* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Human Reproduction
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
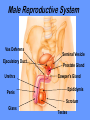
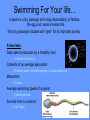
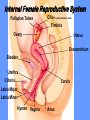
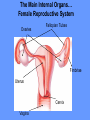
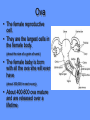
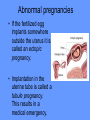
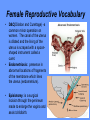
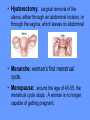
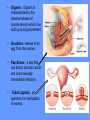
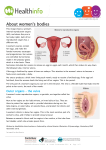
Word Bank • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Ovulation Ovum (Egg) Seminal Vesicles Bladder Prostate Semen Urethra Menstruation Nocturnal Emission Vaginal Endometruim Uterus Fallopian Tubes Ovaries Estrogen Progesterone • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Labia Majora Labia Minora Clitoris Penis Scrotum Testicles or Testes Testosterone Sperm Cowper’s Gland Foreskin Glans Fimbria Epididymus Vas Deferens Hymen Vagina Cervix Vulva Anus Human Reproduction Primary Sex Organs Male -Testes Women-Ovaries Male Reproductive System Vas Deferens Seminal Vesicle Ejaculatory Duct Urethra Prostate Gland Cowper’s Gland Epididymis Penis Scrotum Glans Testes Swimming For Your life… A sperm is a tiny package with a big responsibility; to fertilize the egg and create a human life. That tiny package is loaded with “gear” for its important journey. A few facts: Daily sperm production by a healthily man: – 10 million to 50 million Contents of an average ejaculation: – 50 million sperm, 25 million moving, 20 million deformed. Maturation: – 72 days Average swimming speed of a sperm: – 8 inches per hour Survival time in a woman: – 2 to 7 days Erectile Dysfunction • Impotence is the inability of a man to have an erection. – Causes may include • Injury to nerves, arteries, are muscles • Medications for high blood pressure, antihistamines, and depression • Psychological factors such as anxiety, guilt, depression, and fear of sexual failure cause up to 20 % of all cases Male Reproduction Vocabulary Male Reproductive Circumcision: a process that surgically removes the flap of skin that covers the glans of the penis. This is usually done a few hours or days after birth. Smegma - substance that collects under the foreskin. Ejaculation: the passage of sperm from the penis, a result of a series of muscular contractions. Semen: Contains sperm from the testes, sugar from the seminal vesicles, and fluid from the prostate gland. This fluid nourishes and helps sperm move through the urethra. Nocturnal Emission (wet dream): a normal, involuntary ejaculation of semen while a male is asleep. Impotence: the failure to get or maintain an erection. Vasectomy: surgical procedure for sterilization of the male. Time Line: Infancy Erections begin Ages 11-14 Secondary sex characteristics appear Ages 13-16 Sperm produced in adult amounts (puberty) Late teens Peak sexual urges for boys Throughout life If good health is present, there is the sex urge and ability to father children. Internal Female Reproductive System Fallopian Tubes Cilia- inside Fallopian tubes Fimbria Ovary Uterus Endometrium Bladder Urethra Clitoris Cervix Labia Major Labia Minor Hymen Vagina Anus Vulva… External Female Reproductive System Mons Pubis Clitoris Labia Majora Labia Minora Hymen Opening of the Uretha Opening of the vagina Perineum Anus The Main Internal Organs… Female Reproductive System Ovaries Fallopian Tubes Fimbriae Uterus Cervix Vagina Ovary (Ovaries) • Two solid egg-shaped structures • They are attached to the uterus by ligaments. They are the counterpart of the male testicles. • Ovaries have two main functions: #1-store and release the ova or female egg cell. Some of the ova disappear; others are dormant until each is ripened and released after puberty. #2-produce female sex hormones ESTROGEN and PROGESTERONE Fertilization Ova • The female reproductive cell. • They are the largest cells in the female body. (about the size of a grain of sand.) • The female baby is born with all the ova she will ever have (about 200,000 in each ovary). • About 400-500 ova mature and are released over a lifetime 4 weeks 8 weeks 12 weeks Appearance of the placenta at full term Abnormal pregnancies • If the fertilized egg implants somewhere outside the uterus it is called an ectopic pregnancy. • Implantation in the uterine tube is called a tubule pregnancy. This results in a medical emergency. Female Reproductive Vocabulary • D&C(Dilation and Curettage) -a common minor operation on women. The canal of the uterus is dilated and the lining of the uterus is scraped with a spoonshaped instrument called a curet. • Endometriosis: presence in abnormal locations of fragments of the membrane which lines the uterus (endometrium). • Episiotomy: is a surgical incision through the perineum made to enlarge the vagina and assist childbirth. • Hysterectomy: surgical removal of the uterus, either through an abdominal incision, or through the vagina, which leaves no abdominal scar. • Menarche: woman’s first menstrual cycle. • Menopause: around the age of 45-55, the menstrual cycle stops. A woman is no longer capable of getting pregnant. • Orgasm: Orgasm is characterized by the massive release of muscle tension which has built up during excitement. • Ovulation: release of an egg from the ovaries. • Pap Smear: a test that can detect cervical cancer and some sexually transmitted infections. • Tubal Ligation: an operation for sterilization of women. • PMS (Premenstrual Syndrome): a syndrome whose symptoms may become incapacitating: emotions get out of control, headaches, water retention, irritability, and painful uteral cramps. • Toxic Shock Syndrome: caused by bacteria that live in the vagina, which multiply and causes infection. Time Line: • Ages 9-12 Secondary sex characteristics appear • Ages 11-14 Menstrual cycle begins • Late 20-30’s Peak sexual urges • Ages 45-55 Menopause (cycle stops, but sex urge continues)