* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Directed Reading: Integumentary System
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
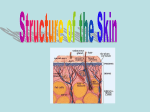
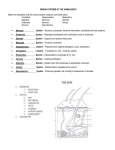
Back Lesson Print Name Class Date Skills Worksheet Directed Reading A Section: The Integumentary System ______ 1. What is the largest organ in the body? a. the heart b. the lungs c. the skin d. the stomach 2. The integumentary system is made up of , , and . FUNCTIONS OF SKIN 3. Skin protects you by keeping in your body and out of your body. 4. You can feel things around you through the in your skin. 5. Small organs in the skin called make sweat and help to regulate body temperature. 6. Skin helps get rid of through sweating. 7. Darker skin has more than lighter skin. 8. How does the melanin in skin help prevent cancer? Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. Holt Science and Technology 7 Body Organization and Structure Back Lesson Print Name Class Date Directed Reading A continued LAYERS OF SKIN ______ 9. How does the dermis differ from the epidermis? a. It is thinner. c. It is made of keratin. b. It is made of dead cells. d. It is thicker. Match the correct description with the correct term. Write the letter in the space provided. a. blood vessels ______10. keep hair flexible and waterproofs the dermis b. nerve fibers ______11. make hair c. hair follicles d. muscle fibers ______12. can contract and cause hair to stand up e. oil glands ______13. help regulate body temperature and transport substances f. sweat glands ______14. carry messages to and from the brain ______15. cool the body and remove waste 16. The outermost layer of the skin is the . 17. The thicker layer of skin beneath the outermost layer of skin is the . 18. The epidermis is made of tissue. 19. Most cells in the epidermis are filled with a protein called . 20. The fibers of the dermis are made of a protein called . HAIR AND NAILS ______21. Hair and nails are made up of a. skin. b. all dead cells. c. all living cells. d. living and dead cells. ______22. Which of the following statements is true about a hair follicle? a. It contains living cells. c. It contains all dead cells. b. It makes new skin. d. It contains keratin. 23. Hair gets its color from . Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. Holt Science and Technology 8 Body Organization and Structure Back Lesson Print Name Class Date Directed Reading A continued 24. How does hair protect your body? 25. The living cells that cause a nail to grow are found in the at the base of the nail. SKIN INJURIES 26. What are some ways in which the skin can become damaged? 27. How does skin heal from a cut? Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. Holt Science and Technology 9 Body Organization and Structure Back Lesson Print PAGE TEACHER RESOURCE 14. resistance exercises 15. weight 16. Answers will vary. Sample answer: 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 27. A blood clot forms over a cut to stop bleeding and keep bacteria from entering the wound. Bacteria-fighting cells then come to the area to kill bacteria. Damaged cells are replaced through cell division. Eventually, all that is left on the surface is a scar. Jogging, cycling, skating, swimming, and walking are examples of aerobic exercise. aerobic exercises A B D Anabolic steroids can damage the heart, liver, and kidneys. They can cause high blood pressure. They can cause bones to stop growing if they are taken before the skeleton is mature. Directed Reading B SECTION: BODY ORGANIZATION 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. SECTION: THE INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. 17. 18. 19. 20. 21. 22. 23. 24. 25. 26. C skin, hair, nails water, foreign particles nerve endings sweat glands wastes melanin Melanin absorbs ultraviolet light from the sun. D E C D A B F epidermis dermis epithelial keratin collagen D A melanin Hair helps protect skin from ultraviolet light. Hair keeps particles out of your eyes and nose. Hair helps regulate body temperature in most mammals. nail root Damage to the genetic material in the skin cells can cause cancer. Acne can develop if excess oil combines with dead skin cells and bacteria to clog hair follicles. A C B D C A B organ muscle tissue nervous tissue epithelial tissue organ system B A D B C C A B D B D A C SECTION: THE SKELETAL SYSTEM 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. 14. 15. 16. cartilage movement ribs minerals marrow B D A B blood vessels compact bone spongy bone C B C A Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved. Holt Science and Technology 91 Body Organization and Structure