* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Inner Ear
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
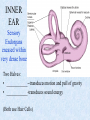
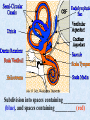
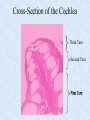
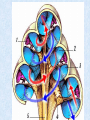
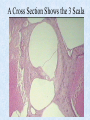
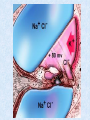
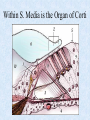
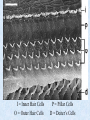
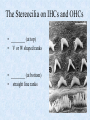
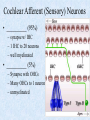
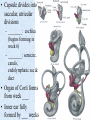
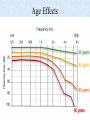
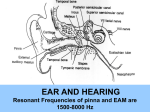
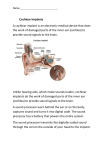
The Inner Ear SPA 4302 Summer 2006 INNER EAR Sensory Endorgans encased within very dense bone Two Halves: • ____________--transduces motion and pull of gravity • ____________-transduces sound energy (Both use Hair Cells) Subdivision into spaces containing ___________ (blue), and spaces containing __________ (red) Cochlea is Divided into 3 “Scala” • Scala Vestibuli – __________ Membrane • Scala Media – __________ Membrane • Scala Tympani • ___________ - the opening between 2 outer Scala Fluids filling the Inner Ear • ___________- in S. Vestibuli and S. Tympani – High Sodium / Low Potassium concentrations – Low Voltage (0 to +5 mV) • ___________- in S. Media – High Potassium / Low Sodium concentrations – High Positive Voltage (85 mV) Cross-Section of the Cochlea Third Turn Second Turn A Cross Section Shows the 3 Scala Within S. Media is the Organ of Corti I = Inner Hair Cells O = Outer Hair Cells P = Pillar Cells D = Deiter’s Cells The Stereocilia on IHCs and OHCs • ________ (at top) • V or W shaped ranks • ________ (at bottom) • straight line ranks Stereocilia bent toward tallest row • ________ flows into cell • ________ flows into cell • Voltage shifts to a less __________ value • More neurotransmitter is released Cochlear Afferent (Sensory) Neurons • __________ (95%) – synapse w/ IHC – 1 IHC to 20 neurons – well myelinated • __________ (5%) – Synapse with OHCs – Many OHCs to 1 neuron – unmyelinated Cochlear Functions • __________- Converting acousticalmechanical energy into electro-chemical energy. • ___________- Breaking sound up into its component frequencies Development of the Inner Ear • Beginning in week 3, ________________ develops, • Invaginates to form _______________, • Which then closes off, leaving an _________________. • Capsule divides into saccular, utricular divisions – ________: cochlea (begins forming in week 6) – ________: semicirc. canals, endolymphatic sac & duct • Organ of Corti forms from week ___ • Inner ear fully formed by ___ weeks Hearing Loss and Disorders of the Inner Ear • Vast majority of SNHL results from inner ear disorder. • Cochlear pts often hear, but cannot distinguish what they hear very clearly: ____________. – Arises from frequency and other distortions associated with changes in inner ear function. Inner Ear Disorders: Prenatal Causes • • • • • • Genetic mutation/inheritance Cytomegalovirus (CMV) __________ Rubella Rh incompatibility __________ Anatomical Anomalies Often seen as Bony malformations Examples: Mondini (incomplete cochlea) Enlarged Duct (shown here) Age Effects Noise Damage • Temporary Threshold Shift (TTS) • Permanent Threshold Shift (PTS) • Duration, Timing and Intensity influence • Typical “Noise Notch” often seen between ____________ first. • Notch widens and deepens over time, with hearing loss spreading to adjacent frequencies, and increasing in degree. Ototoxicity Substances poisonous to the ear • Medicines – ___________ antibiotics – ___________ drugs for CA – ___________ • Industrial Chemicals (tolulene, etc) May affect __________ Degree of hearing loss varies Synergy with noise or other ototoxic agents Meniere’s Disease • Really a Syndrome: – – – – _________ Vertigo Roaring, Low Freq. Tinnitus Fluctuating ___________ Hearing Loss Sensation of Aural Fullness • Thought to be produced by ____________________, a condition in which too much endolymph accumulates in the inner ear.