* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download POPULATIONS
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Source–sink dynamics wikipedia , lookup
The Population Bomb wikipedia , lookup
Two-child policy wikipedia , lookup
Human overpopulation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
World population wikipedia , lookup
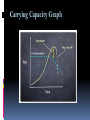
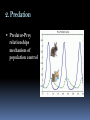
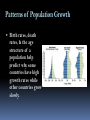
SC STANDARD B-6. 2: Students will demonstrate an understanding of the way populations are affected by density-dependent factors & density-independent factors. POPULATIONS CN page Topic: Populations EQ: What factors affect population size? How do Populations Grow? 3 important characteristics of a population are its : geographic distribution density growth rate Geographic Distribution is the range or area where the organism is found Hooker’s Manzanita found in maritime chaparrel (threatened habitat due to development) Central California (Monterrey County) Franklin’s Bumble Bee Most restricted geographic distribution of any known bee Between Pacific coast & Sierra Nevada in Oregon & northern California Density population density: the # of individuals per unit area Density is one of the main characteristics that describes a natural population. Growth Rate 3 factors affect Immigration: population growth: 1. # of births 2. # of deaths 3. # of individuals that immigrate or emmigrate movement of individuals into an area Emmigration: movement of individuals out of an area EXPONENTIAL GROWTH growth pattern in which the individuals in a population reproduce at a constant rate Under ideal conditions with unlimited resources, a population will grow exponentially LOGISITIC GROWTH growth pattern in which a population’s growth rate slows or stops following a period of exponential growth carrying capacity: largest # of individuals of a population that a given environment can support Carrying Capacity Graph Limiting Factors to Growth In respect to populations a limiting factor is anything that causes population growth to decrease. Limiting factors are either: Density-Dependent Density-Independent Density-Dependent Limiting Factors limiting factor that Include: depends on population size become limiting only when population density reaches a certain level 1. competition 2. predation 3. parasitism & disease 1. Competition When populations become crowded members of same or different species compete for food, shelter, mates, space, sunlight 2. Predation Predator-Prey relationships mechanism of population control 3. Parasitism & Disease Parasites take nourishment from their host host weakens does not usually die Density-Independent Factors affect all the populations in similar ways, regardless of #’s Forest fires Floods Seasonal cycles Human interference (clear-cutting, damming river) Human Population Growth Population of humans on Earth increases with time Patterns of Population Growth Birth rates, death rates, & the age structure of a population help predict why some countries have high growth rates while other countries grow slowly. The Demographic Transition the change in a population from high birth & death rates to low birth & death rates Complete concept map from page 134 of book on page of notebook (landscape)