbols of components in electrical circuits. Switch Lamp Diode Cell Resistor Fuse A Battery V Voltmeter 1 Ammeter MODERN LIVING AND ENERGY - SECTION 3 BUILDING ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS ACTIVITY Look at the following circuit diagrams and identify the components. A V 2 MODERN LIVING AND ENERGY - SECTION 3 BUILDING ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS 3 MODERN LIVING AND ENERGY - SECTION 3 BUILDING ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS CIRCUITS There are two types of electrical circuit: series circuits and parallel circuits. In a series circuit all of the components follow the same path. In a parallel circuit there are branches where the components sit. SERIES CIRCUIT All of the components follow the same path. Also, the current is the same throughout the circuit and the voltage across each component adds up to the voltage of the power supply. 4 MODERN LIVING AND ENERGY - SECTION 3 BUILDING ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS PARALLEL CIRCUIT In a parallel circuit the components are in branches. Here the voltage across all components is the same and the current within each branch is equal to the current of the power supply. 5 MODERN LIVING AND ENERGY - SECTION 3 BUILDING ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS ADVANTAGES, DISADVANTAGES AND EXAMPLES Circuit type Advantages Disadvantages Example Series Very easy and simple to setup. Lamps cannot be controlled individually. Fluorescent lights. You can add more power to increase the output. E.g. more power brighter lamps. A flash light. The more output (lamps) in a circuit the dimmer the lamps. If a single lamp goes out, the entire circuit stops working. Parallel If one component breaks it does not affect the rest of the circuit. More lamps can be added to a parallel circuit without any of them getting dimmer. Harder to setup than a series circuit. Adding more power does not increase the output e.g. if a 5 volt battery which can power a light for two hours is added to an identical battery, the output is still 5 volts but the lamp will now stay on for four hours. 6 Ring main in a house. MODERN LIVING AND ENERGY - SECTION 3 BUILDING ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS MEASURING CURRENT AND VOLTAGE Voltage in a circuit is measured using a voltmeter. To measure the voltage across an electrical component the voltmeter must be added into the circuit in parallel to the component you want to measure. V 7 MODERN LIVING AND ENERGY - SECTION 3 BUILDING ELECTRICAL CIRCUITS The current in a circuit is measured using an ammeter. To measure the current in a circuit the ammeter needs to be added in series. A ACTIVITY Build the first three circuits from the activity on page 3. Measure and record the voltage across each component and current within each circuit. Circuit Voltage Current 1 2 3 8