* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ear
Survey
Document related concepts
Audiology and hearing health professionals in developed and developing countries wikipedia , lookup
Noise-induced hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Sound from ultrasound wikipedia , lookup
Sensorineural hearing loss wikipedia , lookup
Olivocochlear system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
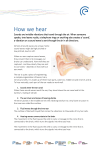
Hearing What’s that you say? Anatomy is your favorite class? Not surprising. The Ear • Complex organ consisting of outer, inner, and middle regions – Outer Ear = transmits sound waves through air – Middle Ear = transmits sound waves through bone – Inner ear = transmits sound waves through liquid • Cochlea converts sound waves into electrical impulses to brain • Vestibular apparatus is involved in equilibrium not hearing Outer and Middle Ear • Sound waves collected and directed down the auditory canal where they hit the tympanic membrane (eardrum) • Vibrations of the eardrum are amplified and transmitted to the inner ear via three tiny bones • Ossicles = tiny bones of the middle ear. Smallest bones of the body. – malleus, incus, stapes Pharyngotympanic Tube • Tube which links the middle ear cavity with the throat. • Tube usually closed but opens when swallowing or yawning. • Helps equalize pressure between the middle ear and outside. Often called Eustacian Tube Inner Ear • Oval window is the beginning of the cochlea • Fluid is pushed through cochlea and bulges outward the round window at the end Inner Ear Cochlea • Movements of the stapes bone hitting the ear drum are transmitted to the oval window (start of cochlea) • Vibrations move through the fluid in the cochlea • Organ of Corti in the cochlea is the sensory organ for hearing • Contain hairs that are triggered as sound vibrations pass through. When activated, sensors causes brain to receive electrical signal. Signal Generation • Change in individual hair position triggers electrical signal to be sent to brain. Each hair a specific sound (“note”). • Signals transmitted to hearing portion of temporal lobe of brain • Brain interprets signals as sound perception • Use vestibulocochlear nerve to reach the auditory cortex of the brain (temporal lobe) Equilibrium Semicircular canals in the vestibular portion of the inner ear detect rotational acceleration or deceleration Small stones inside move around like sand in an hour glass pushing on hairs lining its membrane. Equilibrium The utricle and saccule in the vestibular part of the inner ear detect linear movement in any direction by using otoliths (calcium carbonate) = “rocks” Utricle: horizontal displacement Saccule: vertical displacement Equilibrium