* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Interpreting the Graph
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Hunting oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Derivations of the Lorentz transformations wikipedia , lookup
Length contraction wikipedia , lookup
Minkowski diagram wikipedia , lookup
Speeds and feeds wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Centripetal force wikipedia , lookup
Velocity-addition formula wikipedia , lookup
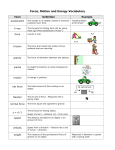
Distance/Time Graphs A distance/time graph shows how far an object travels over a certain time. Always pay attention to the titles on the x axis and the y axis on a graph. Lines have different meanings depending on the axis labels. A straight, horizontal line (flat line) indicates an object at rest. A straight, diagonal line indicates an object traveling at a constant speed. A line curving upward indicates an increase in speed (acceleration). A line curving downward indicates a decrease in speed (acceleration) Distance (m) The graph depicts an object which is at rest. Time (sec) The distance does not change as time goes on. Distance (m) The graph depicts an object moving at a constant speed. Time (sec) The straight line shows that the speed stays the same over time. It is not accelerating. Distance (m) Time (sec) Just like the previous graph, this graph depicts an object moving at a constant speed. It is not slowing down. Distance (m) The curve, in the graph, depicts that the object’s speed is changing as time passes. This is acceleration due to speeding up. Time (sec) The object is covering more distance in shorter time. In the first part of the graph, the object is moving with constant speed. Distance (m) In the second part of the graph, the object is at rest (not moving). It accelerated because it stopped. Time (sec) In the third part, the object is again moving with constant speed while returning to its point of origin. It changed direction; therefore, it has velocity and it accelerated. Velocity (speed)/Time Graphs A velocity (speed)/time graph shows the acceleration of an object. In other words, it shows the change in velocity over time. Always pay attention to the titles on the x axis and the y axis on a graph. Lines have different meanings depending on the axis labels. Velocity includes a speed and direction. Acceleration may be an increase in speed, a decrease in speed, coming to a stop, or changing direction. Interpret the Graph Below: The graph depicts Velocity (speed) m/s an object with a constant velocity. The speed and Time (sec) direction stay the same over time. Interpret the Graph Below: The graph depicts Velocity (speed) m/s an object with constant positive acceleration. The velocity is Time (sec) increasing at a constant rate of speed. Interpret the Graph Below: The graph depicts Velocity (speed) m/s an object with constant negative acceleration. The velocity is Time (sec) decreasing at a constant rate of speed. Interpret the Graph Below: Velocity (speed) m/s The graph depicts an object with increasing acceleration. Time (sec) The velocity is increasing.