* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Hepatitis B in pregnancy
Taura syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex wikipedia , lookup
Canine distemper wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Canine parvovirus wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis wikipedia , lookup
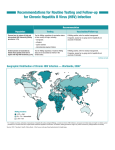
Hepatitis B dan C dalam Kehamilan Viral Hepatitis - Overview Type of Hepatitis A Source of virus Route of transmission Chronic infection Prevention B C D E feces blood/ blood/ blood/ blood-derived blood-derived blood-derived body fluids body fluids body fluids feces fecal-oral percutaneous percutaneous percutaneous permucosal permucosal permucosal fecal-oral no yes yes yes no pre/postpre/postblood donor pre/postensure safe exposure exposure screening; exposure drinking immunization immunization risk behavior immunization; water modification risk behavior modification Estimates of Acute and Chronic Disease Burden for Viral Hepatitis, United States Acute infections (x 1000)/year* HAV HBV HCV HDV 125-200 140-320 35-180 6-13 100 150 ? 35 0 1-1.25 million 3.5 million 70,000 5,000 8-10,000 1,000 Fulminant deaths/year Chronic infections Chronic liver disease deaths/year 0 * Range based on estimated annual incidence, 1984-1994. 100 100 80 80 60 60 Chronic Infection 40 40 20 20 Symptomatic Infection (%) Chronic Infection (%) Outcome of Hepatitis B Virus Infection by Age at Infection Symptomatic Infection 0 Birth 1-6 months 7-12 months 1-4 years Age at Infection 0 Older Children and Adults Elimination of Hepatitis B Virus Transmission in the United States Strategy • • • • Prevent perinatal HBV transmission Routine vaccination of all infants Vaccination of children in high-risk groups Vaccination of adolescents – all unvaccinated children at 11-12 years of age – “high-risk” adolescents at all ages • Vaccination of adults in high-risk groups Interpretation of the Hepatitis B Panel Tests Results Interpretation HBsAg anti-HBc anti-HBs negative negative negative Susceptible HBsAg anti-HBc anti-HBs negative positive positive Immune due to natural infection HBsAg anti-HBc anti-HBs negative negative positive Immune due to hepatitis B vaccination HBsAg anti-HBc IgM anti-HBc anti-HBs positive positive positive negative Acutely infected HBsAg anti-HBc IgM anti-HBc anti-HBs positive positive negative negative Chronically infected HBsAg anti-HBc anti-HBs negative positive negative 1. Might be recovering from acute HBV infection. 2. Might be distantly immune and test not sensitive enough to detect very low level of anti-HBs in serum. 3. Might be susceptible with a false positive anti-HBc. 4. Might be undetectable level of HBsAg present in the serum and the person is actually chronically infected Definitions • Hepatitis B Surface Antigen (HBsAg): A serologic marker on the surface of HBV. It can be detected in high levels in serum during acute or chronic hepatitis. The presence of HBsAg indicates that the person is infectious. The body normally produces antibodies to HBsAg as part of the normal immune response to infection. • Hepatitis B Surface Antibody (anti-HBs): The presence of anti-HBs is generally interpreted as indicating recovery and immunity from HBV infection. Anti-HBs also develops in a person who has been successfully vaccinated against hepatitis B. Definitions • Total Hepatitis B Core Antibody (anti-HBc): Appears at the onset of symptoms in acute hepatitis B and persists for life. The presence of anti-HBc indicates previous or ongoing infection with hepatitis B virus (HBV) in an undefined time frame. • IgM Antibody to Hepatits B Core Antigen (IgM anti-HBc): This antibody appears during acute or recent HBV infection and is present for about 6 months. Transmission of HBV • Transmissibility 100 times greater than HIV1 • Vertical – Infected mother-to-infant during first year of life • Earlier age at exposure increases the risk of developing chronic HBV infection2 1. WHO-CSR 2. WHO and CDC fact sheets, available at www.who.int and www.cdc.gov INTRAUTERINE INFECTION OF HBV • HBsAg Seropositive Rate at Birth : 2.4% (16/665) Among Neonates of HBeAg Positive, HBsAg Positive Mothers • Chronicity : 100% Tang JR et al. J Pediatr 1998 ; 133: 374 Lamivudine Therapy During Pregnancy to Prevent Perinatal Transmission of HBV Infection • • 8 Highly Viraemic (HBV-DNA>1.2 x 109 geq/mL) Mothers Treated With 150 mg of lamivudine Daily Since 34 Wks of Gestation. HBV-DNA, HBsAg, Anti-HBs, Anti-HBc of their Infants were Measured at 0, 3, 6, 12 Months. Historical Control : 24 Children , born to untreated HBsAg-positive mothers with HBV-DNA levels >1.2 x 109 geq/mL All children received passive-active immunization at birth . van Zonneveld M, et al. ( J Viral Hepatitis 2003; 10: 294-7) Lamivudine Treatment During Pregnancy to Prevent Perinatal Transmission of HBV Infection • Lamivudine Group : 1/8 Children (12.5%) was HBsAg and HBV-DNA positive at age 12 months. • Untreated Historical Control Group, Perinatal Transmission Occurred in 7/25 children (28%). M. van Zonneveld M, et al. ( J Viral Hepatitis 2003; 10: 294-7)