* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Pre-Cal
Big O notation wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
History of the function concept wikipedia , lookup
Line (geometry) wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard calculus wikipedia , lookup
Function (mathematics) wikipedia , lookup
Elementary mathematics wikipedia , lookup
Anthony Poole & Keaton Mashtare
2nd Period
X and Y intercepts
The points at which the graph crosses or touches the
coordinate axes are called intercepts. The x-coordinate of a
point at which the graph crosses or touches the x-axis is the
x-int. The y-coordinate of a point at which the graph crosses
or touches the y-axis is the y-int.
Finding X and Y intercepts
To find the x-intercepts, let y=0 in equation and solve for x.
To find the y-intercepts, let x=0 in equation and solve for y.
1.
2.
Find the X and Y intercepts of the graph
y=x²-4
y=x²-4
=0²-4
=-4
y-intercept = -4
0=x²-4
=(x+2) (x-2)
x+2=0 and x-2=0
x=-2
and x=2
x-intercepts=-2 and 2
Find the X and Y intercepts of the graph
y=x²+9
y=x²+9
=0²+9
=9
y-intercept=9
0=x²+9
-9=x²
√9=x
±3=x
x-intercepts=-3 and 3
Try Me!!
Find the X and Y intercept(s) of the
equation y=4x²-8
y=4(0)²+8
=8
y-intercept=8
0=4x²-8
8=4x²
2=x²
√2=x
x-intercept=±2
Try Me!!
Find the X and Y intercepts of the
equation y=4x²-16
y=4(0)²-16
=-16
y-intercept=-16
0=4x²-16
=(2x-4) (2x+4)
2x-4=0 and 2x+4=0
x=2 and x=-2
x-intercept=2 and -2
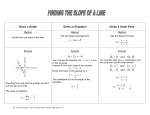
Slope/Point-Slope/Slope-Intercept
The slope of a line is a measurement of
the steepness and direction ofx a nonvertical line.
In order to determine the slope of a line,
y 2 y1
use the formula m=
m
52 3
2
73 4
x 2 x1
If x2 x1 , L is a vertical line and the
slope m of L is undefined (since this
results in division by 0)
Slope Cont.
A line can have a positive slope, a negative slope,
a slope of 0, and an undefined slope.
If the line is declining from right to left the slope is
positive.
If the line is declining from left to right the slope is
negative.
If the line is horizontal the slope is 0.
If the line is vertical the slope is undefined.
Slope Cont.
Find slope of the line that contains the
points (7,5) and (3,2)
y 2 y1
m
x 2 x1
52 3
m
73 4
The slope of the line is
3
4
Try Me!!
Find the slope of the line containing the
point (4,8) and (7,2).
82 6
m
2
4 7 3
The slope of the line is -2
Function, Domain, Range
A function
from set D to a set R is a
rate that assigns to every element in
D a unique element in R. The set D
of all input values is the domain of the
function, and the set R of all output
values is the range of the function.
Function
To determine whether a graph is a
function, use the Vertical Line Test.
A graph (set of points (x,y)) in the xyplane defines y as a function of x if and
only if no vertical line intersects the
graph in more than one point.
The vertical line test states, if you draw a vertical line anywhere on the
graph and it hits the graph in only one place then the graph is a function. If
the line hits the graph in two or more places then the graph is not a function.
Function Cont.
Determine whether the following graphs
are functions.
yes
no
yes
Domain and Range
Often the domain of a function f is not
specified; instead, only the equation
defining the function is given. In even
cases, the domain of f is the largest set
of real numbers for which the value of
f(x) is a real number. The domain of f is
the same as the domain of the variable x
in the expression f(x).
Example #1
Find the domain of each of the following
functions.
a) f(x)=x²+5x
The function f tells us to square the
number and then add 5 times the
number. Since the operations can be
performed on any real number, we
conclude that the domain of f is all real
numbers.
Example #2
Find the domain of the following function
3x
a) g ( x ) 2
x 4
The function tells us to divide the 3x by x²4. Since the division by 0 is not
defined, the denominator x²-4 can
never be equal to 0, so x can never be
equal to -2 or 2. The domain function g
is {x|x≠-2, x≠2}
Try Me!!
Find the domain of the following function
a) h(t ) 4 3t
The function h tells us to take the square
root of 4-3t. But only non-negative
numbers have real square roots, so the
expression under the square root must
be greater than or equal to 0. This
requires that 4-3t≥0. Therefore the
4
4
domain of h is {t|t≤ 3 } or interval (-∞, 3 ]
The Unit Circle
The unit circle is a circle whose radius 1
and whose center is at the origin of a
rectangular coordinate system.
Half-Angle Formulas
x 1 cos x
sin
2
2
2
2
cos
x 1 cos x
2
2
The purpose of the half angle formula is
to determine the exact values of trig and
Testing for Symmetry
Symmetry with respect to the x-axis
means that if the cartesian plane were
folded along the x-axis, the portion of
the graph above the x-axis would
coincide with the portion below the xaxis .
Symmetry with respect to the y-axis and
the origin can be similarly explained.
Symmetry Cont.
A graph is symmetric with respect
to the x-axis if wherever (x,y) is on
the graph (x,-y) is also on the graph.
A graph is symmetric with respect
to the y-axis if whenever (x,y) is on
the graph, (-x,y) is also on the graph
A graph is symmetric with
the origin if whenever (x,y)
is on the graph, (-x,-y) is
also on the graph
Example
Is the equation y=x²-2 symmetric with
respect to the y-axis?
Solution: Yes, because the point (-x,y)
satisfies the equation.
y=x²-2
y=(-x)²-2
y=x²-2
Try Me!!
Is the equation x-y²=1 symmetric with
respect to the x-axis?
Solution: Yes, because when you replace y
with (-y) it yields an equivalent equation.
x-y²=1
x-(-y)²=1
x-y²=1
Try Me!!
x
y
Is the equation
x2 1 symmetric with
respect to the origin?
Solution: Yes, because if you replace x
with (-x) and y with (-y) it yields an
equivalent equation.
y 2x
x 1
( x)
y
( x)2 1
y 2x
x 1
Volume Formulas
Volume of a cylinder – V r h
2
• Note: Think area of circular base times height
Volume of a cone
–V
1
r 2h
3
• Note: Think one-third the volume of the corresponding
cylinder
4 3
Volume of a sphere – V r
3
Volume of rectangular prism – V lwh
○ In order to find the volume, just simply plug in
the information into the correct place.
Example
Find the volume of a cylinder with a
height of 3 and a radius of 2.
V r h
2
V (2) (3)
V 12
2
Try Me!!
Find the volume of a cone with height of
5 and radius of 3.
1 2
V r h
3
1
V (3)2 (5)
3
45
V
3
Recognizing Graphs and their
respective equations
h
c
y
i
p
e
r
b
c
o
l
l
e
a
f ( x) 1
x
( x h)2 ( y k )2 r 2
p
p
n
p
o
a
e
a
s
r
g
r
i
a
a
a
t
b
t
b
i
o
i
o
v
l
v
l
e
a
e
a
f ( x) x 2
f ( x) x 2
Graphs and their respective
equations
y x
( x h) 2 ( y k ) 2
1
b2
a2
( x h) 2 ( y k ) 2
1
a2
b2
Natural Log
The natural logarithm function ln(x) is the
inverse function of the exponential function
Product Rule- ln(xy)= ln(x) + ln(y)
Example: ln(3*7)= ln(3) + ln(7)
Quotient Rule- ln(x/y)= ln(x) – ln(y)
y
Power Rule- ln(x )= yln(x)
8
Example: ln(2 )= 8ln(2)
Derivative Rule- f(x)=ln(x)→f’(x)=1/x
Natural log of a negative number- ln(x) is
undefined when x≤0
Natural log of 1= 0
Natural log of e= 1
e
x
Example
Solve log3(4x-7)=2
We can obtain an exact solution by
changing the logarithm to exponential
form.
log3(4x-7)=2
4x-7=3²
4x-7=9
4x=16
x=4
Try Me!!
Solve logx64=2
We can obtain an exact solution by
changing the logarithm to exponential
form.
log x 64=2
x²=64
x=√64=8
Number e (Euler’s Number)
The number e is defined as the base of
the natural logarithm
▪ it is an irrational number
2.7182818284590452353602874…
http://www.mathexpression.com/find-the-x-and-y-intercept-of-a-linearequation.html
https://algebra1b.wikispaces.com/Linear+Equations+1B-1
http://www.sparknotes.com/math/algebra1/graphingequations/section4.r
html
http://www.mathsisfun.com/sets/domain-range-codomain.html
http://www.s-cool.co.uk/category/subjects/gcse/maths/graphs
http://everobotics.org/projects/robo-magellan/robo-magellan.html
http://homepage.mac.com/shelleywalsh/MathArt/Symmetry.html
http://www.squarecirclez.com/blog/how-to-draw-y2-x-2/2301