* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson 8.01 KEY Main Idea (page #) DEFINITION OR SUMMARY
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Problem of Apollonius wikipedia , lookup
Perceived visual angle wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Tangent lines to circles wikipedia , lookup
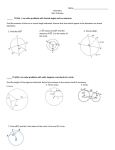
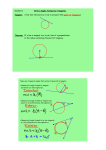
Lesson 8.01 KEY Main Idea (page #) Circle (P1) DEFINITION OR SUMMARY A CIRCLE IS A SET OF ALL POINTS THAT ARE THE SAME DISTANCE AWAY FROM A FIXED POINT, CALLED THE CENTER. CIRCLES ARE NAMED ACCORDING TO THEIR CENTER. Radius (P1) Chord of a circle (P1) EXAMPLE or DRAWING The name of this circle would be Circle C THE RADIUS OF A CIRCLE IS THE DISTANCE BETWEEN THE CENTER OF THE CIRCLE AND A POINT ON THE CIRCLE. The radius of this circle is CE Note: All radii are congruent in length The chord of a circle is a segment on the INTERIOR of a circle with endpoints ON the circle. The chord of this circle is AE THE DIAMETER OF A CIRCLE IS A TYPE OF CHORD THAT PASSES THROUGH THE CENTER OF THE CIRCLE. Diameter of a circle (P1) THE LENGTH OF THE DIAMETER MAY BE FOUND BY DOUBLING THE LENGTH OF A RADIUS IN THE SAME CIRCLE The diameter of this circle is DB THE CIRCUMFERENCE OF A CIRCLE IS THE DISTANCE AROUND THE CIRCLE FROM ONE POINT BACK TO THE SAME POINT Circumference (P1) Arcs (P1) THE FORMULA USED IS C = PI X D, WHERE PI = 3.14 AND D IS THE DIAMETER OR C = 2 X PI X R, WHERE PI = 3.14 AND R IS THE RADIUS. A MINOR ARC IS IDENTIFIED USING 2 LETTERS AND MEASURES LESS THAN 180 DEGREES A MAJOR ARC IS IDENTIFIED USING 3 LETTERS AND MEASURES MORE THAN 180 DEGREES ARC LENGTH IS THE DISTANCE BETWEEN 2 POINTS ON THE CIRCLE. To check your notes for accuracy, please contact me for the key. The circumference measures the red outline or entire distance around the circle Lesson 8.01 KEY SECANT (P1) A line that passes through a circle intersecting it at 2 distinct points. The secant here is FG Tangent (P1) A TANGENT IS A LINE THAT INTERSECTS THE CIRCLE IN EXACTLY 1 POINT. THE POINT WHERE THE TANGENT INTERSECTS THE CIRCLE IS CALLED THE POINT OF TANGENCY Concentric Circles (P1) Concentric circles occur when 2 distinct circles share a COMMON center. Central Angle and the Arc (P2) A CENTRAL ANGLE IS AN ANGLE ON THE INTERIOR, OR INSIDE, OF A CIRCLE WITH ITS VERTEX AT THE CIRCLE’S CENTER. THE CENTRAL ANGLE AND ITS INTERCEPTED ARC ARE CONGRUENT. Semicircle (P2) The tangent here is EJ. Note: The tangent is perpendicular to a radius of the circle at the point of tangency. Angle PTI is 80 degrees so arc PI is also going to measure 80 degrees A SEMICIRCLE IS AN ARC WHERE THE CENTRAL ANGLE IS CREATED BY A DIAMETER OF THE CIRCLE To check your notes for accuracy, please contact me for the key. Lesson 8.01 KEY ADJACENT Arcs (P2) Arcs that share a common point. In circle H, AL and LO are adjacent arcs because they have point L in common Arc Addition Postulate (P2) THE MEASURE OF AN ARC CREATED BY TWO ADJACENT ARCS MAY BE FOUND BY ADDING THE MEASURES OF THE TWO ADJACENT ARCS. mAO = 89° + 65° mAO = 154° Congruent Arcs Theorem (P3) TWO ARCS ARE CONGRUENT IF THE CENTRAL ANGLES THAT INTERCEPT THEM ARE ALSO CONGRUENT. Secant Angles (P4) WHEN TWO SECANTS INTERSECT, SECANT ANGLES ARE CREATED. Secant Interior Angle Theorem (P4) THE MEASURE OF A SECANT ANGLE IS EQUAL TO HALF THE SUM OF THE ARCS IT AND ITS VERTICAL ANGLE INTERCEPT. m∠WSI = 52° and m∠GSN = 52° So, arc IW is congruent to arc NG Notice <BAN and <MAD are secant angles. In the same way, <DAB and <NAM are secant angles. Notice the measure of arc BN is 66 and the measure of arc DM is 78 so in order to find the m<BAN, we To check your notes for accuracy, please contact me for the key. Lesson 8.01 KEY add the 2 arcs and divide by 2. We get 66 + 78 = 144 and then dividing by 2, we get that m<BAN is 72. Review Note: Remember that m<MAD would also be 72 because they are vertical angles. Inscribed Angle (P5) WHEN AN ANGLE IS IN THE INTERIOR OF A CIRCLE AND ITS VERTEX IS A POINT ON THE CIRCLE, THE ANGLE IS CALLED AN INSCRIBED ANGLE. < DOG is an inscribed angle Inscribed Angle Theorem (P5) The measure of an inscribed angle is equal to HALF the measure of its INTERCEPTED arc. Inscribed Angle to a Semicircle (P6) AN INSCRIBED ANGLE THAT INTERCEPTS A SEMICIRCLE IS A RIGHT ANGLE. Congruent Inscribed Angle Theorem (p7) TWO OR MORE DISTINCT INSCRIBED ANGLES THAT INTERCEPT THE SAME ARC, OR CONGRUENT ARCS, ARE CONGRUENT To find the m<ILK we need to take half of 94, so 94/2 = 47. Notice <AED is an inscribed angle and it equal to 90 degrees because it intercepts arc AD, which is a semicircle. ∠OEL and ∠OWL both intercept arc LO. m< OEL = m< OWL To check your notes for accuracy, please contact me for the key. Lesson 8.01 KEY SECANT-Tangent Intersection Theorem (P8) When a secant and tangent intersect at the point of tangency, the angles created at the point of intersection are half the measurement of the arcs they intersect. Line NL is a SECANT. Line IE is TANGENT to circle S at point N. m∠LNE = ½ mNAL 80° = ½ mNAL 160° = mNAL m∠INL = ½ mLPN 100° = ½ mLPN 200° = mLPN Inscribed Quadrilateral Theorem (p9) THE OPPOSITE ANGLES OF AN INSCRIBED QUADRILATERAL TO A CIRCLE ARE SUPPLEMENTARY Quadrilateral HAIR is INSCRIBED within circle Y. m<HAI + m<IRH = 180 m<RHA + m<AIR = 180 To check your notes for accuracy, please contact me for the key. Lesson 8.01 KEY Inscribed angles (p10) When two inscribed angles intercept the same arc, those angles are CONGRUENT m< POM m< PNM (3x + 29) = (5x + 7) EXTERIOR ANGLE TO A CIRCLE THEOREM (P11) The angle measure is equal to ½ the absolute value of the DIFFERENCE of the measures of their intercepted arcs. m< = ½(arc 2 – arc 1) To check your notes for accuracy, please contact me for the key. Lesson 8.01 KEY Two secants intersect in the interior of a circle (p11) The angle measure is equal to ½ the SUM of the measures of their intercepted arcs m< = ½(arc 1 + arc 2) To check your notes for accuracy, please contact me for the key.