* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tides on Earth
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Impact event wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Exploration of Jupiter wikipedia , lookup
Sample-return mission wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
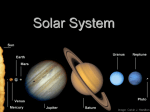
Moon Phase Quiz!! A B C D Ch 28 http://videos.howstuffworks.com/hsw/10000-the-moon-tidesvideo.htm Tides Bulges in Earth’s oceans, called tidal bulges, form because the moon’s gravitational pull on Earth decreases with distance from the moon. As a result, the ocean on Earth’s near side is pulled toward the moon with the greatest force. Tides The solid Earth experiences a lesser force. These differences cause Earth’s tidal bulges. Because Earth rotates, tides occur in a regular rhythm at any given point on Earth’s surface each day. http://www.5min.com/Video/Learn-about-Ocean-Tides117529562 Moon’s on Mars All of the planets in our solar systems except Mercury and Venus have moons. In addition, Saturn, Jupiter, Uranus, and Neptune all have rings. Mars has two tiny moons named Phobos and Deimos, which revolve around Mars relatively quickly. •Asteroids?? •Made mostly of Maria like Earth’s moon. Moon’s on Jupiter Galilean moon any one of the four largest satellites of Jupiter —Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto - that were discovered by by Galileo in 1610. In addition to the four large moons discovered by Galileo, scientists have observed dozens of smaller moons around Jupiter. Moon’s of Saturn Saturn has over 30 moons, but only five moons are fairly large. Saturn’s largest moon is Titan, which has a diameter of over 5,000 km. Saturn’s Moons Most of Saturn’s moons are small, icy bodies that have many craters. Saturn’s icy moons resemble Jupiter’s icy Galilean moons. Saturn’s other smaller moons have irregular shapes. Scientists think that many of the smallest moons were captured by Saturn’s gravitational pull. Moon’s of Uranus & Neptune Uranus’s four largest moons, Oberon, Titania, Umbriel, and Ariel, were known by the mid-1800’s Neptune has at least eight moons. One of these moons, Triton, revolves around Neptune in a retrograde orbit. Pluto’s Moon The relationship between Pluto and its moon Charon is unusual because Charon is almost half the size of Pluto itself. Because Pluto and Charon are similar in size, some scientists consider them to be a double-planet system. Identify two ways Charon is different from other moons. Charon is almost half the size of the planet it orbits. Charon’s orbital period is the same length as Pluto’s day, so only one side of Pluto always faces the moon. Rings of the Gas Giants Saturn’s set of rings was discovered over 300 years ago. Each of the rings circling Saturn is divided into hundreds of small ringlets, which are then composed of billions of pieces of rock and ice. Rings of the Gas Giants Jupiter has a single, thin ring made of microscopic particles that may have been given off by Io. Rings of the Gas Giants Uranus also has a dozen thin rings. Neptune’s relatively small number of rings are clumpy rather than thin and uniform. Review Quiz! What planet has the most complex ring system? A. B. C. D. Mars Jupiter Saturn Neptune Quiz! What two planets do not have moons? A. Mercury and Venus Mars and Saturn C. Mars and Venus D. Neptune and Earth B. Quiz! What is the name of Pluto’s moon? A. Io Charon C. Luna D. Eroupa B. Quiz! Which planet is know for its Galilean moons? A. Neptune Saturn C. Jupiter D. Uranus B. Quiz! The name of Saturn’s largest moon is what? A. Io Triton C. Galilean D. Titan B. Asteroids In addition to the planets and their moons, our solar system includes millions of smaller bodies, such as asteroids, comets, and meteoroids. The largest of these smaller bodies are asteroids, which are fragments of rock that orbit the sun. Asteroids asteroid - a small, rocky object that orbits the sun; most asteroids are located in a band between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter Asteroids The orbits of asteroids are ellipses. Most asteroids are located in a region between the orbits of mars and Jupiter known as the asteroid belt. Not all asteroids are located in the asteroid belt. The closest asteroids to the sun are inside the orbit of Mars. Composition of Asteroids The composition of asteroids is similar to that of the inner planets. Asteroids are classified according to their composition into three main categories. Made of silicate material 2. Made mostly of iron and nickel 3. Made mostly of carbon materials, which give this type of asteroid a dark color. (Most rare) 1. Near Earth Asteroids More than a thousand asteroids have orbits that sometimes bring them very close to Earth. These are called near-Earth asteroids. http://videos.howstuffworks.com/tlc/31638-ultra- science-near-earth-asteroid-tracking-video.htm Question?? What are the three types of asteroids? The most common type is made of silicate rock. Other asteroids are made mostly of metals such as iron and nickel. The third type is composed mostly of carbonbased materials. Comets Comets - a small body of rock, ice, and cosmic dust that follows an elliptical orbit around the sun and that gives off gas and dust in the form of a tail as it passes close to the sun The most famous comet is Halley’s Comet, which passes by Earth every 76 years. It last passed Earth in 1986, and will return in 2061 http://videos.howstuffworks.com/hsw/6335-cometsvideo.htm Composition of Comets A comet has several parts. The core, or nucleus of a comet is made of rock, metals, and ice. A spherical cloud of gas and dust, called the coma, surrounds the nucleus. The coma can extend as far as 1 million kilometers from the nucleus. The nucleus and the coma form the head of the comet. Comet’s Tail The most spectacular part of a comet is its tail. Tails form when sunlight causes the comet’s ice to change to gas. The solar wind pushes the gas away from the comet’s head The comet’s second tail is made of dust and curves backward along the comet’s orbit. The Oort Cloud Oort cloud - a spherical region that surrounds the solar system, that extends from just beyond Pluto’s orbit to almost halfway to the nearest star, and that contains billions of comets Scientists think that most comets originate in the Oort cloud. The Oort cloud surrounds the solar system and may reach as far as halfway to the nearest star. The Oort Cloud Bodies within the Oort cloud circle the sun so slowly that they take a few million years to complete one orbit. But, the gravity of a star that passes near the solar system may cause a comet to fall into a more elliptical orbit around the sun. If a comet takes more than 200 years to complete one orbit of the sun, the comet is called a long-period comet. The Kuiper Belt Kuiper belt the flat region beyond Neptune’s orbit that extends about twice as far as Neptune’s orbit, that contains leftover planetesimals, and that is the source of many short-period comets. Pluto is located in the Kuiper belt during much of its orbit. Short Period Comets Comets called short-period comets take less than 200 years to complete one orbit around the sun. Astronomers have discovered that most short- period comets come from the Kuiper belt. Halley’s comet, which has a period of 76 years, is a short-period comet. Meteoroids meteoroids a relatively small, rocky body that travels through space Scientists think that most meteoroids have a diameter of less than 1 mm. Meteoroids Large meteoroids, which are more than 1 cm in diameter, are probably the result of collisions between asteroids. Meteor meteor - a bright streak of light that results when a meteoroid burns up in the Earth’s atmosphere When a meteoroid enters Earth’s atmosphere, friction between the object and the air molecules heats the meteoroid’s surface. As a result of the friction and heat, most meteoroids burn up in Earth’s atmosphere. As the meteoroid burns up, it produces a bright streak of light called a meteor. Meteors are often called shooting stars. Review!!! Multiple Choice 1. Which of the following statements accurately describes each ring of Saturn? A. It is divided into smaller ringlets, all of which orbit Saturn together. B. It consists of a single ring composed of rock and ice pieces. C. It is divided into smaller ringlets, each of which has an individual orbit. D. It is part of a set of rings that are unlike those found anywhere else. C 2. Approximately how long does it take the moon to make one orbit around Earth? About 27.3 days (or one month) Review Short Response, continued 3. What are the names of the four moons of Jupiter known as the Galilean moons? Io, Europa, Ganymede, and Callisto Review!! Phase 1 is called what? Phase 6 is called what? Phase 2 is called what??