* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Homework
Eisenstein's criterion wikipedia , lookup
History of algebra wikipedia , lookup
System of polynomial equations wikipedia , lookup
Root of unity wikipedia , lookup
Factorization wikipedia , lookup
Elementary algebra wikipedia , lookup
Quadratic equation wikipedia , lookup
Quartic function wikipedia , lookup
Cubic function wikipedia , lookup
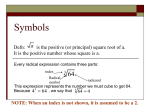
18 Days Four Days Definition of the nth root: For any real numbers a and b, and any positive integer n, if a n b, then a is an nth root of b. (2)3 8 2 is the 3rd root of 8 (2) 4 16 and (2) 4 16 2 and - 2 are 4th roots of 16 Radicand - the number under the root (a) Index - the degree of the root n (n) a Lets start with a few familiar examples: 16 24 4x2 36 x 4 100 x 3 y 2 3 27 x 6 3 16 x 4 .25 x 2 4 3 81x 6 64 x 3 y 6 z 4 1 x2 x3 x4 x5 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 pg 372 (# 1-27 odd) Three Days 8 2 24 2 5 125 36 3 16 3 54 For a Radical Expression to be in simplest for the following conditions must be met: ◦ No perfect nth power factors, other than 1. ◦ No fractions in the radicand. ◦ No radicals in the denominator. If n a and n b are real numbers, then n a n b n a b n n n If a and b are real numbers, then n a n a b b 3 12 3 33 9 3 4 x 2 y 3 16 xy5 4 27 x 3 y 4 3 xy6 47 36 3 3 216 3 8 27 x 6 y 3 3 8 12 x 4 3x Rationalizing the denominator of an expression is the process of re-writing so that there are no radicals in any denominator and there are no denominators in any radical. 2 3 1 3x x3 5 xy 3 3 4 6x pg 377 (# 1-35 odd) Practice 7.2 WS (1-33 odd, 34) Practice 6-5 (#1-35 odd) - Glencoe Three Days Three Days First of all, what is a rational number? It’s a number that can be written as a fraction of integer values. Definition of Rational Exponents If the nth root of a is a real number and m and n are integers, then n xx 1 n and m n x x n m x n m 3 2 x y 3 .5 a5 3 z 4 5 4 16 4 2.5 2 7 5 14 x x 27 x 6 1 3 pg 388 (# 1-25 odd, 39-49 odd) Three Days Solve the following radical expression: 2 2x 4 6 2 2x 4 6 2 2 x 4 6 1 2 1. Convert the radical to rational exponents. 2. Isolate the “radical” part of the equation. 3. Raise both sides of the equation to the reciprocal power of the rational exponent. 4. You’ve now “cleared” the radical, solve using the appropriate method for the resulting equation. 2x 2 4 22 2 3 x 7 5 x The maximum flow of water in a pipe is modeled by the formula Q=Av, where A is the cross sectional area of the pipe, v is the velocity of the water, and Q is the maximum volume of water than can flow through the pipe per minute. Find the diameter of a pipe that allows a maximum flow of 50 cubic feet per minute at a velocity of 600ft/min. Round to the nearest inch. pg 394 (# 1-25 odd) Practice 7.5 WS (#2-32 Even) Practice 6-7 WS (# 2-22 even) - Glencoe Three Days Parent: Shift up k units: Shift down k units: Shift right h units: Shift left h units Combined Shift: y x y f ( x) y x k y f ( x) k y x k y f ( x) k y xh y f ( x h) y xh y f ( x h) y xh k ◦ (right h units, up k units) y f ( x h) k Parent: Reflection in x-axis: Vertical Stretch a>1 Vertical Shrink 0<a<1 y x y f ( x) y a x y a f ( x) y a x y a f ( x) Horizontal Stretch 0<c<1 : Horizontal Compression c>1: Combined Transformation: y a x h k y c x y f (c x ) y a f ( x h) k -Name of Family f x = x 8 Square Root 6 -Parent Equation 4 y x -General Equation 2 -15 -10 -5 5 10 -2 y a xh k -Locator Point Endpoint : (h, k ) -4 -6 -8 -Domain -Range [0, ) [0, ) x 0 1 4 9 16 y 0 1 2 3 4 -Name of Family 1 f x = x 3 8 Cube Root 6 -Parent Equation 4 y x 3 2 -General Equation y a3 x h k -Locator Point -15 -10 -5 5 -2 -4 -6 Inflection : (h, k ) -8 -Domain -Range x y -8 -2 -1 -1 0 0 1 1 8 2 10 y x 3 y x 1 y x2 y x4 y x 1 3 y3 x y 3 x4 y 3 x4 2 https://www.desmos.com/calculator/renedj48tv pg 417 (# 1-23 odd) Practice 7.8 WS (# 1-15 odd, 28, 29, 31, 35, 37)