* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
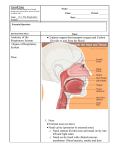
Nasal Cavity & Paranasal sinuses Head & Neck Unit – Lecture 9 حيدر جليل األعسم.د The Nose Human Nose consists of external nose & nasal cavity; both are divided by nasal septum into right & left halves. External Nose It has two elliptical orifices called Nostrils (or Nares). Ala Nasi are rounded mobile lateral margin of external nose. The framework of the external nose is made up above by nasal bones, frontal processes of maxillae, and nasal part of frontal bone. Below, the framework is formed of plates of hyaline cartilage. Blood Supply: is by branches of ophthalmic, maxillary & facial arteries. Nerve Supply: is by ophthalmic nerve (through infra-trochlear & external nasal nerve) and infraorbital branch of maxillary nerve. Nasal Cavity Nasal cavity extends from nostrils in front to posterior nasal apertures or (choanae). Nasal choanae are oval-shaped openings between nasal cavities and the nasopharynx. Boundaries of Nasal Choanae: Inferiorly: posterior border of horizontal plate of the palatine bone; Laterally: posterior margin of medial plate of pterygoid process; Medially: posterior border of vomer. Roof: (Anteriorly: ala of vomer & vaginal process of medial plate of pterygoid process; Posteriorly: body of sphenoid bone. Nasal Cavity Nasal cavity is divided into right & left halves by nasal septum that is made up of septal cartilage, vertical plate of ethmoid, and vomer bone. Nasal cavity consists of 3 regions: 1. Nasal vestibule : small dilated space just internal to nostrils & is lined by skin containing hair follicles; 2. Respiratory region: largest part of nasal cavity. It has a large plexus of veins in the sub-mucosa. It is lined by respiratory epithelium composed of ciliated and mucous cells. 3. Olfactory region: small region located at apex of nasal cavity & is lined by olfactory epithelium containing olfactory receptors. Function of Warm Blood and Mucus? Nasal Cavity Walls of Nasal cavity: each half of the nasal cavity has a floor, a roof, a lateral wall, and a medial or septal wall. Floor: palatine process of maxilla and horizontal plate of palatine bone. Roof: anteriorly beneath bridge of nose by nasal and frontal bones, in the middle by cribriform plate of ethmoid, and posteriorly by body of sphenoid. Medial Wall: is formed by nasal septum. The upper part is formed by vertical plate of ethmoid & vomer. Anterior part is formed by septal cartilage. The septum rarely lies in midline. Nasal Cavity Lateral Wall: it has three projections of bone called superior, middle & inferior nasal conchae. The space below each concha is called a meatus. 1. Inferior Meatus: receives opening of lower end of nasolacrimal duct, which is guarded by a fold of mucous membrane. Nasal Cavity 2. Middle Meatus: lies below middle concha. It has a rounded swelling called bulla ethmoidalis formed by middle ethmoidal air sinuses, which open on its upper border. Hiatus Semilunaris ia a curved opening lying just below the bulla & receives opening of maxillary sinus. Infundibulum is a funnel-shaped channel at anterior end of hiatus. 3. Superior Meatus receives openings of posterior ethmoid sinuses. 4. Sphenoethmoidal Recess: is a small area above superior concha & receives the opening of sphenoid air sinus. Nasal Cavity Blood Supply to the Nasal Cavity Arterial supply is from branches of maxillary & facial arteries (ECA). The most important branch is sphenopalatine artery from maxillary artery that anastomoses with septal branch of superior labial branch of facial artery in the vestibule (little’s area) which is the area most commonly bleed (epistaxis) Internal Carotid artery (ICA) also supplies nasal cavity through ethmoidal branches of ophthalmic artery. Venous Drainage of Nasal Cavity Submucous venous plexus is drained by veins accompanying arteries. Nerve Supply of the Nasal Cavity Olfaction: (Smell) is carried by olfactory nerves that ascend from olfactory mucous membrane through cribriform plate of ethmoid to olfactory bulbs General sensation: is by branches of the ophthalmic & maxillary divisions of trigeminal nerve. Nerve Supply of the Nasal Cavity Parasympathetic fibers: to all glands by in the facial nerve (through greater petrosal nerve), which joins branches of the maxillary nerve in the pterygopalatine fossa. Sympathetic fibers are ultimately derived from superior cervical sympathetic ganglion and postganglionic fibers reach the nasal cavities along blood vessels. Lymph Drainage of the Nasal Cavity Lymph vessels draining the vestibule, end in submandibular nodes. The rest of nasal cavity is drained to upper deep cervical nodes. Paranasal Sinuses They are cavities found inside the maxillary, frontal, sphenoid and ethmoid bones. They are lined with mucoperiosteum & filled with air. They communicate with nasal cavity through relatively small apertures. Function of Paranasal Sinuses: 1. Act as resonators of voice. 2. Reduce weight of the skull. 3. Help in formation of facial characteristics. Paranasal Sinuses Maxillary Sinus: is pyramidal in shape within body of maxillary bone. Roof is formed by floor of orbit, and Floor is related to roots of the premolars and molar teeth. The maxillary sinus opens into middle meatus of nose through hiatus semilunaris. Frontal Sinuses: are contained within frontal bone and separated from each other by a bony septum. Each sinus is roughly triangular, extending upward above medial end of eyebrow and backward into medial part of roof of orbit. Each frontal sinus opens into middle meatus of the nose through the infundibulum. Sphenoidal Sinuses: lie within the body of sphenoid bone. Each sinus opens into the sphenoethmoidal recess. Ethmoid Sinuses: are contained within ethmoid bone, between nose & orbit. They are anterior, middle and posterior. Anterior sinuses open into the infundibulum; Middle sinuses into middle meatus on bulla ethmoidalis; & Posterior sinuses into superior meatus. Paranasal Sinuses End of the Lecture GOOD LUCK