* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Global
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
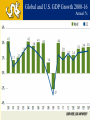
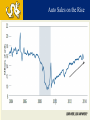
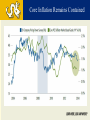
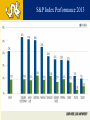
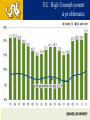
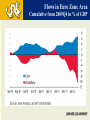
DREXEL UNIVERSIY LeBow College of Business The Global Economy and the US Markets PRESENTED BY GEORGE TSETSEKOS Dean Emeritus and Francis Professor of Finance March 26, 2014 “Linked” Markets…Amplify Crisis US Subprime Crisis EZ Sovereign Debt Crisis Global Crisis Global and U.S. GDP Growth 2000-16 Annual % Transition: From Crisis to Stability Crisis in US Global Amplification Policy Responses Stability Transition Challenges during the transition Normalize monetary conditions Handle risk/volatility Transition in USA: From Crisis to Stability Crisis in US Financial Crisis Low Growth and Unemployment Policy Responses Monetary Easing Stability Transition Home Prices Rise, Helped by Low Inventory Auto Sales on the Rise Core Inflation Remains Contained Net Worth Climbs as Debt Burden Plummets S&P Index Performance 2013 Overall Market Performance Unemployment is Declining Slow Recovery in USA Spending Levels still Low Stalled Velocity of Money Supports Low Inflation Outlook US Monetary transition and global impact Possible Risks with the reduction of the Fed’s buying program in the near term: Long-term rates could overshoot Sharp increases in Bond yields Volatility Higher rates may impact investment vehicles Transition: From Crisis to Stability EU response Crisis in US Banking Crisis in EU Sovereign CrisisAusterity Policy Responses Stability Transition Common Currency EuroZone 17 Countries Transitional Issues in the EZ 1. Core Countries vs. Periphery 2. Excessive Corporate Debt 3. Developing Institutions/Architecture of EU EU: High Unemployment is problematic Unemployment and domestic demand in the periphery Unemployment Rate (%) Domestic Demand (volume) Key Concerns for the Corporate Sector • Capital flight to safer Euro-zone countries • Private capital has been replaced by public sector flows • Liquidity in the core is not recycled in the periphery • Funding asymmetries (corporate costs are very high) • Current account imbalances Flows in Euro Zone Area Cumulative from 2009Q4 in % of GDP Challenges for the Corporate Sector in the Eurozone • • • • High Corporate Leverage Credit Tightening Revenue and profits contraction Global Competitiveness Corporate Debt Debt - 2002Q1=100 Debt as % of GDP Corporate Fundamentals Real Long-term Rates are still high in the EZ Real Progress in the Euro Zone? » Tail risk of break-up/FRAGEMTATION appears very low » Euro zone recovery VERY SLOW in light of persistently high unemployment and structural imbalances » Greece is moving into recovery, encouraging market optimism and foreign investment CONSOLIDATED PRIVATE DEBT, % OF GDP EUROSTAT MACROECONOMICS IMBALANCE PROCEDURE SCOREBOARD •GREECE’S ANNUAL GDP GROWTH FORECAST •Source: GK Research, “Ideas,” September 20, 2013 , World Bank and European Commission (Greece GDP) 28 Euro Area Increases in interest rates in US • Credit is hindered by financial fragmentation • Corporate debt is owned by firms with weak debt servicing capacity; debt overhang • Banking system will experience loan losses • Need for Bank Re-Capitalization • Weak corporate and bank balance sheets • Asymmetric impact Emerging Markets and China Interest Rates and Capital Flows to EM Volatility and EM Capital Flows High Volatility Low Volatility EM Growth has decelerated Growth Forecast for China Average 7% in next 5 years China Exports Have NOT Recovered China’s Consumption is lower than BRICs/EM Leverage is Concentrated in a Few Sectors in China Emerging Markets Potential Risks • • • • Bond outflows will place at risk corporate borrowing Financial stability concerns Economic growth is slowing Market liquidity is at risk The Japanese experiment (Abenomics) • Japan has enacted its stimulus/QE • Fiscal and structural reforms • The risk of deflation is persistent JAPAN: Money Supply and GDP Global Outlook: Cautiously Optimistic US: Economic Recovery Poised to Continue at Moderate Pace » A number of important metrics beat expectations last week • Strength in job growth, GDP, auto sales, manufacturing while unemployment fell below 7.0% » FOMC has decided to begin tapering » Grand rotation may have begun; money flowing out of bonds and into equities – RISK ON! » A resilient consumer is well positioned to support recovery Euro zone: GDP Growth Improving, More Work Ahead » Promising strides for EU, structural imbalances remain » Valuations in Europe compelling; pointing toward economic improvement EMs: Still a Source of Global Growth » Near-term growth has slowed, but secular stories remain intact » Growth of EM middle class important long-term theme Global: Dominant Theme of Synchronized Global Expansion » Global manufacturing numbers improved significantly » Recent positive data for Eurozone, Spain, UK, Japan, Indonesia, India, Canada, Australia, Malaysia and Taiwan » Global economic growth; good for the U.S.! 41 US Equity Market Performance Rising rates Led to Sideways Market Sector Allocation Considerations for Rising Interest Rate Environments •During Periods of Rising Interest Rates… •Cyclical sectors •historically outperform defensive sectors •Past performance is no guarantee of future results. Source: Wells Capital “Confidence Runs Through Stock Market. Sectors shown have material differences and represent segments of the S&P 500. Daily fluctuations in specific market sectors are often more extreme than fluctuations in the overall market. 4 4 Cointegrated Global Markets THANK YOU LEARN HERE, LEAD ANYWHERE® COPYRIGHT 2011 DREXEL UNIVERSITY’S LEBOW COLLEGE OF BUSINESS